Abstract
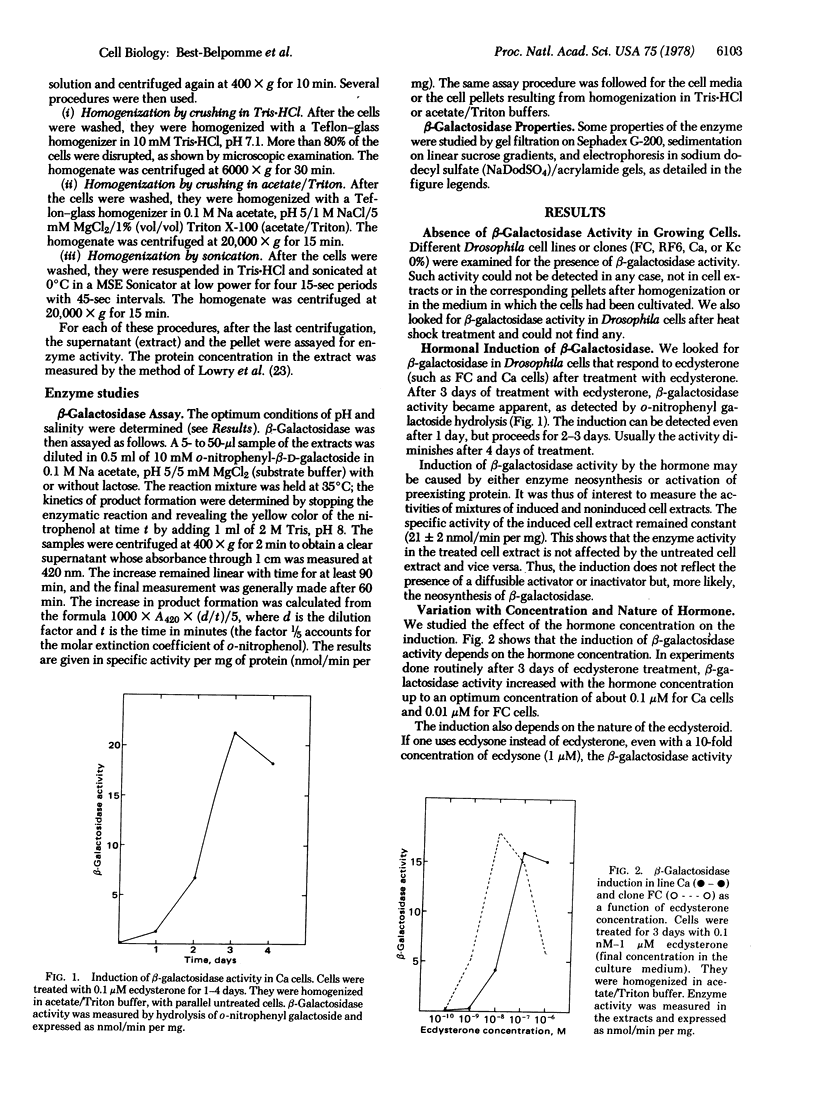
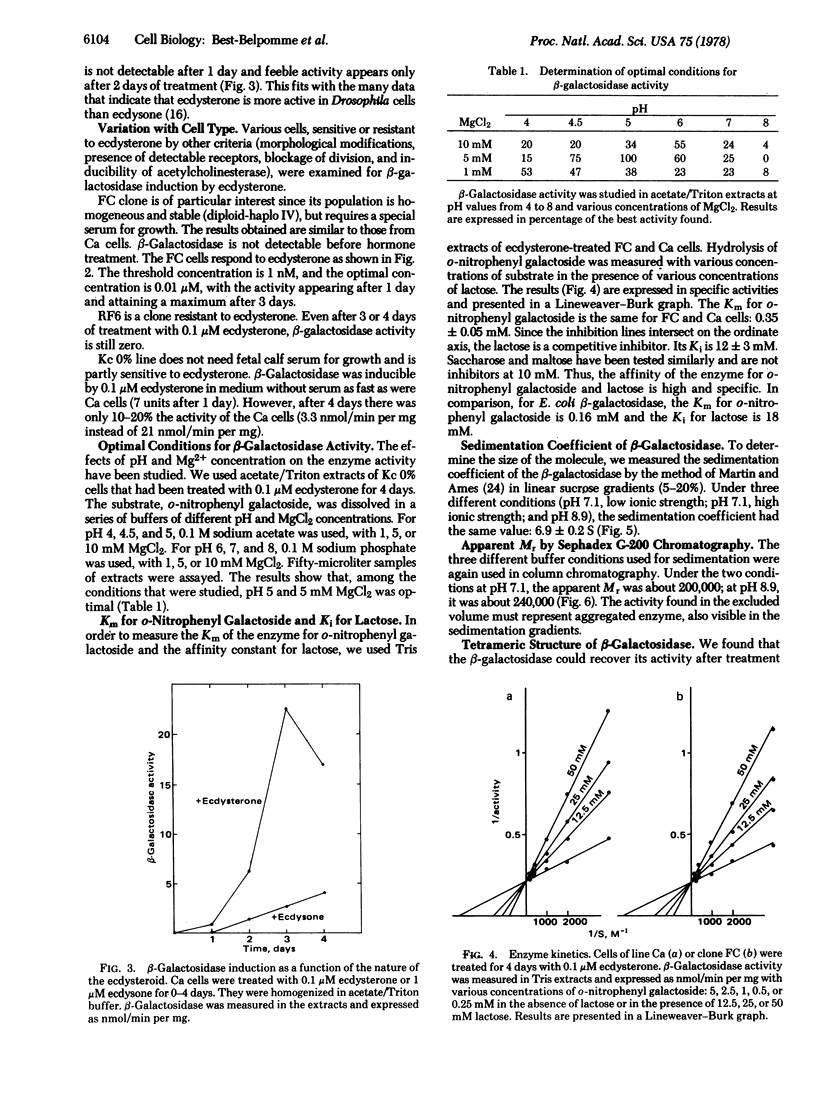
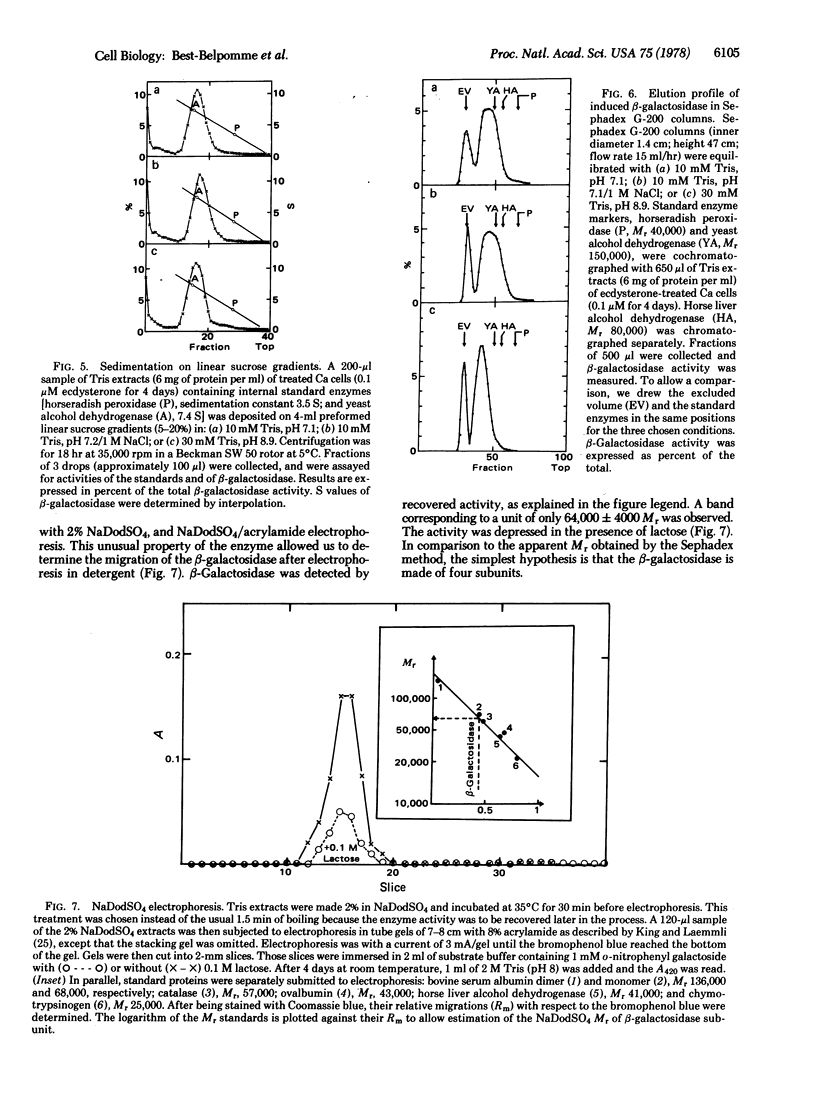
Drosophila melanogaster cell lines Kc and Ca and clones FC and RF6, cultured in vitro, have no detectable beta-galactosidase (beta-galactoside galactohydrolase, EC 3.2.1.23) activity (as measured by hydrolysis of o-nitrophenyl-beta-D-galoctoside). Ecdysterone, a hormonal steroid of critical importance in insect physiology, clearly induces beta-galactosidase activity in D. melanogaster cells cultured in vitro. Induction occurs in cell lines or clones known to be sensitive to ecdysterone (K, Ca, and Fc) and does not occur in clones known to be resistant to the hormone (RF6). Some properties of the hormone-induced beta-galactosidase activity were studied. The Km for o-nitrophenyl galactoside is 0.35 mM and the Ki for lactose is 12 mM (similar to those of Escherichia coli beta-galactosidase); the activity can be recovered after sodium dodecyl sulfate treatment; the enzyme is a tetramer (Mr of the monomer is 64,000).
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Best-Belpomme M., Courgeon A. M. Ecdysterone and acetylcholinesterase activity in cultured Drosophila cells. Inducible, non-inducible and constitutive clones or lines. FEBS Lett. 1977 Oct 15;82(2):345–347. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80617-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARTER H. E., GREENWOOD F. L. Biochemistry of the sphingolipides. VII. Structure of the cerebrosides. J Biol Chem. 1952 Nov;199(1):283–288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherbas P., Cherbas L., Williams C. M. Induction of acetylcholinesterase activity by beta-ecdysone in a Drosophila cell line. Science. 1977 Jul 15;197(4300):275–277. doi: 10.1126/science.877552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courgeon A. M. Action of insect hormones at the cellular level. II. Differing sensitivity to beta-ecdysone of several lines and clones of Drosophila melanogaster cells. Exp Cell Res. 1975 Sep;94(2):283–291. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(75)90494-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courgeon A. M. Action of insect hormones at the cellular level. Morphological changes of a diploid cell line of Drosophila melanogaster, treated with ecdysone and several analogues in vitro. Exp Cell Res. 1972 Oct;74(2):327–336. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(72)90384-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courgeon A. M. Effects of - and -ecdysone on in vitro diploid cell multiplication in Drosophila melanogaster. Nat New Biol. 1972 Aug 23;238(86):250–251. doi: 10.1038/newbio238250a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Reggi M. L., Hirn M. H., Delaage M. A. Radioimmunossay of ecdysone. An application to Drosophila larvae and pupae. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Oct 27;66(4):1307–1315. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90502-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debec A. Haploid cell cultures of Drosophila melanogaster. Nature. 1978 Jul 20;274(5668):255–256. doi: 10.1038/274255a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echalier G., Ohanessian A. In vitro culture of Drosophila melanogaster embryonic cells. In Vitro. 1970 Nov-Dec;6(3):162–172. doi: 10.1007/BF02617759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echalier G., Ohanessian A. Isolement, en cultures in vitro, de lignées cellulaires diploïdes de Drosophila melanogaster. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1969 Mar 31;268(13):1771–1773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACOB F., MONOD J. Genetic regulatory mechanisms in the synthesis of proteins. J Mol Biol. 1961 Jun;3:318–356. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(61)80072-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King J., Laemmli U. K. Polypeptides of the tail fibres of bacteriophage T4. J Mol Biol. 1971 Dec 28;62(3):465–477. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90148-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN R. G., AMES B. N. A method for determining the sedimentation behavior of enzymes: application to protein mixtures. J Biol Chem. 1961 May;236:1372–1379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie S. L., Henikoff S., Meselson M. Localization of RNA from heat-induced polysomes at puff sites in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1117–1121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mraz W., Jatzkewitz H. Cerebroside sulphatase activity of arylsulphatases from various invertebrates. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1974 Jan;355(1):33–44. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1974.355.1.33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rambach A., Hogness D. S. Translation of Drosophila melanogaster sequences in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):5041–5045. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.5041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spradling A., Penman S., Pardue M. L. Analysis of drosophila mRNA by in situ hybridization: sequences transcribed in normal and heat shocked cultured cells. Cell. 1975 Apr;4(4):395–404. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90160-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tissières A., Mitchell H. K., Tracy U. M. Protein synthesis in salivary glands of Drosophila melanogaster: relation to chromosome puffs. J Mol Biol. 1974 Apr 15;84(3):389–398. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90447-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wensink P. C., Finnegan D. J., Donelson J. E., Hogness D. S. A system for mapping DNA sequences in the chromosomes of Drosophila melanogaster. Cell. 1974 Dec;3(4):315–325. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(74)90045-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


