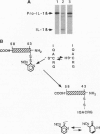
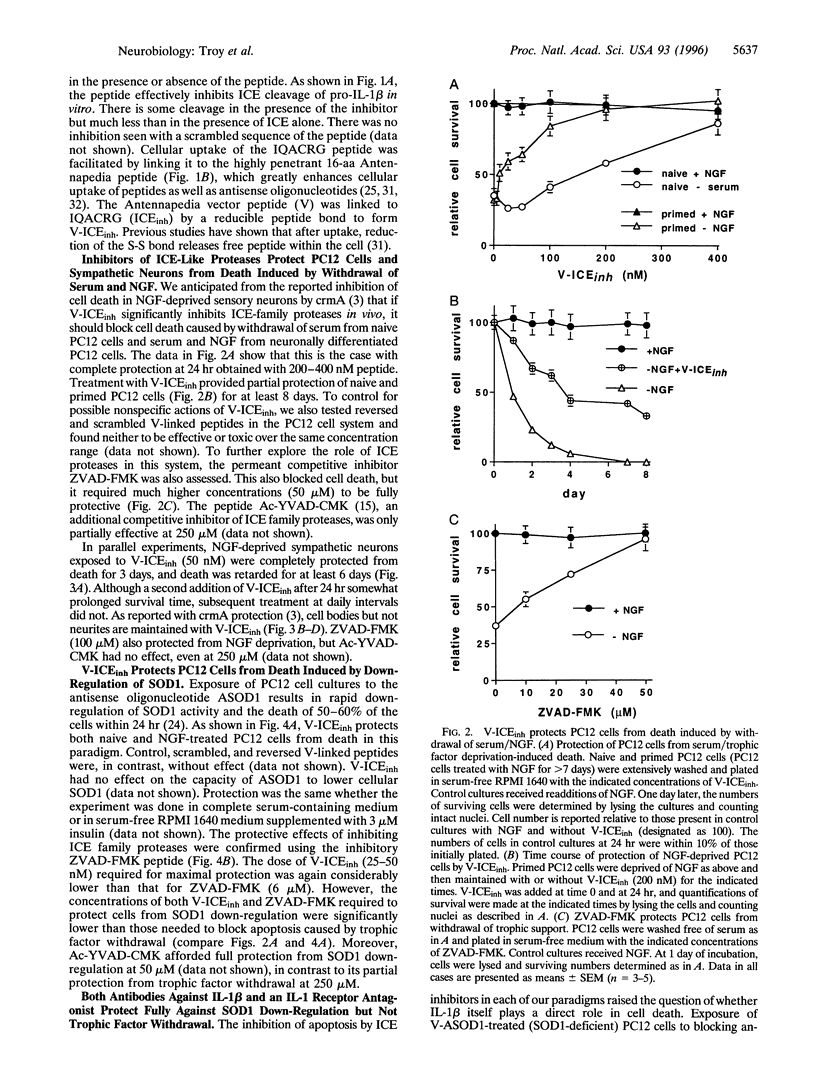
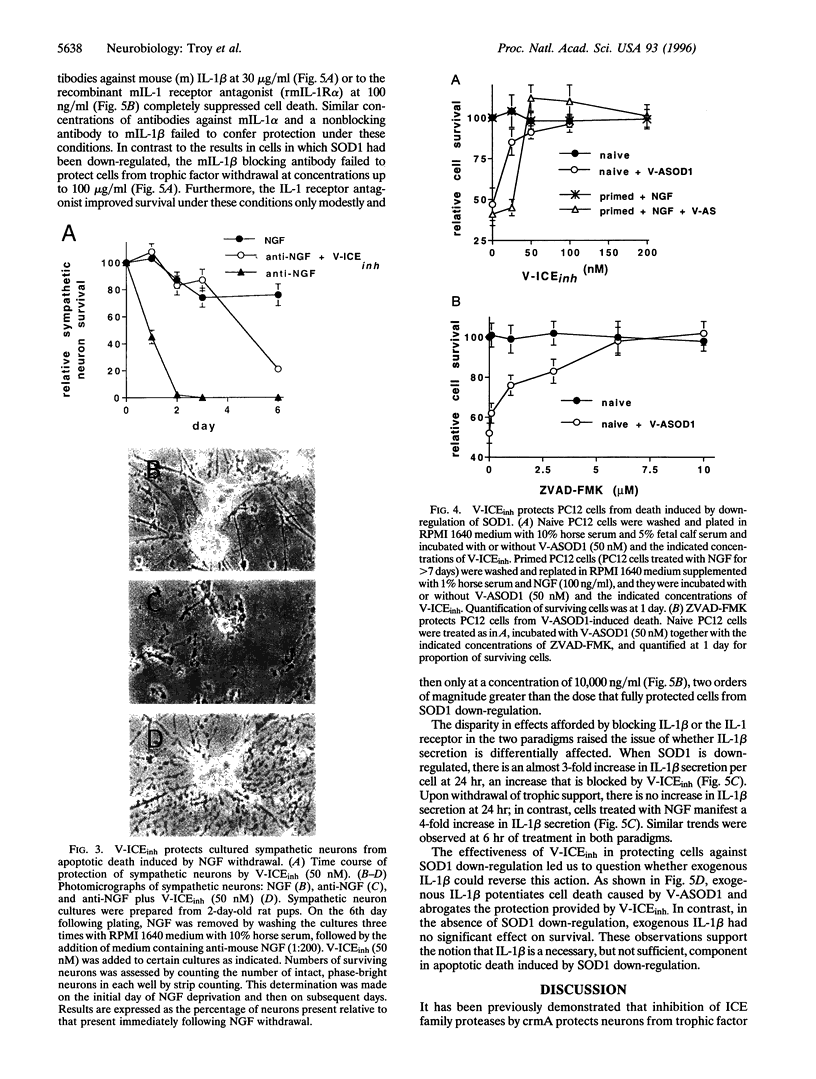
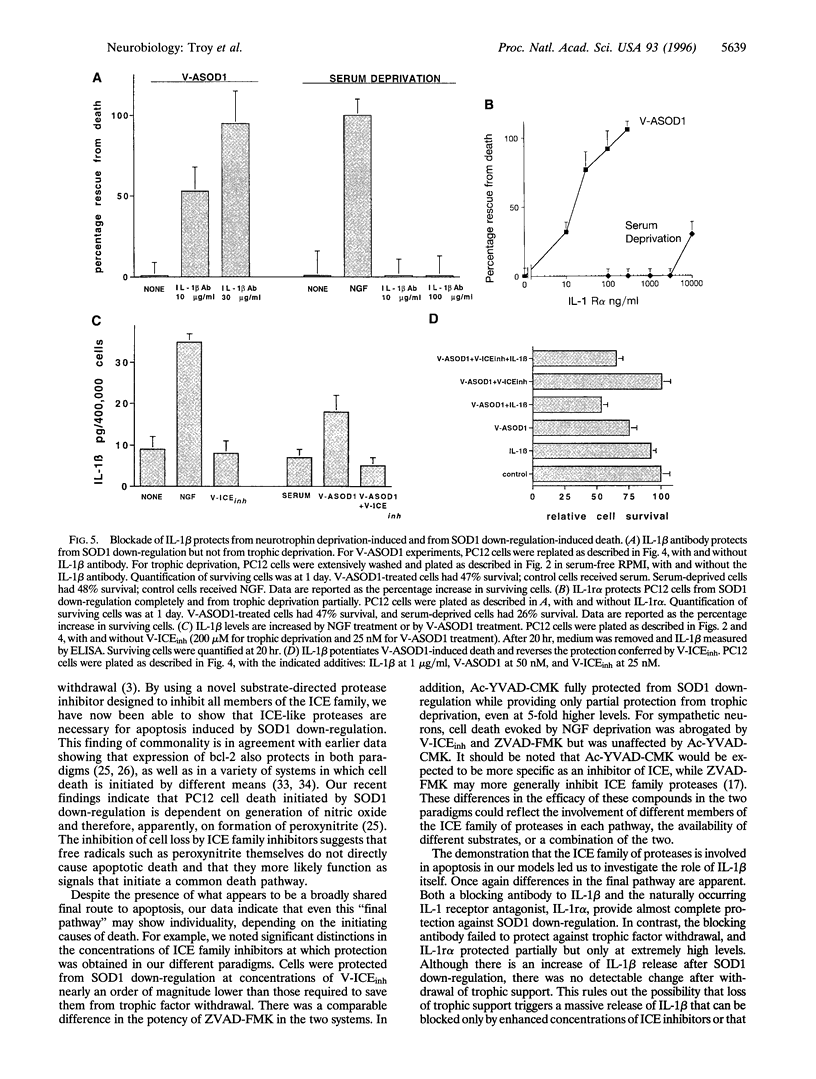
Abstract
We compare here the mechanisms of apoptotic death of PC12 cells induced by down-regulation of Cu2+,Zn2+ superoxide dismutase (SOD1) and withdrawal of trophic support (serum/nerve growth factor). Our previous results indicated that the initiating causes of death are different in each paradigm. However, bcl-2 rescues cells in either paradigm, suggesting common downstream elements to the cell death pathway. To determine whether the ICE [interleukin 1beta converting enzyme] family of proteases, which is required for apoptosis on trophic factor withdrawal, is also required for apoptosis induced by oxidative stress, we have developed a novel peptide inhibitor that mimics the common catalytic site of these enzymes and thereby blocks their access to substrates. This differs from the more usual pseudosubstrate approach to enzyme inhibition. Blockade of ICE family proteases by either this inhibitor or by a permeant competitive ICE family antagonist rescues PC12 cells from apoptotic death following apoptosis induced by down-regulation of SOD1, as well as from trophic factor/nerve growth factor deprivation. SOD1 down-regulation results in an increase in interleukin 1beta (IL- 1beta) production by the cells, and cell death under these conditions can be prevented by either blocking antibodies against IL-1beta or the IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1Ralpha). In contrast, trophic factor withdrawal does not increase IL-1beta secretion, and the blocking antibody failed to protect PC12 cells from trophic factor withdrawal, whereas the receptor antagonist was only partially protective at very high concentrations. There were substantial differences in the concentrations of pseudosubstrate inhibitors which rescued cells from SOD1 down-regulation and trophic factor deprivation. These results suggest the involvement of different members of the ICE family, different substrates, or both in the two different initiating causes of cell death.
Full text
PDF
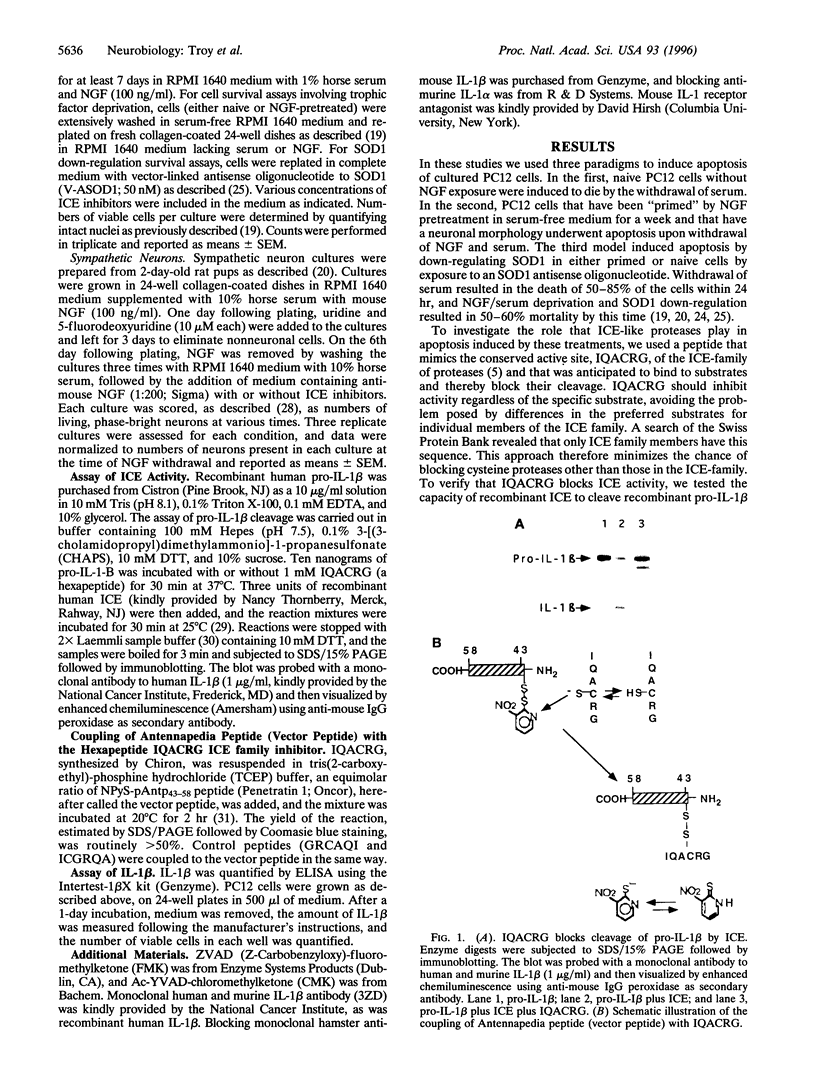

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ankarcrona M., Dypbukt J. M., Brüne B., Nicotera P. Interleukin-1 beta-induced nitric oxide production activates apoptosis in pancreatic RINm5F cells. Exp Cell Res. 1994 Jul;213(1):172–177. doi: 10.1006/excr.1994.1187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batistatou A., Greene L. A. Aurintricarboxylic acid rescues PC12 cells and sympathetic neurons from cell death caused by nerve growth factor deprivation: correlation with suppression of endonuclease activity. J Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;115(2):461–471. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.2.461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batistatou A., Merry D. E., Korsmeyer S. J., Greene L. A. Bcl-2 affects survival but not neuronal differentiation of PC12 cells. J Neurosci. 1993 Oct;13(10):4422–4428. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-10-04422.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boudreau N., Sympson C. J., Werb Z., Bissell M. J. Suppression of ICE and apoptosis in mammary epithelial cells by extracellular matrix. Science. 1995 Feb 10;267(5199):891–893. doi: 10.1126/science.7531366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breitner J. C., Gau B. A., Welsh K. A., Plassman B. L., McDonald W. M., Helms M. J., Anthony J. C. Inverse association of anti-inflammatory treatments and Alzheimer's disease: initial results of a co-twin control study. Neurology. 1994 Feb;44(2):227–232. doi: 10.1212/wnl.44.2.227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coyle J. T., Puttfarcken P. Oxidative stress, glutamate, and neurodegenerative disorders. Science. 1993 Oct 29;262(5134):689–695. doi: 10.1126/science.7901908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enari M., Hug H., Nagata S. Involvement of an ICE-like protease in Fas-mediated apoptosis. Nature. 1995 May 4;375(6526):78–81. doi: 10.1038/375078a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farinelli S. E., Park D. S., Greene L. A. Nitric oxide delays the death of trophic factor-deprived PC12 cells and sympathetic neurons by a cGMP-mediated mechanism. J Neurosci. 1996 Apr 1;16(7):2325–2334. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.16-07-02325.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes-Alnemri T., Litwack G., Alnemri E. S. CPP32, a novel human apoptotic protein with homology to Caenorhabditis elegans cell death protein Ced-3 and mammalian interleukin-1 beta-converting enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1994 Dec 9;269(49):30761–30764. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari G., Greene L. A. Proliferative inhibition by dominant-negative Ras rescues naive and neuronally differentiated PC12 cells from apoptotic death. EMBO J. 1994 Dec 15;13(24):5922–5928. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06937.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari G., Yan C. Y., Greene L. A. N-acetylcysteine (D- and L-stereoisomers) prevents apoptotic death of neuronal cells. J Neurosci. 1995 Apr;15(4):2857–2866. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.15-04-02857.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gagliardini V., Fernandez P. A., Lee R. K., Drexler H. C., Rotello R. J., Fishman M. C., Yuan J. Prevention of vertebrate neuronal death by the crmA gene. Science. 1994 Feb 11;263(5148):826–828. doi: 10.1126/science.8303301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene L. A., Tischler A. S. Establishment of a noradrenergic clonal line of rat adrenal pheochromocytoma cells which respond to nerve growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2424–2428. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin W. S., Stanley L. C., Ling C., White L., MacLeod V., Perrot L. J., White C. L., 3rd, Araoz C. Brain interleukin 1 and S-100 immunoreactivity are elevated in Down syndrome and Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(19):7611–7615. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.19.7611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hengartner M. O., Ellis R. E., Horvitz H. R. Caenorhabditis elegans gene ced-9 protects cells from programmed cell death. Nature. 1992 Apr 9;356(6369):494–499. doi: 10.1038/356494a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hensley K., Carney J. M., Mattson M. P., Aksenova M., Harris M., Wu J. F., Floyd R. A., Butterfield D. A. A model for beta-amyloid aggregation and neurotoxicity based on free radical generation by the peptide: relevance to Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Apr 12;91(8):3270–3274. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.8.3270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korsmeyer S. J. Bcl-2 initiates a new category of oncogenes: regulators of cell death. Blood. 1992 Aug 15;80(4):879–886. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korsmeyer S. J. Bcl-2: a repressor of lymphocyte death. Immunol Today. 1992 Aug;13(8):285–288. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(92)90037-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuida K., Lippke J. A., Ku G., Harding M. W., Livingston D. J., Su M. S., Flavell R. A. Altered cytokine export and apoptosis in mice deficient in interleukin-1 beta converting enzyme. Science. 1995 Mar 31;267(5206):2000–2003. doi: 10.1126/science.7535475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar S., Kinoshita M., Noda M., Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A. Induction of apoptosis by the mouse Nedd2 gene, which encodes a protein similar to the product of the Caenorhabditis elegans cell death gene ced-3 and the mammalian IL-1 beta-converting enzyme. Genes Dev. 1994 Jul 15;8(14):1613–1626. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.14.1613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazebnik Y. A., Kaufmann S. H., Desnoyers S., Poirier G. G., Earnshaw W. C. Cleavage of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase by a proteinase with properties like ICE. Nature. 1994 Sep 22;371(6495):346–347. doi: 10.1038/371346a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu C., Bai Y., Ganea D., Hart R. P. Species-specific activity of rat recombinant interleukin-1 beta. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 1995 Nov;15(11):985–992. doi: 10.1089/jir.1995.15.985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Los M., Van de Craen M., Penning L. C., Schenk H., Westendorp M., Baeuerle P. A., Dröge W., Krammer P. H., Fiers W., Schulze-Osthoff K. Requirement of an ICE/CED-3 protease for Fas/APO-1-mediated apoptosis. Nature. 1995 May 4;375(6526):81–83. doi: 10.1038/375081a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeer P. L., McGeer E., Rogers J., Sibley J. Anti-inflammatory drugs and Alzheimer disease. Lancet. 1990 Apr 28;335(8696):1037–1037. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)91101-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeer P. L., Rogers J. Anti-inflammatory agents as a therapeutic approach to Alzheimer's disease. Neurology. 1992 Feb;42(2):447–449. doi: 10.1212/wnl.42.2.447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan C. E., Prevette D., Yaginuma H., Homma S., Cardwell C., Fritz L. C., Tomaselli K. J., Oppenheim R. W., Schwartz L. M. Peptide inhibitors of the ICE protease family arrest programmed cell death of motoneurons in vivo and in vitro. Neuron. 1995 Aug;15(2):385–393. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(95)90042-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miura M., Zhu H., Rotello R., Hartwieg E. A., Yuan J. Induction of apoptosis in fibroblasts by IL-1 beta-converting enzyme, a mammalian homolog of the C. elegans cell death gene ced-3. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):653–660. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90486-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson D. W., Ali A., Thornberry N. A., Vaillancourt J. P., Ding C. K., Gallant M., Gareau Y., Griffin P. R., Labelle M., Lazebnik Y. A. Identification and inhibition of the ICE/CED-3 protease necessary for mammalian apoptosis. Nature. 1995 Jul 6;376(6535):37–43. doi: 10.1038/376037a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittman R. N., Wang S., DiBenedetto A. J., Mills J. C. A system for characterizing cellular and molecular events in programmed neuronal cell death. J Neurosci. 1993 Sep;13(9):3669–3680. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-09-03669.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prochiantz A., Théodore L. Nuclear/growth factors. Bioessays. 1995 Jan;17(1):39–44. doi: 10.1002/bies.950170109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rukenstein A., Rydel R. E., Greene L. A. Multiple agents rescue PC12 cells from serum-free cell death by translation- and transcription-independent mechanisms. J Neurosci. 1991 Aug;11(8):2552–2563. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-08-02552.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rydel R. E., Greene L. A. cAMP analogs promote survival and neurite outgrowth in cultures of rat sympathetic and sensory neurons independently of nerve growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):1257–1261. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.1257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tewari M., Beidler D. R., Dixit V. M. CrmA-inhibitable cleavage of the 70-kDa protein component of the U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein during Fas- and tumor necrosis factor-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 1995 Aug 11;270(32):18738–18741. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.32.18738. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tewari M., Dixit V. M. Fas- and tumor necrosis factor-induced apoptosis is inhibited by the poxvirus crmA gene product. J Biol Chem. 1995 Feb 17;270(7):3255–3260. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.7.3255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tewari M., Quan L. T., O'Rourke K., Desnoyers S., Zeng Z., Beidler D. R., Poirier G. G., Salvesen G. S., Dixit V. M. Yama/CPP32 beta, a mammalian homolog of CED-3, is a CrmA-inhibitable protease that cleaves the death substrate poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase. Cell. 1995 Jun 2;81(5):801–809. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90541-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornberry N. A. Interleukin-1 beta converting enzyme. Methods Enzymol. 1994;244:615–631. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(94)44045-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Théodore L., Derossi D., Chassaing G., Llirbat B., Kubes M., Jordan P., Chneiweiss H., Godement P., Prochiantz A. Intraneuronal delivery of protein kinase C pseudosubstrate leads to growth cone collapse. J Neurosci. 1995 Nov;15(11):7158–7167. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.15-11-07158.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troy C. M., Derossi D., Prochiantz A., Greene L. A., Shelanski M. L. Downregulation of Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase leads to cell death via the nitric oxide-peroxynitrite pathway. J Neurosci. 1996 Jan;16(1):253–261. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.16-01-00253.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troy C. M., Shelanski M. L. Down-regulation of copper/zinc superoxide dismutase causes apoptotic death in PC12 neuronal cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jul 5;91(14):6384–6387. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.14.6384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L., Miura M., Bergeron L., Zhu H., Yuan J. Ich-1, an Ice/ced-3-related gene, encodes both positive and negative regulators of programmed cell death. Cell. 1994 Sep 9;78(5):739–750. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(94)90422-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan S. D., Chen X., Schmidt A. M., Brett J., Godman G., Zou Y. S., Scott C. W., Caputo C., Frappier T., Smith M. A. Glycated tau protein in Alzheimer disease: a mechanism for induction of oxidant stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Aug 2;91(16):7787–7791. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.16.7787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan J., Shaham S., Ledoux S., Ellis H. M., Horvitz H. R. The C. elegans cell death gene ced-3 encodes a protein similar to mammalian interleukin-1 beta-converting enzyme. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):641–652. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90485-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]