Abstract
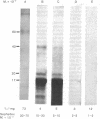
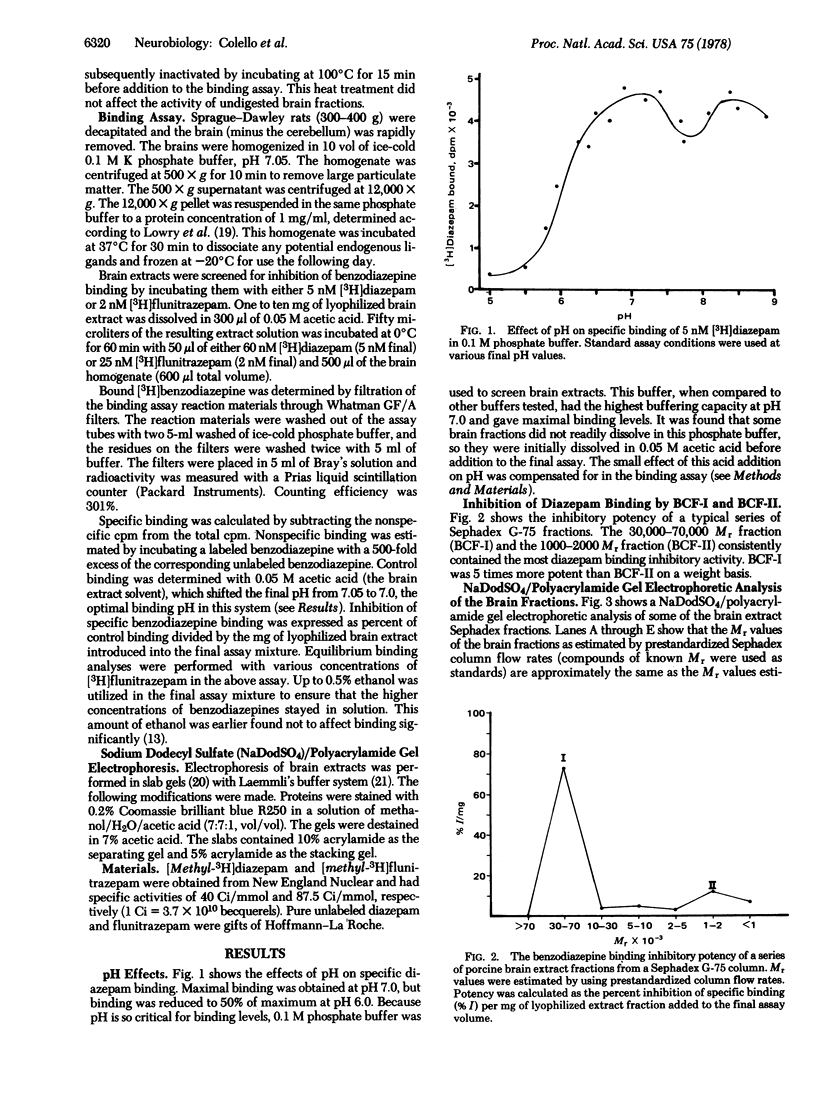
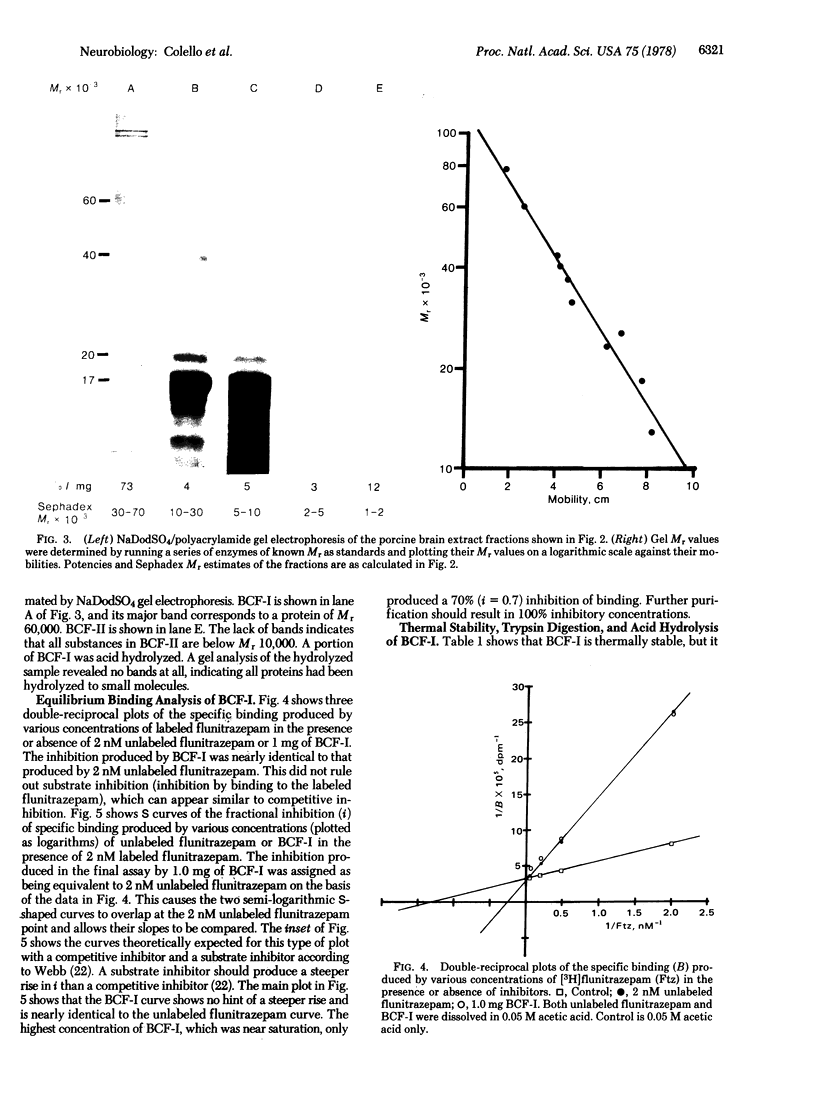
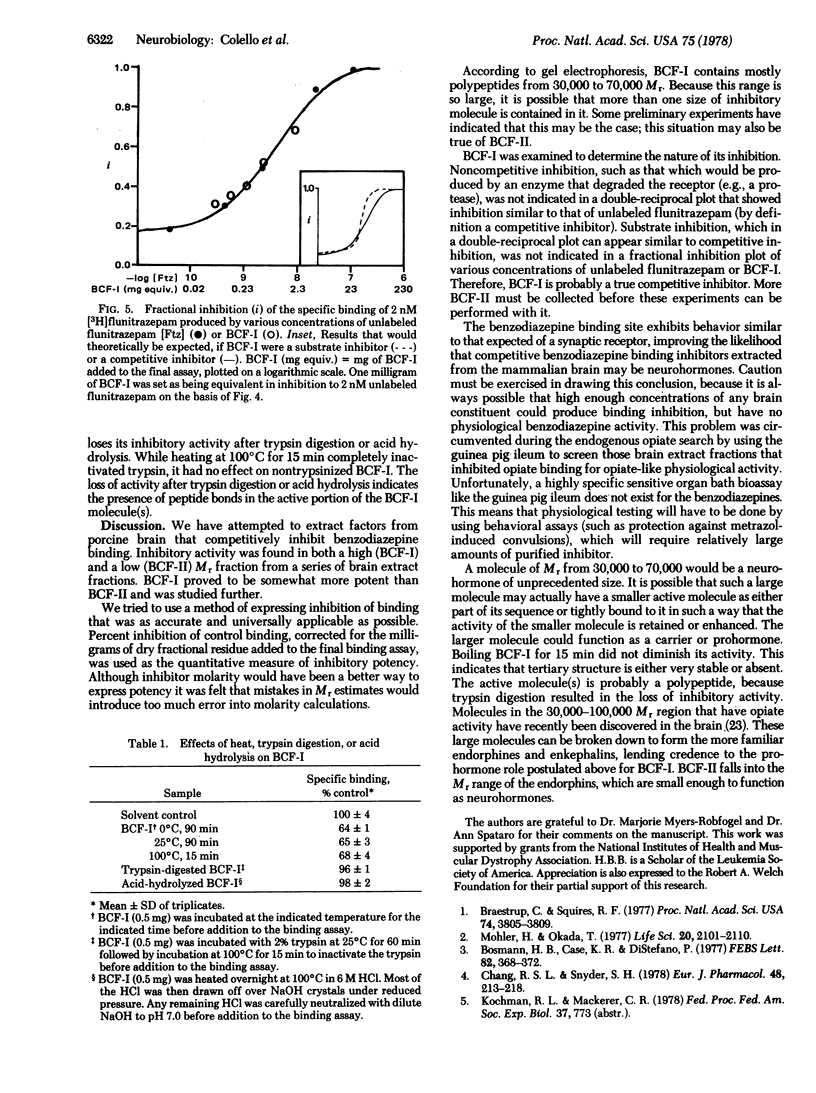
Fractions of porcine cerebral cortex extract separated by molecular weight on a Sephadex G-75 column were tested for their activities and potencies to inhibit [3H]benzodiazepine binding to rat brain homogenates. The fractions spanned molecular weights from 500 to 100,000. A potent inhibitor (benzodiazepine-competitive factor I, BCF-I) was discovered in the fraction containing substances with molecular weights from 40,000 to 70,000. Equilibrium binding studies indicated that BCF-I was a competitive inhibitor, making it a candidate as a benzodiazepine endogenous factor or profactor. BCF-I was heat stable, but trypsin digestion destroyed its activity. Another inhibitory fraction (BCF-II) was 1/5th as active as BCF-I and contained substances with molecular weights from 1000 to 2000.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bosmann H. B., Case K. R., DiStefano P. Diazepam receptor characterization: specific binding of a benzodiazepine to macromolecules in various areas of rat brain. FEBS Lett. 1977 Oct 15;82(2):368–372. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80623-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosmann H. B., Penney D. P., Case K. R., DiStefano P., Averill K. Diazepam receptor: specific binding of [3H] diazepam and [3H] flunitrazepam to rat brain subfractions. FEBS Lett. 1978 Mar 15;87(2):199–202. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80331-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braestrup C., Albrechtsen R., Squires R. F. High densities of benzodiazepine receptors in human cortical areas. Nature. 1977 Oct 20;269(5630):702–704. doi: 10.1038/269702a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braestrup C., Squires R. F. Pharmacological characterization of benzodiazepine receptors in the brain. Eur J Pharmacol. 1978 Apr 1;48(3):263–270. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(78)90085-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braestrup C., Squires R. F. Specific benzodiazepine receptors in rat brain characterized by high-affinity (3H)diazepam binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3805–3809. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang R. S., Snyder S. H. Benzodiazepine receptors: labeling in intact animals with [3H] flunitrazepam. Eur J Pharmacol. 1978 Mar 15;48(2):213–218. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(78)90330-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karobath M., Sperk G., Schönbeck G. Evidence for an endogenous factor interfering with 3H-diazepam binding to rat brain membranes. Eur J Pharmacol. 1978 Jun 1;49(3):323–326. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(78)90111-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis R. V., Stein S., Gerber L. D., Rubinstein M., Udenfriend S. High molecular weight opioid-containing proteins in striatum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):4021–4023. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.4021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marangos P. J., Paul S. M., Greenlaw P., Goodwin F. K., Skolnick P. Demonstration of an endogenous, competitive inhibitor(s) of [3H] diazepam binding in bovine brain. Life Sci. 1978 Jun 5;22(21):1893–1900. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(78)90476-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möhler H., Okada T. Benzodiazepine receptor: demonstration in the central nervous system. Science. 1977 Nov 25;198(4319):849–851. doi: 10.1126/science.918669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möhler H., Okada T. Properties of 3H-diazepam binding to benzodiazepine receptors in rat cerebral cortex. Life Sci. 1977 Jun 15;20(12):2101–2110. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(77)90191-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen M., Braestrup C., Squires R. F. Evidence for a late evolutionary appearance of brain-specific benzodiazepine receptors: an investigation of 18 vertebrate and 5 invertebrate species. Brain Res. 1978 Feb 10;141(2):342–346. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90203-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubinstein M., Stein S., Gerber L. D., Udenfriend S. Isolation and characterization of the opioid peptides from rat pituitary: beta-lipotropin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):3052–3055. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.3052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simantov R., Snowman A. M., Snyder S. H. Temperature and ionic influences on opiate receptor binding. Mol Pharmacol. 1976 Nov;12(6):977–986. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squires R. F., Brastrup C. Benzodiazepine receptors in rat brain. Nature. 1977 Apr 21;266(5604):732–734. doi: 10.1038/266732a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W. Analysis of bacteriophage T7 early RNAs and proteins on slab gels. J Mol Biol. 1973 Sep 15;79(2):237–248. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]