Abstract
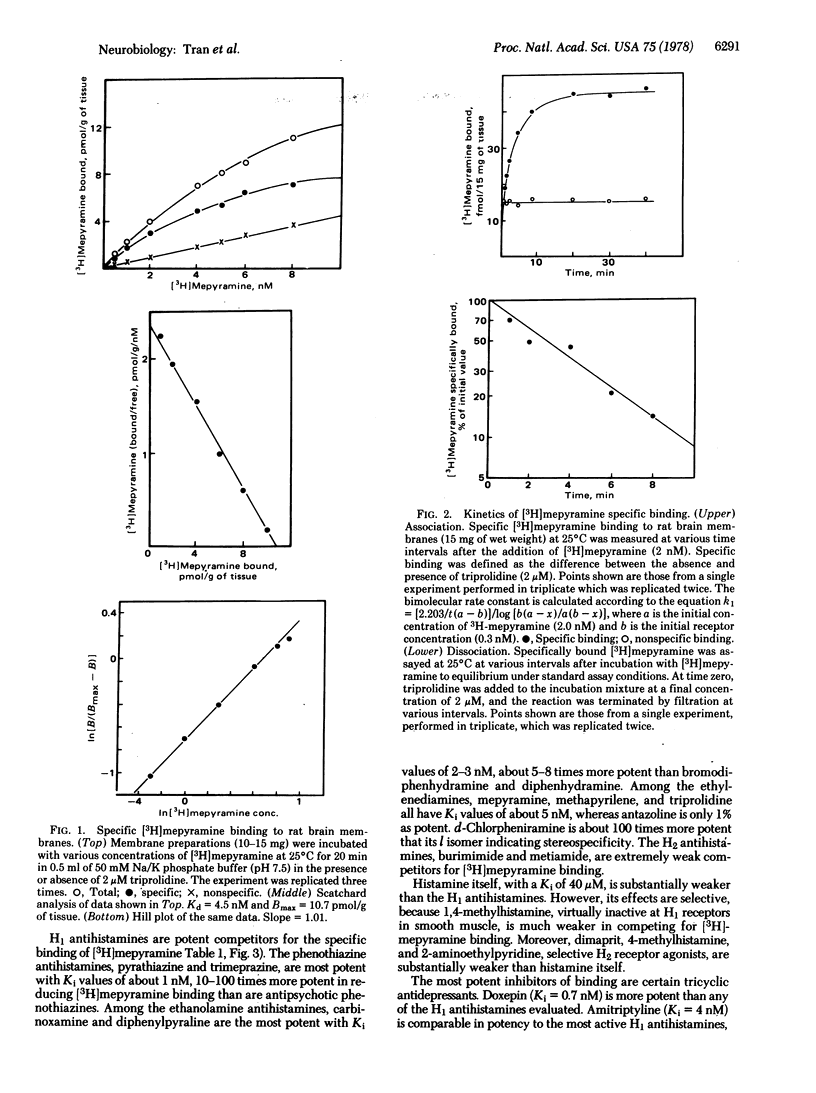
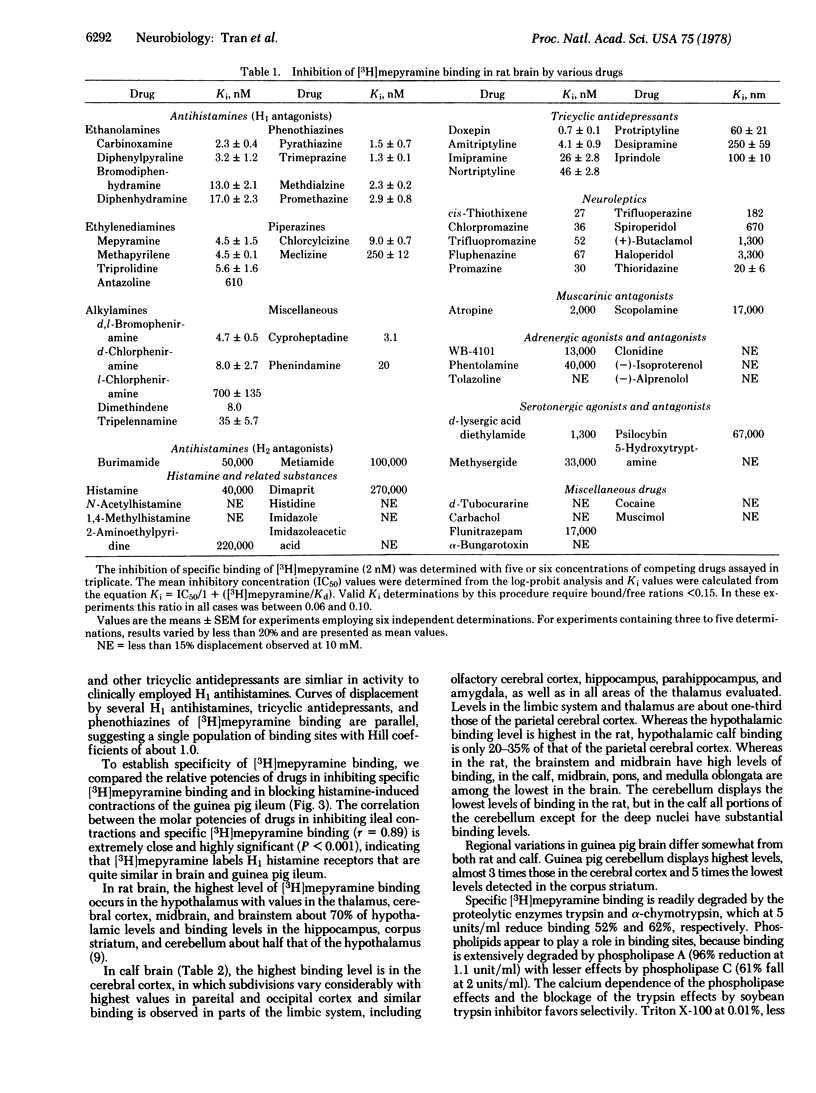
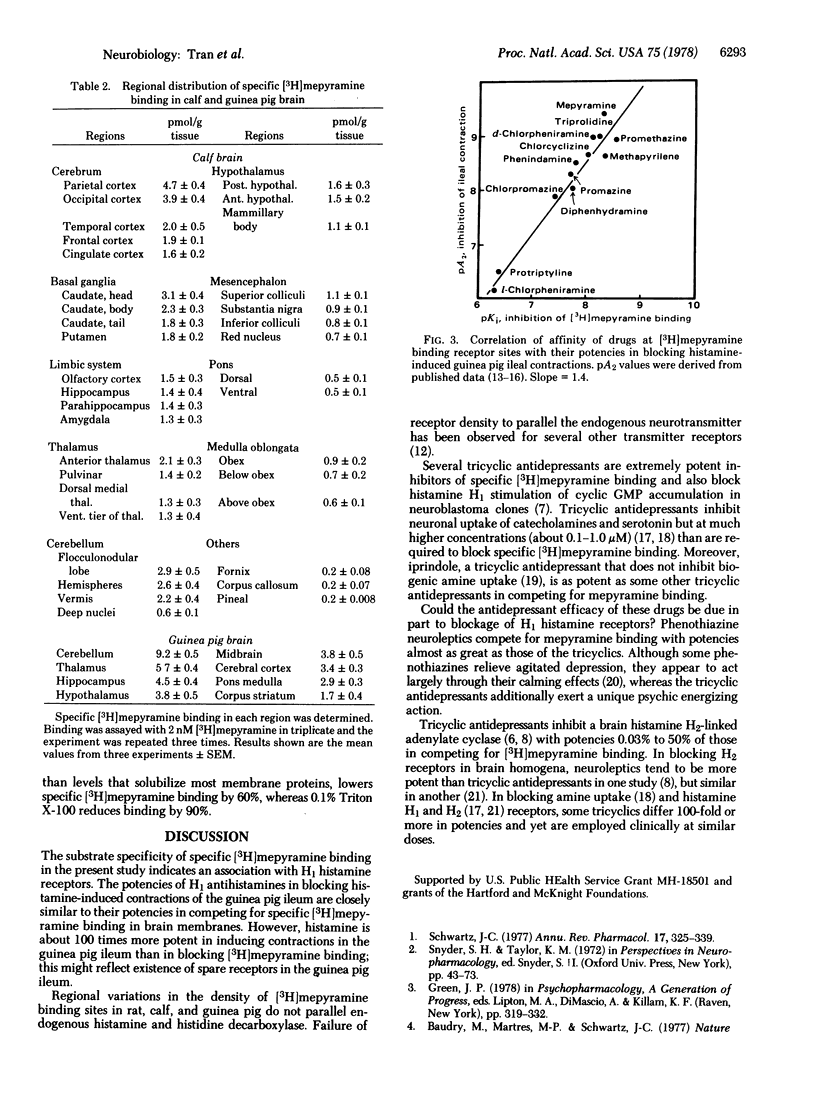
The antihistamine [3H]mepyramine binds to H1 histamine receptors in mammalian brain membranes. Potencies of H1 antihistamines at the binding sites correlate with their pharmacological antihistamine effects in the guinea pig ileum. Specific [3H]mepyramine binding is saturable with a dissociation constant of about 4 nM in both equilibrium and kinetic experiments and a density of 10 pmol per gram of whole kinetic experiments and a density of 10 pmol per gram of whole brain. Some tricyclic antidepressants are potent inhibitors of specific [3H]mepyramine binding. Regional variations of [3H]mepyramine binding do not correlate with variations in endogeneous histamine and histidine decarboxylase activity.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chang K. J., Jacobs S., Cuatrecasas P. Quantitative aspects of hormone-receptor interactions of high affinity. Effect of receptor concentration and measurement of dissociation constants of labeled and unlabeled hormones. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Oct 6;406(2):294–303. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90011-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang R. S., Tran V. T., Snyder S. H. Histamine H1-receptors in brain labeled with 3H-mepyramine. Eur J Pharmacol. 1978 Apr 15;48(4):463–464. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(78)90177-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluckman M. I., Baum T. The pharmacology of iprindole, a new antidepressant. Psychopharmacologia. 1969;15(3):169–185. doi: 10.1007/BF00411167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green J. P., Maayani S. Tricyclic antidepressant drugs block histamine H2 receptor in brain. Nature. 1977 Sep 8;269(5624):163–165. doi: 10.1038/269163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill S. J., Young J. M., Marrian D. H. Specific binding of 3H-mepyramine to histamine H1 receptors in intestinal smooth muscle. Nature. 1977 Nov 24;270(5635):361–363. doi: 10.1038/270361a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn A. S., Coyle J. T., Snyder S. H. Catecholamine uptake by synaptosomes from rat brain. Structure-activity relationships of drugs with differential effects on dopamine and norepinephrine neurons. Mol Pharmacol. 1971 Jan;7(1):66–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ison R. R., Franks F. M., Soh K. S. The binding of conformationally restricted antihistamines to histamine receptors. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1973 Nov;25(11):887–894. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1973.tb09968.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanof P. D., Greengard P. Brain histamine receptors as targets for antidepressant drugs. Nature. 1978 Mar 23;272(5651):329–333. doi: 10.1038/272329a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARSHALL P. B. Some chemical and physical properties associated with histamine antagonism. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1955 Sep;10(3):270–278. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1955.tb00870.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROTH F. E. Antihistamine activity of the optical isomers of pheniramine and its chlor- and brom-substituted derivatives. Chemotherapia (Basel) 1961;3:120–127. doi: 10.1159/000219537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richelson E. Tricyclic antidepressants block histamine H1 receptors of mouse neuroblastoma cells. Nature. 1978 Jul 13;274(5667):176–177. doi: 10.1038/274176a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross S. B., Renyi A. L. Inhibition of the uptake of tritiated catecholamines by antidepressant and related agents. Eur J Pharmacol. 1967 Dec;2(3):181–186. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(67)90084-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruffolo R. R., Patil P. N. Kinetics of blockade of different receptors by chlorpromazine in rabbit stomach strips. Eur J Pharmacol. 1978 Mar 15;48(2):151–157. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(78)90324-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz J. C. Histaminergic mechanisms in brain. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1977;17:325–339. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.17.040177.001545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder S. H., Bennett J. P., Jr Neurotransmitter receptors in the brain: biochemical identification. Annu Rev Physiol. 1976;38:153–175. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.38.030176.001101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



