Abstract
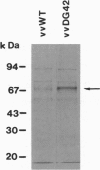
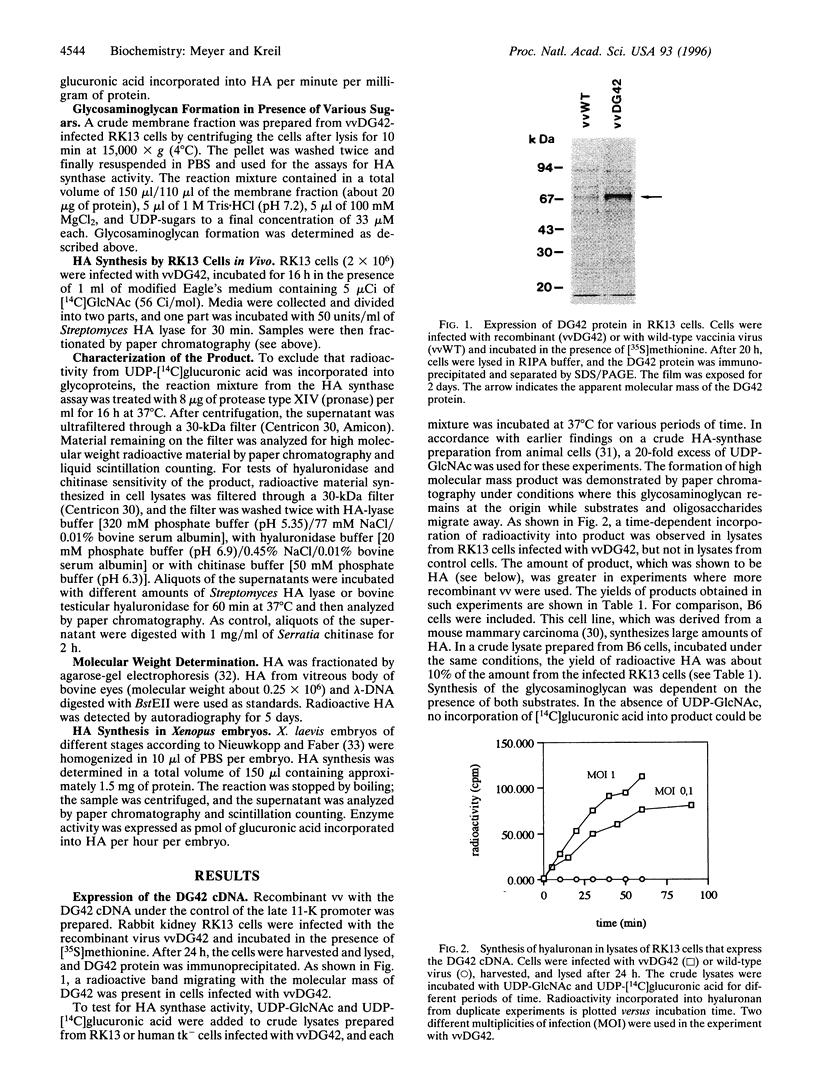
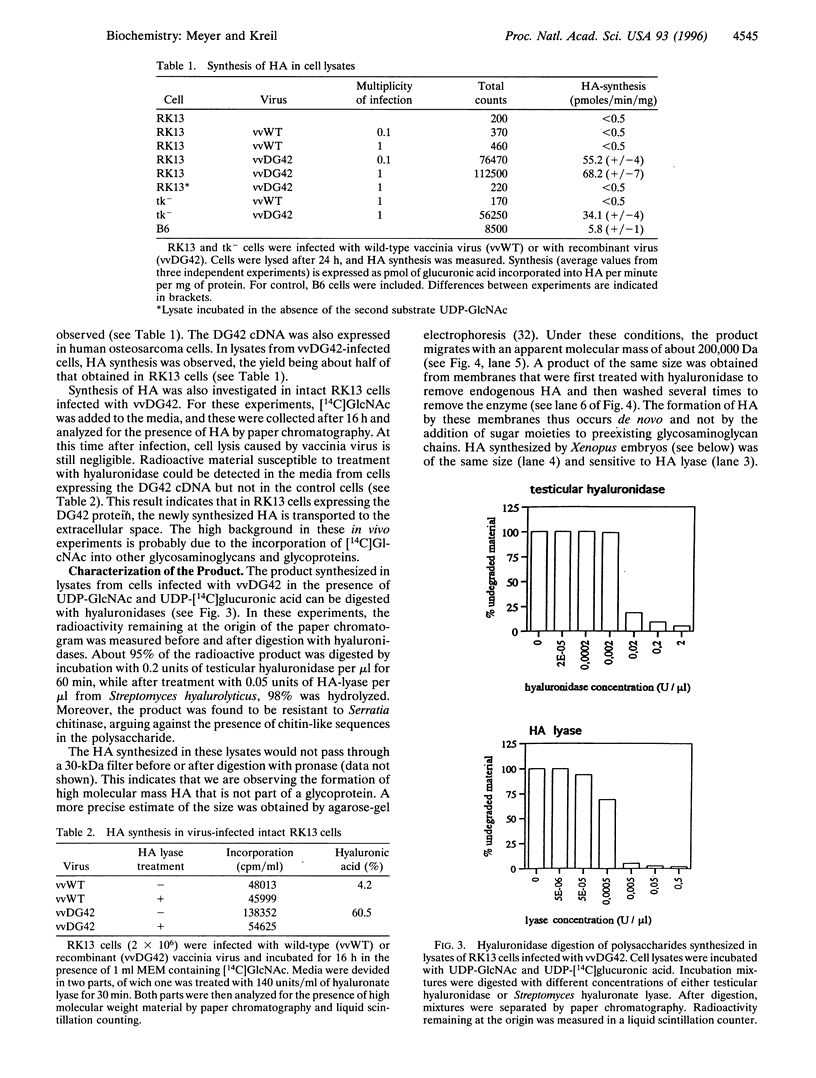
DG42 is one of the main mRNAs expressed during gastrulation in embryos of Xenopus laevis. Here we demonstrate that cells expressing this mRNA synthesize hyaluronan. The cloned DG42 cDNA was expressed in rabbit kidney (RK13) and human osteosarcoma (tk-) cells using a vaccinia virus system. Lysates prepared from infected cells were incubated in the presence of UDP-N-acetylglucosamine and UDP-[14C]glucuronic acid. This yielded a glycosaminoglycan with a molecular mass of about 200,000 Da. Formation of this product was only observed in the presence of both substrates. The glycosaminoglycan could be digested with testicular hyaluronidase and with Streptomyces hyaluronate lyase but not with Serratia chitinase. Hyaluronan synthase activity could also be detected in homogenates of early Xenopus embryos, and the activity was found to correlate with the expression of DG42 mRNA at different stages of development. Synthesis of hyaluronan is thus an early event after midblastula transition, indicating its importance for the ensuing cell movements in the developing embryo. Our results are at variance with a recent report (Semino, C. E. & Robbins, P. W. (1995) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92, 3498-3501) that DG42 codes for an enzyme that catalyzes the synthesis of chitin-like oligosaccharides.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aruffo A., Stamenkovic I., Melnick M., Underhill C. B., Seed B. CD44 is the principal cell surface receptor for hyaluronate. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1303–1313. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90694-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulawa C. E., Wasco W. Chitin and nodulation. Nature. 1991 Oct 24;353(6346):710–710. doi: 10.1038/353710b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Culty M., Miyake K., Kincade P. W., Sikorski E., Butcher E. C., Underhill C., Silorski E. The hyaluronate receptor is a member of the CD44 (H-CAM) family of cell surface glycoproteins. J Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;111(6 Pt 1):2765–2774. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.6.2765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeAngelis P. L., Papaconstantinou J., Weigel P. H. Molecular cloning, identification, and sequence of the hyaluronan synthase gene from group A Streptococcus pyogenes. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 15;268(26):19181–19184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeAngelis P. L., Yang N., Weigel P. H. The Streptococcus pyogenes hyaluronan synthase: sequence comparison and conservation among various group A strains. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Feb 28;199(1):1–10. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.1184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dénarié J., Cullimore J. Lipo-oligosaccharide nodulation factors: a minireview new class of signaling molecules mediating recognition and morphogenesis. Cell. 1993 Sep 24;74(6):951–954. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90717-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gmachl M., Sagan S., Ketter S., Kreil G. The human sperm protein PH-20 has hyaluronidase activity. FEBS Lett. 1993 Dec 28;336(3):545–548. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80873-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall C. L., Yang B., Yang X., Zhang S., Turley M., Samuel S., Lange L. A., Wang C., Curpen G. D., Savani R. C. Overexpression of the hyaluronan receptor RHAMM is transforming and is also required for H-ras transformation. Cell. 1995 Jul 14;82(1):19–26. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90048-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardwick C., Hoare K., Owens R., Hohn H. P., Hook M., Moore D., Cripps V., Austen L., Nance D. M., Turley E. A. Molecular cloning of a novel hyaluronan receptor that mediates tumor cell motility. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;117(6):1343–1350. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.6.1343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishimoto N., Temin H. M., Strominger J. L. Studies of carcinogenesis by avian sarcoma viruses. II. Virus-induced increase in hyaluronic acid synthetase in chicken fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1966 May 10;241(9):2052–2057. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaworski D. M., Kelly G. M., Hockfield S. BEHAB, a new member of the proteoglycan tandem repeat family of hyaluronan-binding proteins that is restricted to the brain. J Cell Biol. 1994 Apr;125(2):495–509. doi: 10.1083/jcb.125.2.495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klewes L., Turley E. A., Prehm P. The hyaluronate synthase from a eukaryotic cell line. Biochem J. 1993 Mar 15;290(Pt 3):791–795. doi: 10.1042/bj2900791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koyama H., Yatabe I., Ono T. Isolation and characterization of hybrids between mouse and Chinese hamster cell lines. Exp Cell Res. 1970 Oct;62(2):455–463. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(70)90577-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurent T. C., Fraser J. R. Hyaluronan. FASEB J. 1992 Apr;6(7):2397–2404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee H. G., Cowman M. K. An agarose gel electrophoretic method for analysis of hyaluronan molecular weight distribution. Anal Biochem. 1994 Jun;219(2):278–287. doi: 10.1006/abio.1994.1267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerouge P., Roche P., Faucher C., Maillet F., Truchet G., Promé J. C., Dénarié J. Symbiotic host-specificity of Rhizobium meliloti is determined by a sulphated and acylated glucosamine oligosaccharide signal. Nature. 1990 Apr 19;344(6268):781–784. doi: 10.1038/344781a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCourt P. A., Ek B., Forsberg N., Gustafson S. Intercellular adhesion molecule-1 is a cell surface receptor for hyaluronan. J Biol Chem. 1994 Dec 2;269(48):30081–30084. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyake K., Underhill C. B., Lesley J., Kincade P. W. Hyaluronate can function as a cell adhesion molecule and CD44 participates in hyaluronate recognition. J Exp Med. 1990 Jul 1;172(1):69–75. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.1.69. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philipson L. H., Schwartz N. B. Subcellular localization of hyaluronate synthetase in oligodendroglioma cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 25;259(8):5017–5023. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosa F., Sargent T. D., Rebbert M. L., Michaels G. S., Jamrich M., Grunz H., Jonas E., Winkles J. A., Dawid I. B. Accumulation and decay of DG42 gene products follow a gradient pattern during Xenopus embryogenesis. Dev Biol. 1988 Sep;129(1):114–123. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(88)90166-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salustri A., Ulisse S., Yanagishita M., Hascall V. C. Hyaluronic acid synthesis by mural granulosa cells and cumulus cells in vitro is selectively stimulated by a factor produced by oocytes and by transforming growth factor-beta. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 15;265(32):19517–19523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargent T. D., Dawid I. B. Differential gene expression in the gastrula of Xenopus laevis. Science. 1983 Oct 14;222(4620):135–139. doi: 10.1126/science.6688681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargent T. D., Jamrich M., Dawid I. B. Cell interactions and the control of gene activity during early development of Xenopus laevis. Dev Biol. 1986 Mar;114(1):238–246. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(86)90399-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semino C. E., Robbins P. W. Synthesis of "Nod"-like chitin oligosaccharides by the Xenopus developmental protein DG42. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Apr 11;92(8):3498–3501. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.8.3498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman L., Sleeman J., Herrlich P., Ponta H. Hyaluronate receptors: key players in growth, differentiation, migration and tumor progression. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1994 Oct;6(5):726–733. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(94)90100-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stunnenberg H. G., Lange H., Philipson L., van Miltenburg R. T., van der Vliet P. C. High expression of functional adenovirus DNA polymerase and precursor terminal protein using recombinant vaccinia virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Mar 25;16(6):2431–2444. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.6.2431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West D. C., Hampson I. N., Arnold F., Kumar S. Angiogenesis induced by degradation products of hyaluronic acid. Science. 1985 Jun 14;228(4705):1324–1326. doi: 10.1126/science.2408340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]