Abstract
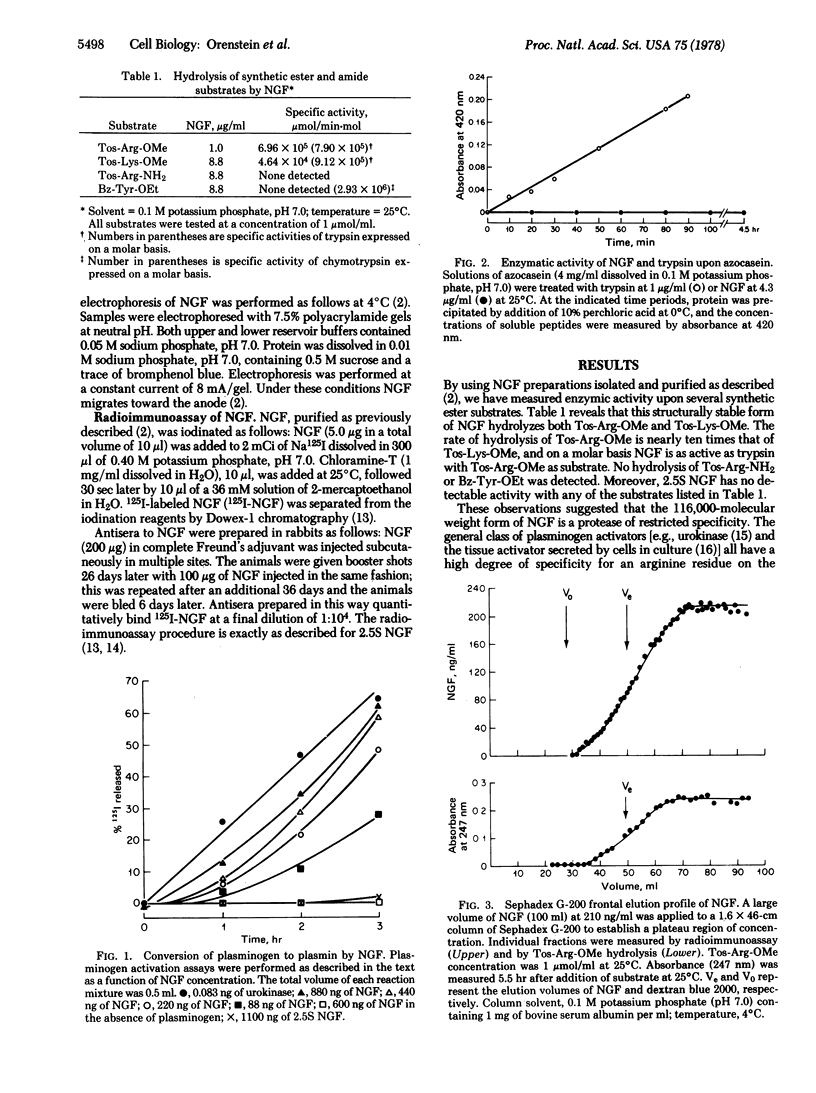
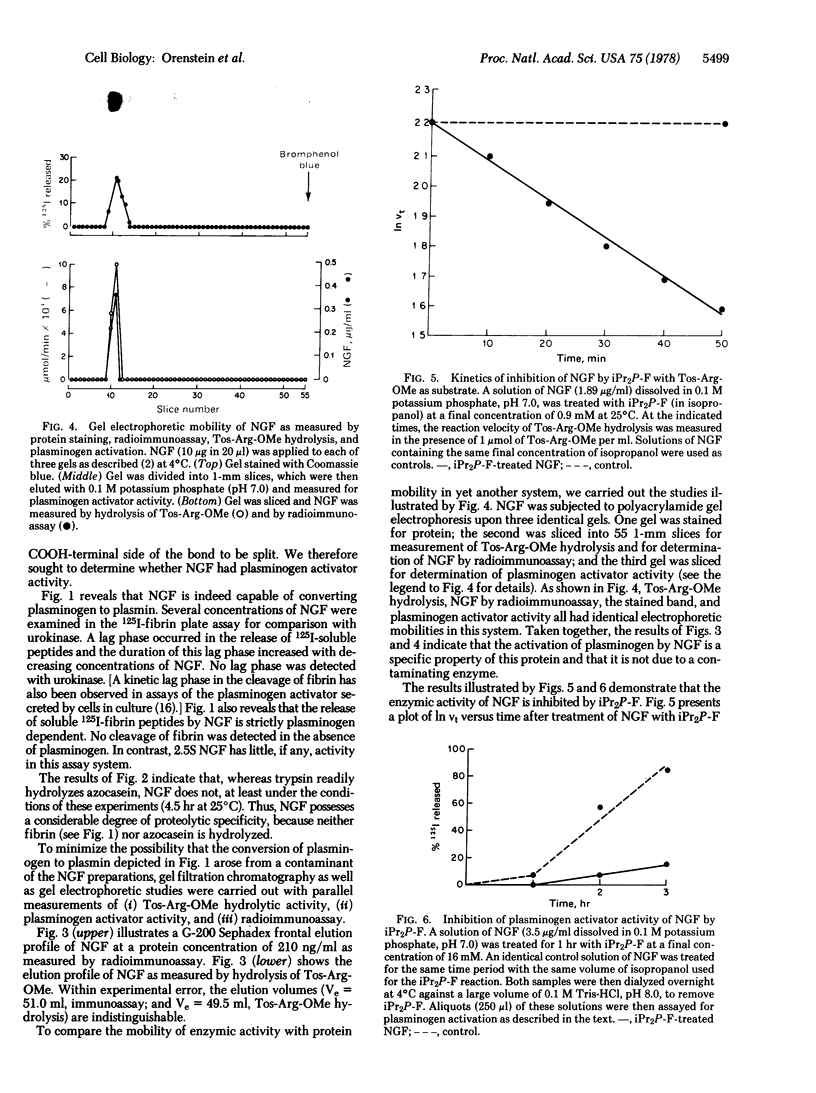
The single, highly stable form of mouse submandibular gland nerve growth factor (NGF), prepared as described by Young et al. [(1978) Biochemistry 17, 1490--1498] is a protease of restricted specificity that can convert plasminogen to plasmin. In the absence of plasminogen, NGF is not fibrinolytic, nor does it hydrolyze casein at a measurable rate. Treatment of NGF with diisopropyl fluorophosphate inhibits its ability to activate plasminogen as well as its capacity to hydrolyze certain synthetic arginine esters. These results indicate that NGF is a member of the class of serine proteases. Since NGF is known to be secreted at high concentrations in mouse saliva, it may serve to activate plasminogen (with subsequent fibrinolysis) somewhere in the alimentary tract. Plasminogen activation is the only known action of NGF upon a biologically important non-neural substrate.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker M. E. Molecular weight and structure of 7 S nerve growth factor protein. J Biol Chem. 1975 Mar 10;250(5):1714–1717. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bocchini V., Angeletti P. U. The nerve growth factor: purification as a 30,000-molecular-weight protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Oct;64(2):787–794. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.2.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davie E. W., Fujikawa K. Basic mechanisms in blood coagulation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:799–829. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.004055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutsch D. G., Mertz E. T. Plasminogen: purification from human plasma by affinity chromatography. Science. 1970 Dec 4;170(3962):1095–1096. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3962.1095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvorak H. F., Orenstein N. S., Rypysc J., Colvin R. B., Dvorak A. M. Plasminogen activator of guinea pig basophilic leukocytes: probable localization to the plasma membrane. J Immunol. 1978 Mar;120(3):766–773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiedler F. Pig pancreatic kallikreins A and B. Methods Enzymol. 1976;45:289–303. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(76)45027-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene L. A., Shooter E. M., Varon S. Enzymatic activities of mouse nerve growth factor and its subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Aug;60(4):1383–1388. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.4.1383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene L. A., Shooter E. M., Varon S. Subunit interaction and enzymatic activity of mouse 7S nerve growth factor. Biochemistry. 1969 Sep;8(9):3735–3741. doi: 10.1021/bi00837a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HELMKAMP R. W., GOODLAND R. L., BALE W. F., SPAR I. L., MUTSCHLER L. E. High specific activity iodination of gamma-globulin with iodine-131 monochloride. Cancer Res. 1960 Nov;20:1495–1500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy R. A., Pantazis N. J., Arnason B. G., Young M. Secretion of a nerve growth factor by mouse neuroblastoma cells in culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 May;72(5):1895–1898. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.5.1895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy R. A., Saide J. D., Blanchard M. H., Young M. Molecular properties of the nerve growth factor secreted in mouse saliva. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):2672–2676. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.2672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Eberhard H. J. Complement. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:697–724. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.003405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pantazis N. J., Murphy R. A., Saide J. D., Blanchard M. H., Young M. Dissociation of the 7S-nerve growth factor complex in solution. Biochemistry. 1977 Apr 5;16(7):1525–1530. doi: 10.1021/bi00626a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins K. C., Summaria L., Hsieh B., Shah R. J. The peptide chains of human plasmin. Mechanism of activation of human plasminogen to plasmin. J Biol Chem. 1967 May 25;242(10):2333–2342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unkeless J., Dano K., Kellerman G. M., Reich E. Fibrinolysis associated with oncogenic transformation. Partial purification and characterization of the cell factor, a plasminogen activator. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 10;249(13):4295–4305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varon S., Nomura J., Shooter E. M. The isolation of the mouse nerve growth factor protein in a high molecular weight form. Biochemistry. 1967 Jul;6(7):2202–2209. doi: 10.1021/bi00859a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace L. J., Partlow L. M. alpha-Adrenergic regulation of secretion of mouse saliva rich in nerve growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):4210–4214. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.4210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young M., Saide J. D., Murphy R. A., Blanchard Nerve growth factor: multiple dissociation products in homogenates of the mouse submandibular gland. Purification and molecular properties of the intact undissociated form of the protein. Biochemistry. 1978 Apr 18;17(8):1490–1498. doi: 10.1021/bi00601a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]