Abstract
Antibodies to group A streptococcal carbohydrate, demonstrable by radioimmunoassay, were elicited in Pacific hagfish, Eptatretus stoutii, after prolonged immunization with whole cell vaccine. This hagfish antibody, isolated by ion-exchange chromatography of immune serum, exhibited a single precipitin line after immunoelectrophoresis against rabbit antiserum to hagfish serum. The isolated antibodies retained high binding activity for the streptococcal carbohydrate, but lacked the natural hemagglutinating activity found in both nonimmune and immune sera. Analysis by gel filtration in neutral and dissociating buffers and by sodium dodecyl sulfate/polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis under nonreducing conditions indicated an intact molecule of molecular weight approximately 160,000 that may be noncovalently associated in a polymer of higher molecular weight. Heavy chains of mobility identical to that of murine μ chains and light chains of mobility significantly slower than murine λ chains were obtained after sodium dodecyl sulfate gel electrophoresis under reducing conditions. Instability of the tertiary structure of the antibody molecule was indicated by partial dissociation in buffers containing sodium dodecyl sulfate and by dissociation at low concentrations of reducing agent. In contrast to its well-developed system of cell-mediated immunity, only a minimal system of circulating antibody production is evident in this primitive fish. No evidence for divergence of cyclostome lymphocytes into separate T- and B-cell systems has yet been discerned.
Keywords: immunophylogeny, radioiodination, polypeptide chains, electrophoresis
Full text
PDF
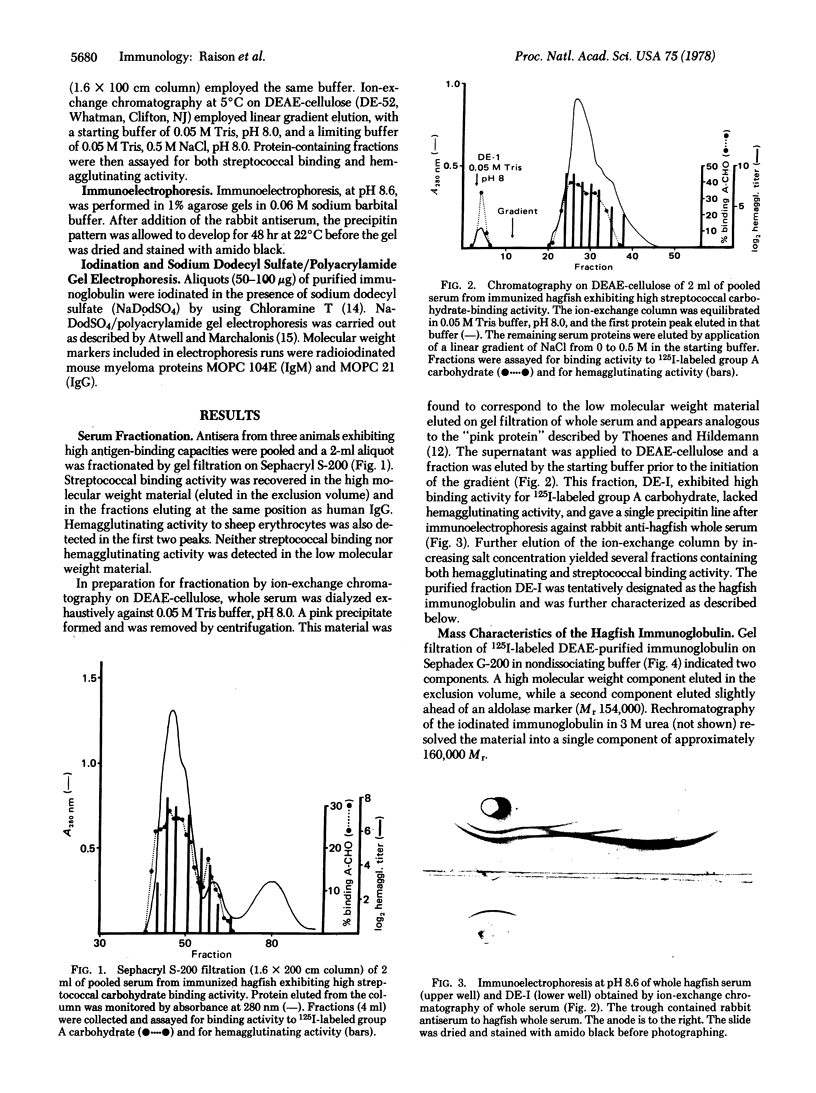
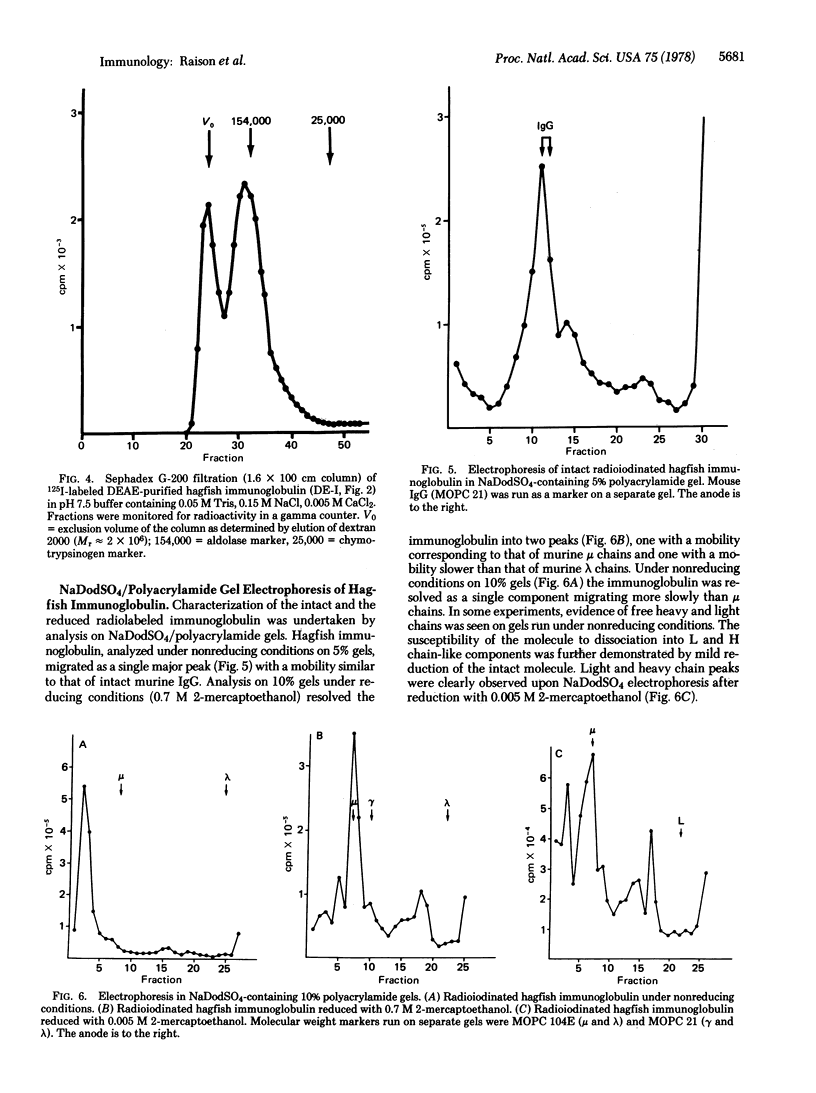

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acton R. T., Weinheimer P. F., Dupree H. K., Evans E. E., Bennett J. C. Phylogeny of immunoglobulins. Characterization of a 14S immunoglobulin from the gar, Lepisosteus osseus. Biochemistry. 1971 May 25;10(11):2028–2036. doi: 10.1021/bi00787a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray D., Brownlee S. M. Peptide mapping of proteins from acrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1973 Sep;55(1):213–221. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90306-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hildemann W. H., Thoenes G. H. Immunological responses of Pacific hagfish. I. Skin transplantation immunity. Transplantation. 1969 Jun;7(6):506–521. doi: 10.1097/00007890-196906000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston W. H., Jr, Acton R. T., Weinheimer P. F., Niedermeier W., Evans E. E., Shelton E., Bennett J. C. Isolation and physico-chemical characterization of the "IgM-like" immunologlobulin from the stingray Dasyatis americana. J Immunol. 1971 Sep;107(3):782–793. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klapper D. G., Clem L. W. Phylogeny of immunoglobulin structure and function; characterization of the cysteine-containing peptide involved in the pentamerization of shark IgM. Dev Comp Immunol. 1977 Apr;1(2):81–91. doi: 10.1016/s0145-305x(77)80002-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linthicum D. S., Hildemann W. H. Immunologic responses of Pacific hagfish. 3. Serum antibodies to cellular antigens. J Immunol. 1970 Oct;105(4):912–918. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litman G. W., Finstad F. J., Howell J., Pollara B. W., Good R. A. The evolution of the immune response. VIII. Structural studies of the lamprey immuoglobulin. J Immunol. 1970 Nov;105(5):1278–1285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchalonis J. J., Cone R. E. The phylogenetic emergence of vertebrate immunity. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1973 Aug;51(4):461–488. doi: 10.1038/icb.1973.44. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchalonis J. J., Edelman G. M. Phylogenetic origins of antibody structure. 3. Antibodies in the primary immune response of the sea lamprey, Petromyzon marinus. J Exp Med. 1968 May 1;127(5):891–914. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.5.891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCumber L. J., Clem L. W. A comparative study of J chain structure and stoichiometry in human and nurse shark IgM. Immunochemistry. 1976 Jun;13(6):479–484. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(76)90322-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moseley J. M., Marchalonis J. J., Harris A. W., Pye J. Molecular properties of T lymphoma immunoglobulin. I. Serological and general physicochemical properties. J Immunogenet. 1977 Aug;4(4):233–248. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-313x.1977.tb00906.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raison R. L., Hull C. J., Hildemann W. H. Production and specificity of antibodies to streptococci in the Pacific hagfish, Eptatretus stoutii. Dev Comp Immunol. 1978 Apr;2(2):253–261. doi: 10.1016/s0145-305x(78)80068-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warr G. W., Decker J. M., Marchalonis J. J. Evolutionary and developmental aspects of T-cell recognition. Immunol Commun. 1976;5(4):281–301. doi: 10.3109/08820137609044281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]