Abstract
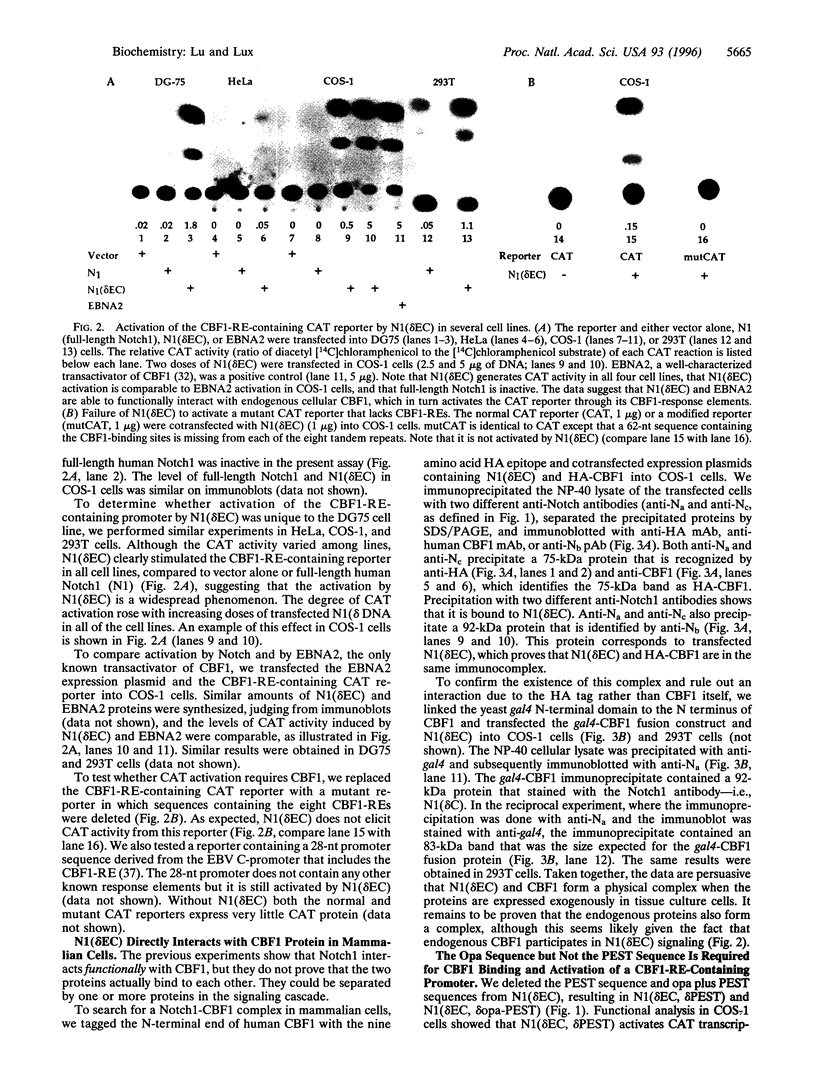
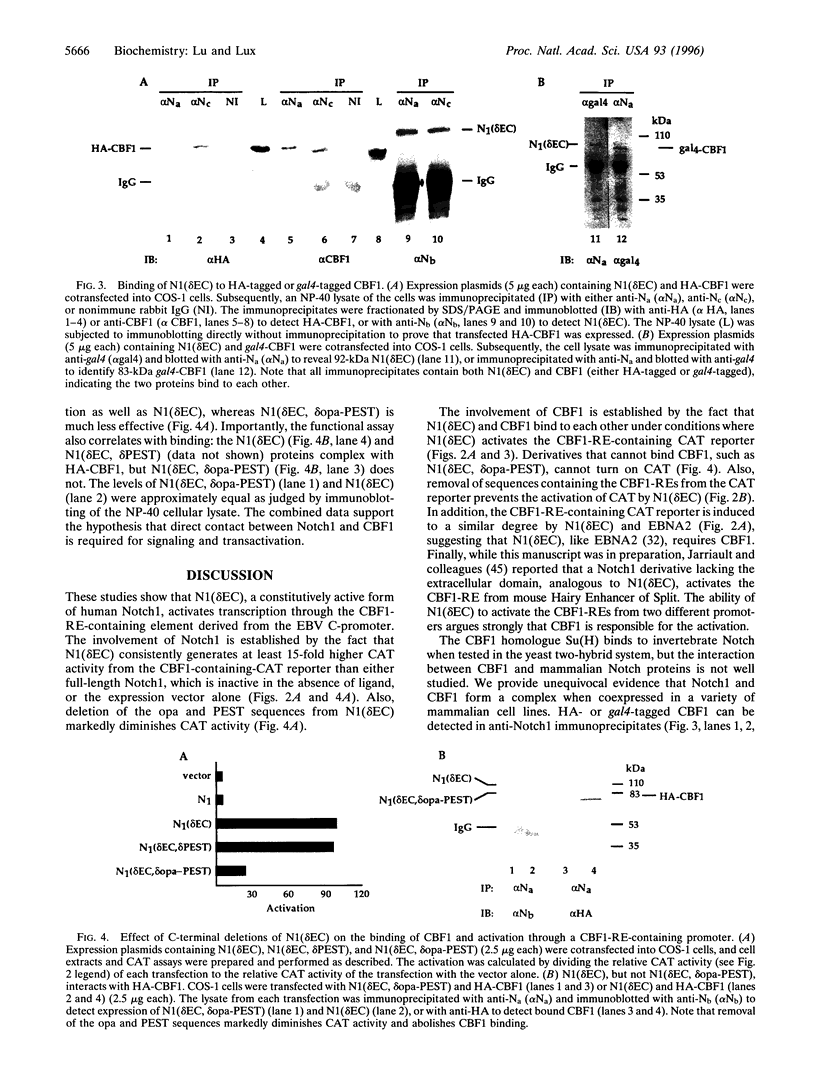
Notch is a transmembrane receptor that plays a critical role in cell fate determination. In Drosophila, Notch binds to and signals through Suppressor of Hairless. A mammalian homologue of Suppressor of Hairless, named CBF1 (or RBPJk), is a ubiquitous transcription factor whose function in mammalian Notch signaling is unknown. To determine whether mammalian Notch can stimulate transcription through a CBF1-responsive element (RE), we cotransfected a CBF1-RE-containing chloramphenicol acetyltransferase reporter and N1(deltaEC), a constitutively active form of human Notch1 lacking the extracellular domain, into DG75, COS-1, HeLa, and 293T cells, which all contain endogenous CBF1. N1(deltaEC) dramatically increased chloramphenicol acetyltransferase activity in these cells, indicating functional coupling of Notch1 and CBF1. The activity was comparable to that produced by the Epstein-Barr virus protein EBNA2, a well-characterized, potent transactivator of CBF1. To test whether CBF1 and Notch1 interact physically, we tagged CBF1 with an epitope from the influenza virus hemagglutinin or with the N-terminal domain of gal4, and transfected the tagged CBF1 plus N1(deltaEC) into COS-1 cells. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated and immunoblotted with several anti-Notch1 antibodies [to detect N1(deltaEC)] or with antibodies to hemagglutinin or gal4 (to detect CBF1). Each immunoprecipitate contained a complex of N1(deltaEC) and CBF1. In summary, we find that the truncated, active form of human Notch1, N1(deltaEC), binds CBF1 and activates transcription through a CBF1-RE-containing promoter. We conclude that CBF1 is a critical downstream protein in the human Notch1 signaling pathway.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alfieri C., Birkenbach M., Kieff E. Early events in Epstein-Barr virus infection of human B lymphocytes. Virology. 1991 Apr;181(2):595–608. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90893-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Artavanis-Tsakonas S., Matsuno K., Fortini M. E. Notch signaling. Science. 1995 Apr 14;268(5208):225–232. doi: 10.1126/science.7716513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breeden L., Nasmyth K. Similarity between cell-cycle genes of budding yeast and fission yeast and the Notch gene of Drosophila. Nature. 1987 Oct 15;329(6140):651–654. doi: 10.1038/329651a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffman C. R., Skoglund P., Harris W. A., Kintner C. R. Expression of an extracellular deletion of Xotch diverts cell fate in Xenopus embryos. Cell. 1993 May 21;73(4):659–671. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90247-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Amo F. F., Smith D. E., Swiatek P. J., Gendron-Maguire M., Greenspan R. J., McMahon A. P., Gridley T. Expression pattern of Motch, a mouse homolog of Drosophila Notch, suggests an important role in early postimplantation mouse development. Development. 1992 Jul;115(3):737–744. doi: 10.1242/dev.115.3.737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diederich R. J., Matsuno K., Hing H., Artavanis-Tsakonas S. Cytosolic interaction between deltex and Notch ankyrin repeats implicates deltex in the Notch signaling pathway. Development. 1994 Mar;120(3):473–481. doi: 10.1242/dev.120.3.473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellisen L. W., Bird J., West D. C., Soreng A. L., Reynolds T. C., Smith S. D., Sklar J. TAN-1, the human homolog of the Drosophila notch gene, is broken by chromosomal translocations in T lymphoblastic neoplasms. Cell. 1991 Aug 23;66(4):649–661. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90111-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fehon R. G., Johansen K., Rebay I., Artavanis-Tsakonas S. Complex cellular and subcellular regulation of notch expression during embryonic and imaginal development of Drosophila: implications for notch function. J Cell Biol. 1991 May;113(3):657–669. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.3.657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fortini M. E., Artavanis-Tsakonas S. Notch: neurogenesis is only part of the picture. Cell. 1993 Dec 31;75(7):1245–1247. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90611-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fortini M. E., Artavanis-Tsakonas S. The suppressor of hairless protein participates in notch receptor signaling. Cell. 1994 Oct 21;79(2):273–282. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90196-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fortini M. E., Rebay I., Caron L. A., Artavanis-Tsakonas S. An activated Notch receptor blocks cell-fate commitment in the developing Drosophila eye. Nature. 1993 Oct 7;365(6446):555–557. doi: 10.1038/365555a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frangioni J. V., Neel B. G. Solubilization and purification of enzymatically active glutathione S-transferase (pGEX) fusion proteins. Anal Biochem. 1993 Apr;210(1):179–187. doi: 10.1006/abio.1993.1170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furukawa T., Maruyama S., Kawaichi M., Honjo T. The Drosophila homolog of the immunoglobulin recombination signal-binding protein regulates peripheral nervous system development. Cell. 1992 Jun 26;69(7):1191–1197. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90640-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodbourn S. Signal transduction. Notch takes a short cut. Nature. 1995 Sep 28;377(6547):288–289. doi: 10.1038/377288a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwald I., Rubin G. M. Making a difference: the role of cell-cell interactions in establishing separate identities for equivalent cells. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):271–281. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90470-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman S. R., Johannsen E., Tong X., Yalamanchili R., Kieff E. The Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 transactivator is directed to response elements by the J kappa recombination signal binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Aug 2;91(16):7568–7572. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.16.7568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heitzler P., Simpson P. The choice of cell fate in the epidermis of Drosophila. Cell. 1991 Mar 22;64(6):1083–1092. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90263-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henkel T., Ling P. D., Hayward S. D., Peterson M. G. Mediation of Epstein-Barr virus EBNA2 transactivation by recombination signal-binding protein J kappa. Science. 1994 Jul 1;265(5168):92–95. doi: 10.1126/science.8016657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarriault S., Brou C., Logeat F., Schroeter E. H., Kopan R., Israel A. Signalling downstream of activated mammalian Notch. Nature. 1995 Sep 28;377(6547):355–358. doi: 10.1038/377355a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaelin W. G., Jr, Krek W., Sellers W. R., DeCaprio J. A., Ajchenbaum F., Fuchs C. S., Chittenden T., Li Y., Farnham P. J., Blanar M. A. Expression cloning of a cDNA encoding a retinoblastoma-binding protein with E2F-like properties. Cell. 1992 Jul 24;70(2):351–364. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90108-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidd S., Baylies M. K., Gasic G. P., Young M. W. Structure and distribution of the Notch protein in developing Drosophila. Genes Dev. 1989 Aug;3(8):1113–1129. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.8.1113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopan R., Nye J. S., Weintraub H. The intracellular domain of mouse Notch: a constitutively activated repressor of myogenesis directed at the basic helix-loop-helix region of MyoD. Development. 1994 Sep;120(9):2385–2396. doi: 10.1242/dev.120.9.2385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lardelli M., Dahlstrand J., Lendahl U. The novel Notch homologue mouse Notch 3 lacks specific epidermal growth factor-repeats and is expressed in proliferating neuroepithelium. Mech Dev. 1994 May;46(2):123–136. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(94)90081-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsell C. E., Shawber C. J., Boulter J., Weinmaster G. Jagged: a mammalian ligand that activates Notch1. Cell. 1995 Mar 24;80(6):909–917. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90294-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling P. D., Rawlins D. R., Hayward S. D. The Epstein-Barr virus immortalizing protein EBNA-2 is targeted to DNA by a cellular enhancer-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Oct 15;90(20):9237–9241. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.20.9237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling P. D., Ryon J. J., Hayward S. D. EBNA-2 of herpesvirus papio diverges significantly from the type A and type B EBNA-2 proteins of Epstein-Barr virus but retains an efficient transactivation domain with a conserved hydrophobic motif. J Virol. 1993 Jun;67(6):2990–3003. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.6.2990-3003.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lux S. E., John K. M., Bennett V. Analysis of cDNA for human erythrocyte ankyrin indicates a repeated structure with homology to tissue-differentiation and cell-cycle control proteins. Nature. 1990 Mar 1;344(6261):36–42. doi: 10.1038/344036a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsunami N., Hamaguchi Y., Yamamoto Y., Kuze K., Kangawa K., Matsuo H., Kawaichi M., Honjo T. A protein binding to the J kappa recombination sequence of immunoglobulin genes contains a sequence related to the integrase motif. Nature. 1989 Dec 21;342(6252):934–937. doi: 10.1038/342934a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rebay I., Fehon R. G., Artavanis-Tsakonas S. Specific truncations of Drosophila Notch define dominant activated and dominant negative forms of the receptor. Cell. 1993 Jul 30;74(2):319–329. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90423-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roehl H., Kimble J. Control of cell fate in C. elegans by a GLP-1 peptide consisting primarily of ankyrin repeats. Nature. 1993 Aug 12;364(6438):632–635. doi: 10.1038/364632a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers S., Wells R., Rechsteiner M. Amino acid sequences common to rapidly degraded proteins: the PEST hypothesis. Science. 1986 Oct 17;234(4774):364–368. doi: 10.1126/science.2876518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweisguth F., Posakony J. W. Suppressor of Hairless, the Drosophila homolog of the mouse recombination signal-binding protein gene, controls sensory organ cell fates. Cell. 1992 Jun 26;69(7):1199–1212. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90641-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl G., Fitzgerald K., Greenwald I. Intrinsic activity of the Lin-12 and Notch intracellular domains in vivo. Cell. 1993 Jul 30;74(2):331–345. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90424-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swiatek P. J., Lindsell C. E., del Amo F. F., Weinmaster G., Gridley T. Notch1 is essential for postimplantation development in mice. Genes Dev. 1994 Mar 15;8(6):707–719. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.6.707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang F., Kikutani H., Tsang S. F., Kishimoto T., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus nuclear protein 2 transactivates a cis-acting CD23 DNA element. J Virol. 1991 Aug;65(8):4101–4106. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.8.4101-4106.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinmaster G., Roberts V. J., Lemke G. A homolog of Drosophila Notch expressed during mammalian development. Development. 1991 Sep;113(1):199–205. doi: 10.1242/dev.113.1.199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinmaster G., Roberts V. J., Lemke G. Notch2: a second mammalian Notch gene. Development. 1992 Dec;116(4):931–941. doi: 10.1242/dev.116.4.931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wharton K. A., Johansen K. M., Xu T., Artavanis-Tsakonas S. Nucleotide sequence from the neurogenic locus notch implies a gene product that shares homology with proteins containing EGF-like repeats. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):567–581. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90229-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wharton K. A., Yedvobnick B., Finnerty V. G., Artavanis-Tsakonas S. opa: a novel family of transcribed repeats shared by the Notch locus and other developmentally regulated loci in D. melanogaster. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):55–62. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90308-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- del Amo F. F., Gendron-Maguire M., Swiatek P. J., Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G., Gridley T. Cloning, analysis, and chromosomal localization of Notch-1, a mouse homolog of Drosophila Notch. Genomics. 1993 Feb;15(2):259–264. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]