Abstract
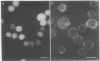
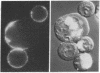
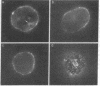
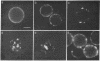
Phosphatidylethanolamine bearing the 2,4,6-trinitrophenyl hapten was introduced into the surface membrane of mammalian fibroblasts by incubating the cells with small unilamellar vesicles containing this hapten-conjugated lipid. Consistent with integration of the antigen into the plasma membrane lipid bilayer, the exogenously supplied lipid was observed by immunofluorescence to diffuse rapidly (D greater than or equal to 0.6 X 10(-8) cm2/sec) over the surface of polykaryons formed between vesicle- and non-vesicle-treated cells. Association of the exogenous lipids with cells via adsorption of vesicles to the plasma membrane was rigorously excluded by a combination of ultrastructural and immunofluorescence studies. The distribution of the integrated antigenic lipid in the plasma membranes of vesicle-treated cells was followed by immunofluorescence microscopy. The exogenously supplied hapten-conjugated phospholipid was observed to be uniformly distributed and remained so for up to 1 hr at 37 degrees C. However, upon the addition of bivalent, but not monovalent, antihapten antibodies, the phospholipid underwent a rapid temperature-dependent redistribution, forming small patches that eventually coalesced into one or more large aggregates. This unexpected finding is discussed in terms of the mode of insertion of the lipid into the cell surface and the possible mechanisms by which bivalent ligands might alter the mobility and distribution of cell surface phospholipids.
Full text
PDF

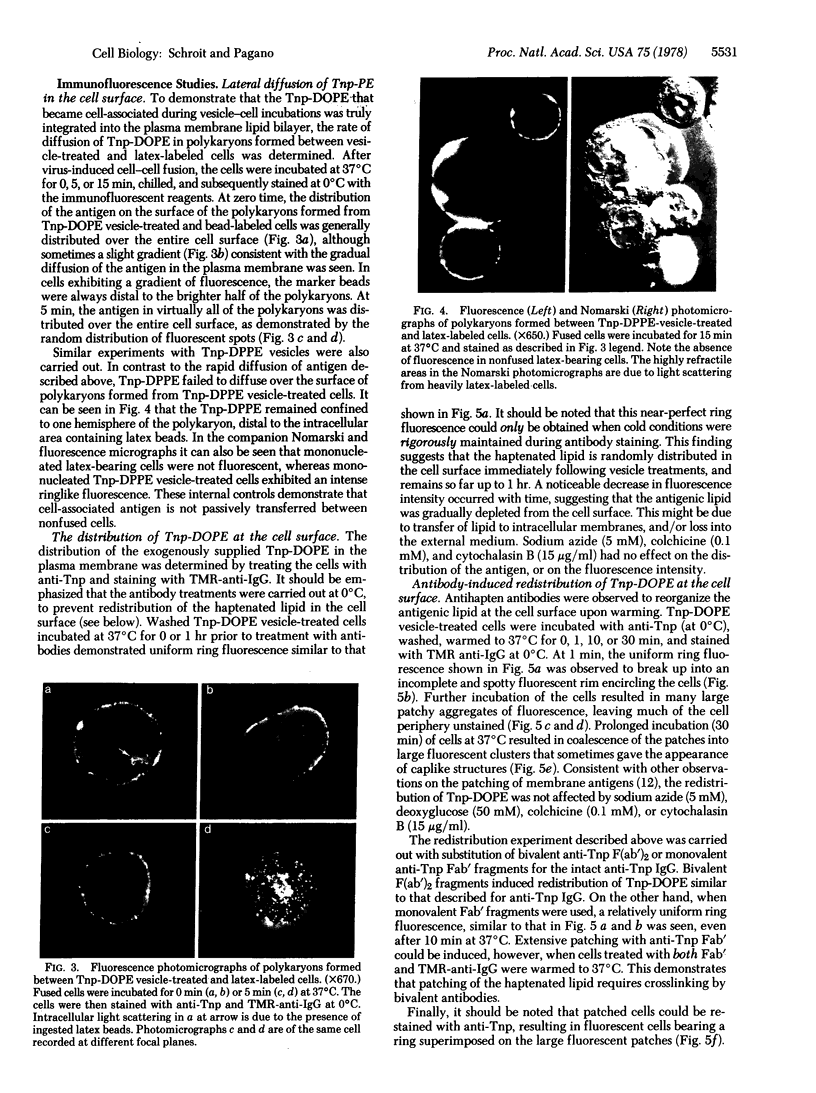
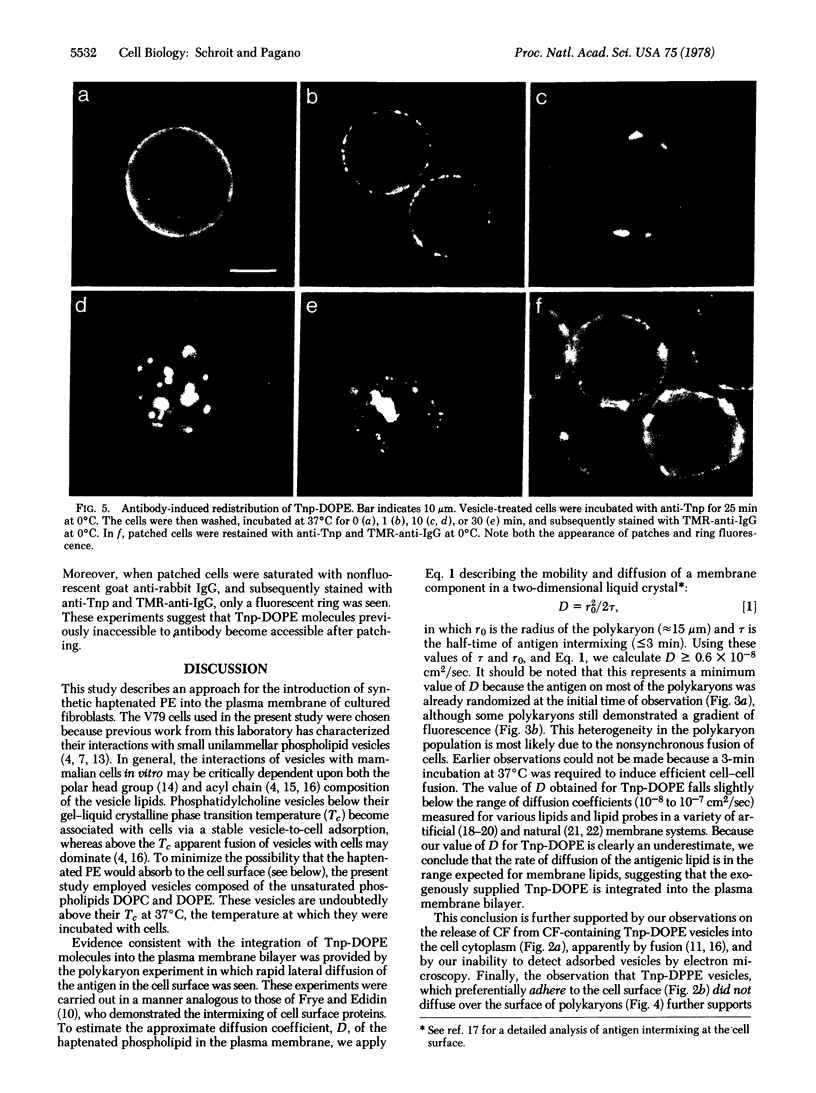

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bretscher M. S. Directed lipid flow in cell membranes. Nature. 1976 Mar 4;260(5546):21–23. doi: 10.1038/260021a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comfurius P., Zwaal R. F. The enzymatic synthesis of phosphatidylserine and purification by CM-cellulose column chromatography. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Jul 20;488(1):36–42. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(77)90120-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig S. W., Cuatrecasas P. Mobility of cholera toxin receptors on rat lymphocyte membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3844–3848. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edidin M. Rotational and translational diffusion in membranes. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1974;3(0):179–201. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.03.060174.001143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fahey P. F., Koppel D. E., Barak L. S., Wolf D. E., Elson E. L., Webb W. W. Lateral diffusion in planar lipid bilayers. Science. 1977 Jan 21;195(4275):305–306. doi: 10.1126/science.831279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frye L. D., Edidin M. The rapid intermixing of cell surface antigens after formation of mouse-human heterokaryons. J Cell Sci. 1970 Sep;7(2):319–335. doi: 10.1242/jcs.7.2.319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershon N. D. Model for capping of membrane receptors based on boundary surface effects. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1357–1360. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang H. W. Mobility and diffusion in the plane of cell membrane. J Theor Biol. 1973 Jul;40(1):11–17. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(73)90161-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang L., Ozato K., Pagano R. E. Interactions of phospholipid vesicles with murine lymphocytes. I. Vesicle-cell adsorption and fusion as alternate pathways of uptake. Membr Biochem. 1978;1(1-2):1–25. doi: 10.3109/09687687809064156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang L., Pagano R. E. Interaction of phospholipid vesicles with cultured mammalial cells. I. Characteristics of uptake. J Cell Biol. 1975 Oct;67(1):38–48. doi: 10.1083/jcb.67.1.38. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphries G. M., McConnell H. M. Antibodies against nitroxide spin labels. Biophys J. 1976 Mar;16(3):275–277. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(76)85687-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVY H. B., SOBER H. A. A simple chromatographic method for preparation of gamma globulin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1960 Jan;103:250–252. doi: 10.3181/00379727-103-25476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litman B. J. Determination of molecular asymmetry in the phosphatidylethanolamine surface distribution in mixed phospholipid vesicles. Biochemistry. 1974 Jul 2;13(14):2844–2848. doi: 10.1021/bi00711a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin F. J., MacDonald R. C. Lipid vesicle-cell interactions. III. Introduction of a new antigenic determinant into erythrocyte membranes. J Cell Biol. 1976 Sep;70(3):515–526. doi: 10.1083/jcb.70.3.515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NISONOFF A., MARKUS G., WISSLER F. C. Separation of univalent fragments of rabbit antibody by reduction of a single, labile disulphide bond. Nature. 1961 Jan 28;189:293–295. doi: 10.1038/189293a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolson G. L. Transmembrane control of the receptors on normal and tumor cells. I. Cytoplasmic influence over surface components. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Apr 13;457(1):57–108. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(76)90014-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagano R. E., Huang L. Interaction of phospholipid vesicles with cultured mammalian cells. II. Studies of mechanism. J Cell Biol. 1975 Oct;67(1):49–60. doi: 10.1083/jcb.67.1.49. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagano R. E., Takeichi M. Adhesion of phospholipid vesicles to Chinese hamster fibroblasts. Role of cell surface proteins. J Cell Biol. 1977 Aug;74(2):531–546. doi: 10.1083/jcb.74.2.531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagano R. E., Weinstein J. N. Interactions of liposomes with mammalian cells. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1978;7:435–468. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.07.060178.002251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poste G., Papahadjopoulos D. Lipid vesicles as carriers for introducing materials into cultured cells: influence of vesicle lipid composition on mechanism(s) of vesicle incorporation into cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 May;73(5):1603–1607. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.5.1603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sackmann E., Träuble H., Galla H. J., Overath P. Lateral diffusion, protein mobility, and phase transitions in Escherichia coli membranes. A spin label study. Biochemistry. 1973 Dec 18;12(26):5360–5369. doi: 10.1021/bi00750a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scandella C. J., Devaux P., McConnell H. M. Rapid lateral diffusion of phospholipids in rabbit sarcoplasmic reticulum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Aug;69(8):2056–2060. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.8.2056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlessinger J., Axelrod D., Koppel D. E., Webb W. W., Elson E. L. Lateral transport of a lipid probe and labeled proteins on a cell membrane. Science. 1977 Jan 21;195(4275):307–309. doi: 10.1126/science.556653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedlacek H. H., Stärk J., Seiler F. R., Ziegler W., Wiegandt H. Cholera toxin induced redistribution of sialoglycolipid receptor at the lymphocyte membrane. FEBS Lett. 1976 Jan 15;61(2):272–276. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)81055-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Six H. R., Uemura K. I., Kinsky S. C. Effect of immunoglobulin class and affinity on the initiation of complement-dependent damage to liposomal model membranes sensitized with dinitrophenylated phospholipids. Biochemistry. 1973 Sep 25;12(20):4003–4011. doi: 10.1021/bi00744a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uemura K., Kinsky S. C. Active vs. passive sensitization of liposomes toward antibody and complement by dinitrophenylated derivatives of phosphatidylethanolamine. Biochemistry. 1972 Oct 24;11(22):4085–4094. doi: 10.1021/bi00772a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein J. N., Yoshikami S., Henkart P., Blumenthal R., Hagins W. A. Liposome-cell interaction: transfer and intracellular release of a trapped fluorescent marker. Science. 1977 Feb 4;195(4277):489–492. doi: 10.1126/science.835007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]