Abstract
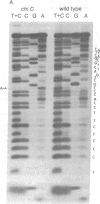
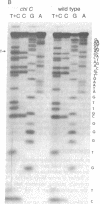
X4+ mutations, responsible for the Chi phenotype in phage lambda, locally increase the rate of recombination promoted by the Escherichia coli recombination system (Rec). X+ mutations in the cII gene, one of a few sites in lambda at which such mutations arise, were located genetically and physically with overlapping deletions. DNA sequence analysis of the deletion segment containing the X+ C mutations showed that two independent X+ C mutations arose by the same A-T to T-A transversion. Presumably, this change creates a nucleotide sequence recognized by a protein involved in a rate-limiting step of recombination.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Belfort M., Noff D., Oppenheim A. B. Isolation, characterization and deletion mapping of amber mutations in the cll gene of phage lambda. Virology. 1975 Jan;63(1):147–159. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90380-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkner K. L., Folk W. R. Polynucleotide kinase exchange reaction: quantitave assay for restriction endonuclease-generated 5'-phosphoroyl termini in DNA. J Biol Chem. 1977 May 25;252(10):3176–3184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chessin H., Summers W. C. Initiation by RNA polymerase on UV or x-ray damaged T7 DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Jan 6;38(1):40–45. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)91080-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Condit R. C., Steitz J. A. F factor-mediated inhibition of bacteriophage T7 growth: analysis of T7 RNA and protein synthesis in vivo and in vitro using male and female Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1975 Oct 15;98(1):31–43. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80099-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furth M. E., Blattner F. R., McLeester C., Dove W. F. Genetic structure of the replication origin of bacteriophage lambda. Science. 1977 Dec 9;198(4321):1046–1051. doi: 10.1126/science.929186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galibert F., Sedat J., Ziff E. Direct determination of DNA nucleotide sequences: structure of a fragment of bacteriophage phiX172 DNA. J Mol Biol. 1974 Aug 15;87(3):377–407. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90093-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson D., Weil J. Recombination-deficient deletions in bacteriophage lambda and their interaction with chi mutations. Genetics. 1975 Feb;79(2):143–174. doi: 10.1093/genetics/79.2.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malone R. E., Chattoraj D. K., Faulds D. H., Stahl M. M., Stahl F. W. Hotspots for generalized recombination in the Escherichia coli chromosome. J Mol Biol. 1978 Jun 5;121(4):473–491. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90395-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray K., Murray N. E. Phage lambda receptor chromosomes for DNA fragments made with restriction endonuclease III of Haemophilus influenzae and restriction endonuclease I of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):551–564. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80086-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts R. J., Myers P. A., Morrison A., Murray K. A specific endonuclease from Arthrobacter luteus. J Mol Biol. 1976 Mar 25;102(1):157–165. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90079-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson L. H., Landy A. HindII, HindIII, and HpaI restriction fragment maps of the left arm of bacteriophage lambda DNA. Gene. 1977 Sep;2(1):33–54. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(77)90020-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Court D., Shimatake H., Brady C., Wulff D. L. The relationship between function and DNA sequence in an intercistronic regulatory region in phage lambda. Nature. 1978 Mar 30;272(5652):414–423. doi: 10.1038/272414a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz E., Scherer G., Hobom G., Kössel H. Nucleotide sequence of cro, cII and part of the O gene in phage lambda DNA. Nature. 1978 Mar 30;272(5652):410–414. doi: 10.1038/272410a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. A., Sugden B., Sambrook J. Detection of two restriction endonuclease activities in Haemophilus parainfluenzae using analytical agarose--ethidium bromide electrophoresis. Biochemistry. 1973 Jul 31;12(16):3055–3063. doi: 10.1021/bi00740a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibatani A. Precipitation and counting of minute quantities of labeled nucleic acids as cetyltrimethylammonium salt. Anal Biochem. 1970 Feb;33(2):279–285. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(70)90298-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. R. Deletion mutations of the immunity region of coliphage lambda. Virology. 1975 Apr;64(2):544–552. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90131-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl F. W., Crasemann J. M., Stahl M. M. Rec-mediated recombinational hot spot activity in bacteriophage lambda. III. Chi mutations are site-mutations stimulating rec-mediated recombination. J Mol Biol. 1975 May 15;94(2):203–212. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90078-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl F. W., Stahl M. M. Recombination pathway specificity of Chi. Genetics. 1977 Aug;86(4):715–725. doi: 10.1093/genetics/86.4.715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas M., Davis R. W. Studies on the cleavage of bacteriophage lambda DNA with EcoRI Restriction endonuclease. J Mol Biol. 1975 Jan 25;91(3):315–328. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90383-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]