Abstract
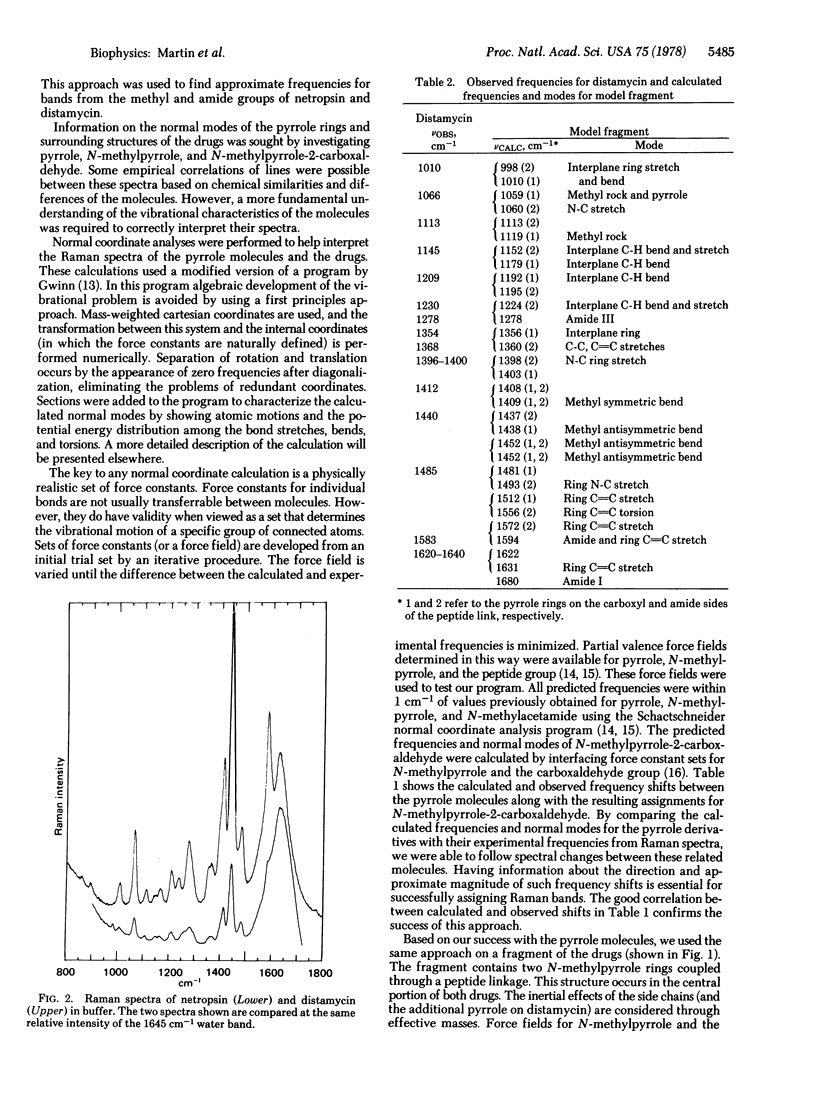
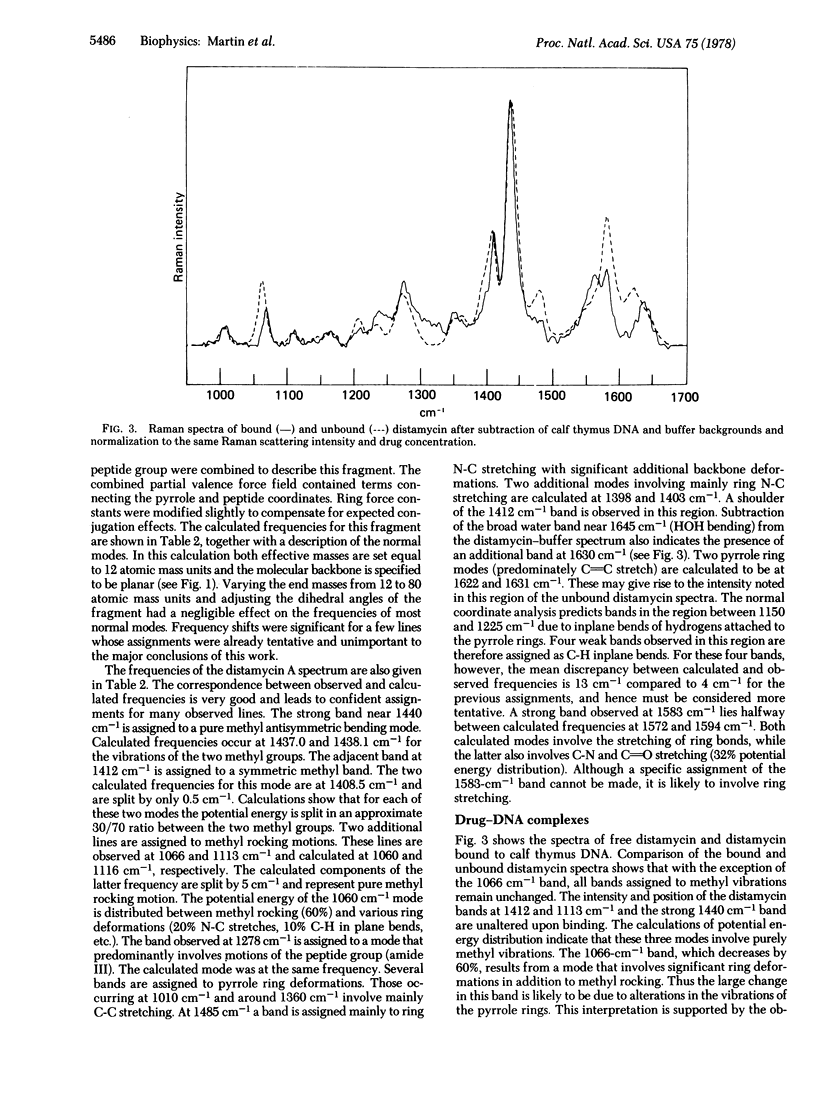
The binding of distamycin and netropsin to duplex DNA has been studied by Raman spectroscopy. Several changes occur in the Raman spectra of these drugs upon binding DNA. These changes were analyzed by assigning specific motions to the observed Raman bands through the use of molecular subunits of the drugs and normal mode calculations. Our analysis indicates that pyrrole ring and peptide group vibrations are altered upon binding to DNA. The environments of the pyrrole ring methyl groups are not affected by the binding. These data provide physical evidence consistent with a binding model in which the methyl groups on the pyrroles project away from the DNA and the peptide N-H groups form hydrogen bonds with the DNA.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chen M. C., Lord R. C. Laser-excited Raman spectroscopy of biomolecules. VI. Some polypeptides as conformational models. J Am Chem Soc. 1974 Jul 24;96(15):4750–4752. doi: 10.1021/ja00822a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolchinskii A. M., Mirzabekov A. D., Zasedatelev A. C., Gurskii G. V., Grokhovskii S. L., Zhuze A. L., Gottikh B. P. O strukture kompleksov antibiotikov distamitsinovogo tipa i atkinomitsina D s DNK: novye eksperimental'nye dannye o lokalizatsii antibiotnkov v uzkoi borozdke DNK. Mol Biol (Mosk) 1975 Jan-Feb;9(1):19–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krey A. K., Allison R. G., Hahn F. E. Interactions of the antibiotic, distamycin A, with native DNA and with synthetic duplex polydeoxyribonucleotides. FEBS Lett. 1973 Jan 1;29(1):58–62. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80015-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luck G., Triebel H., Waring M., Zimmer C. Conformation dependent binding of netropsin and distamycin to DNA and DNA model polymers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1974 Mar;1(3):503–530. doi: 10.1093/nar/1.3.503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel D. J., Canuel L. L. Netropsin-poly(dA-dT) complex in solution: structure and dynamics of antibiotic-free base pair regions and those centered on bound netropsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5207–5211. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinert K. E. Adenosine-thymidine cluster-specific elongation and stiffening of DNA induced by the oligopeptide antibiotic netropsin. J Mol Biol. 1972 Dec 30;72(3):593–607. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90178-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wartell R. M., Larson J. E., Wells R. D. Netropsin. A specific probe for A-T regions of duplex deoxyribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1974 Nov 10;249(21):6719–6731. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu N. T. Raman spectroscopy: a conformational probe in biochemistry. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1977;4(3):229–280. doi: 10.3109/10409237709102559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zasedatelev A. S., Gursky G. V., Zimmer C., Thrum H. Binding of netropsin to DNA and synthetic polynucleotides. Mol Biol Rep. 1974 Mar;1(6):337–342. doi: 10.1007/BF00309567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zasedatelev A. S., Zhuze A. L., Tsimmer K., Grokhovskii S. L., Tumanian V. G. Stereokhimicheskaia model' molekuliarnogo mekhanizma "uznavaniia" AT-par pri sviazyvanii s DNK antibiotikov distamitsina a i netropsina. Dokl Akad Nauk SSSR. 1976 Dec 1;231(4):1006–1009. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmer C., Reinert K. E., Luck G., Wähnert U., Löber G., Thrum H. Interaction of the oligopeptide antibiotics netropsin and distamycin A with nucleic acids. J Mol Biol. 1971 May 28;58(1):329–348. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90250-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


