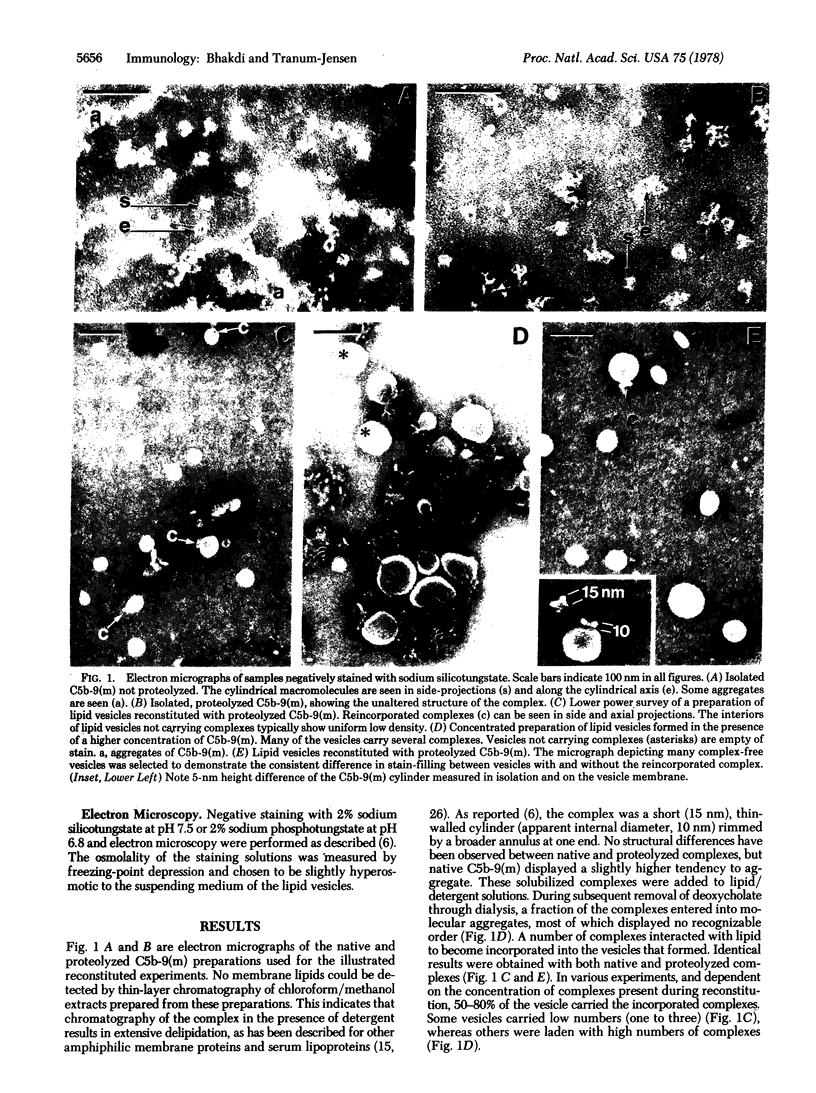
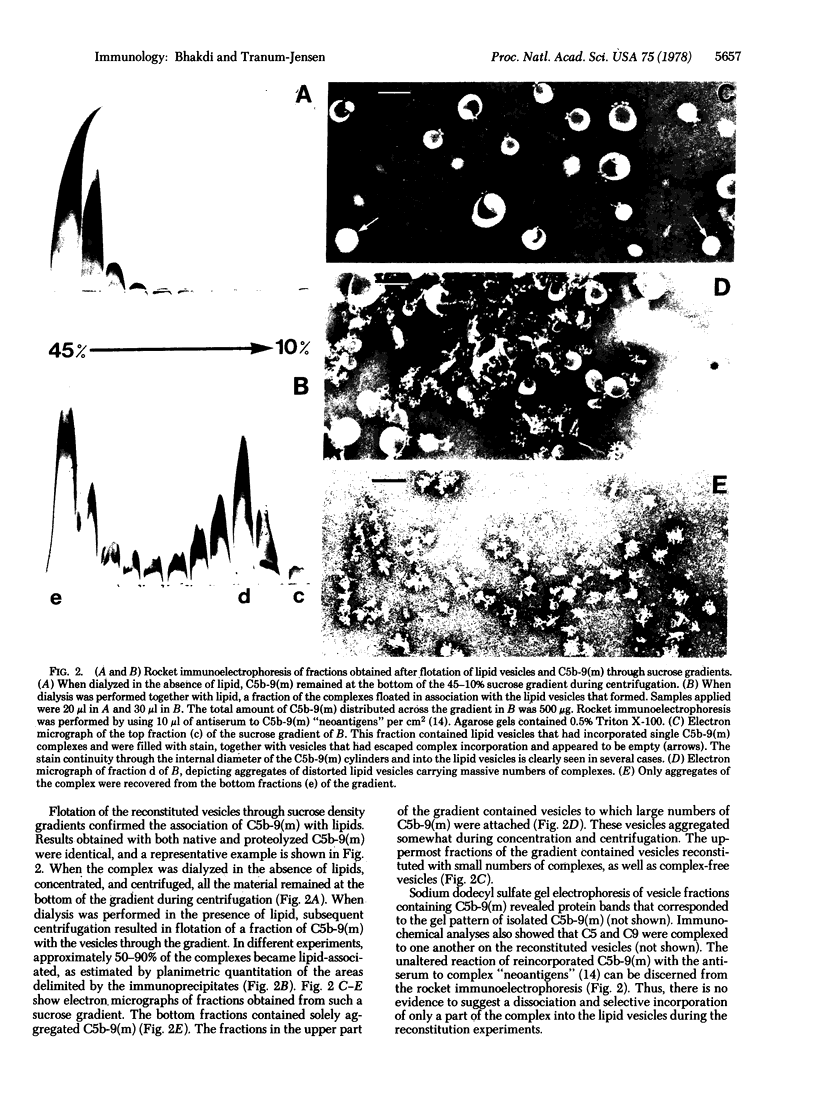
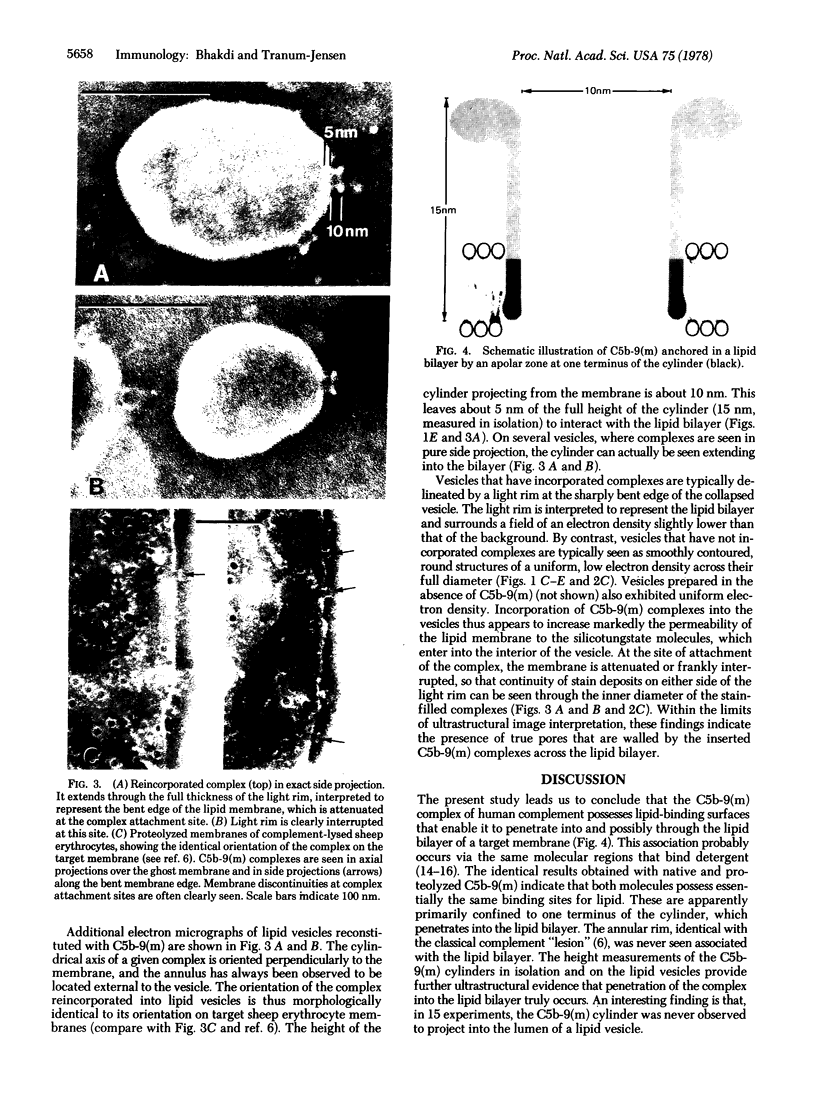
Abstract
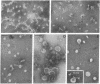
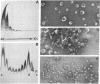
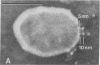
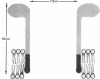
The principle molecular event leading to membrane perturbation by complement is the assembly of the terminal five serum complement components (C5b-C9) into a macromolecular C5b-9 complex on the target membrane [Müller-Eberhard, H.-J. (1975) Ann. Rev. Biochem. 44, 697--723]. The present communication reports on the ability of purified C5b-9 complexes isolated from target membranes to become reincorporated into artificial lipid vesicles. The data indicate that the complex is a vertically oriented, hollow, cylindrical macromolecule possessing lipid-binding regions that enable one terminus to penetrate into the lipid bilayer. A transmembrane pore appears to be created at the attachment site of the C5b-9 complex.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BORSOS T., DOURMASHKIN R. R., HUMPHREY J. H. LESIONS IN ERYTHROCYTE MEMBRANES CAUSED BY IMMUNE HAEMOLYSIS. Nature. 1964 Apr 18;202:251–252. doi: 10.1038/202251a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Bjerrum O. J., Rother U., Knüfermann H., Wallach D. F. Immunochemical analyses of membrane-bound complement. Detection of the terminal complement complex and its similarity to "intrinsic" erythrocyte membrane proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Sep 16;406(1):21–35. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90039-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Ey P., Bhakdi-Lehnen B. Isolation of the terminal complement complex from target sheep erythrocyte membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Feb 6;419(3):445–457. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90258-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Speth V., Knüfermann H., Wallach D. F., Fischer H. Complement-induced changes in the core structure of sheep erythrocyte membranes: a study by freeze-etch electron microscopy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Aug 9;356(3):300–308. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90270-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretscher M. S., Raff M. C. Mammalian plasma membranes. Nature. 1975 Nov 6;258(5530):43–49. doi: 10.1038/258043a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DODGE J. T., MITCHELL C., HANAHAN D. J. The preparation and chemical characteristics of hemoglobin-free ghosts of human erythrocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1963 Jan;100:119–130. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(63)90042-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dourmashkin R. R. The structural events associated with the attachment of complement components to cell membranes in reactive lysis. Immunology. 1978 Aug;35(2):205–212. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferber E., De Pasquale G. G., Resch K. Phospholipid metabolism of stimulated lymphocytes. Composition of phospholipid fatty acids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Sep 19;398(3):364–376. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(75)90187-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giavedoni E. B., Dalmasso A. P. The indiction by complement of a change in KSCN-dissociable red cell membrane lipids. J Immunol. 1976 Apr;116(4):1163–1169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammer C. H., Nicholson A., Mayer M. M. On the mechanism of cytolysis by complement: evidence on insertion of C5b and C7 subunits of the C5b,6,7 complex into phospholipid bilayers of erythrocyte membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):5076–5080. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.5076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammer C. H., Shin M. L., Abramovitz A. S., Mayer M. M. On the mechanism of cell membrane damage by complement: evidence on insertion of polypeptide chains from C8 and C9 into the lipid bilayer of erythrocytes. J Immunol. 1977 Jul;119(1):1–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helenius A., Fries E., Kartenbeck J. Reconstitution of Semliki forest virus membrane. J Cell Biol. 1977 Dec;75(3):866–880. doi: 10.1083/jcb.75.3.866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helenius A., Simons K. Solubilization of membranes by detergents. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 25;415(1):29–79. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(75)90016-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helenius A., Simons K. The binding of detergents to lipophilic and hydrophilic proteins. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 10;247(11):3656–3661. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hesketh T. R., Dourmashkin R. R., Payne S. N., Humphrey J. H., Lachmann P. J. Lesions due to complement in lipid membranes. Nature. 1971 Oct 29;233(5322):620–623. doi: 10.1038/233620a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey J. H., Dourmashkin R. R. The lesions in cell membranes caused by complement. Adv Immunol. 1969;11:75–115. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60478-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinoshita T., Inoue K., Okada M., Akiyama Y. Release of phospholipids from liposomal model membrane damaged by antibody and complement. J Immunol. 1977 Jul;119(1):73–76. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinsky S. C. Antibody-complement interaction with lipid model membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Feb 14;265(1):1–23. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(72)90017-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolb W. P., Haxby J. A., Arroyave C. M., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Molecular analysis of the membrane attack mechanism of complement. J Exp Med. 1972 Mar 1;135(3):549–566. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.3.549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolb W. P., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Mode of action of human C9: adsorption of multiple C9 molecules to cell-bound C8. J Immunol. 1974 Aug;113(2):479–488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachmann P. J., Bowyer D. E., Nicol P., Dawson R. M., Munn E. A. Studies on the terminal stages of complement lysis. Immunology. 1973 Jan;24(1):135–145. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachmann P. J., Munn E. A., Weissmanng Complement-mediated lysis of liposomes produced by the reactive lysis procedure. Immunology. 1970 Dec;19(6):983–986. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachmann P. J., Thompson R. A. Reactive lysis: the complement-mediated lysis of unsensitized cells. II. The characterization of activated reactor as C56 and the participation of C8 and C9. J Exp Med. 1970 Apr 1;131(4):643–657. doi: 10.1084/jem.131.4.643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. M. Mechanism of cytolysis by complement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Oct;69(10):2954–2958. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.10.2954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meissner G., Fleischer S. Dissociation and reconstitution of functional sarcoplasmic reticulum vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 10;249(1):302–309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaels D. W., Abramovitz A. S., Hammer C. H., Mayer M. M. Increased ion permeability of planar lipid bilayer membranes after treatment with the C5b-9 cytolytic attack mechanism of complement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2852–2856. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Eberhard H. J. Complement. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:697–724. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.003405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Packman C. H., Rosenfeld S. I., Weed R. I., Leddy J. P. Complement-induced ultrastructural membrane lesions: requirement for terminal components. J Immunol. 1976 Nov;117(5 PT2):1883–1889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shin M. L., Paznekas W. A., Abramovitz A. S., Mayer M. M. On the mechanism of membrane damage by C: exposure of hydrophobic sites on activated C proteins. J Immunol. 1977 Oct;119(4):1358–1364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer S. J., Nicolson G. L. The fluid mosaic model of the structure of cell membranes. Science. 1972 Feb 18;175(4023):720–731. doi: 10.1126/science.175.4023.720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strittmatter P., Rogers M. J. Apparent dependence of interactions between cytochrome b5 and cytochrome b5 reductase upon translational diffusion in dimyristoyl lecithin liposomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jul;72(7):2658–2661. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.7.2658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanford C., Reynolds J. A. Characterization of membrane proteins in detergent solutions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Oct 26;457(2):133–170. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(76)90009-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tranum-Jensen J., Bhakdi S., Bhakdi-Lehnen B., Bjerrum O. J., Speth V. Complement lysis: the ultrastructure and orientation of the C5b-9 complex on target sheep erythrocyte membranes. Scand J Immunol. 1978;7(1):45–46. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1978.tb00425.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valet G., Opferkuch W. Mechanism of complement-induced cell lysis. Demonstration of a three-step mechanism of EAC1-8 cell lysis by C9 and of a non-osmotic swelling of erythrocytes. J Immunol. 1975 Oct;115(4):1028–1033. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren G. B., Toon P. A., Birdsall N. J., Lee A. G., Metcalfe J. C. Reconstitution of a calcium pump using defined membrane components. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Mar;71(3):622–626. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.3.622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]