Abstract
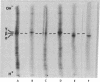
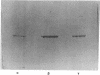
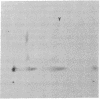
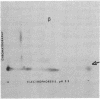
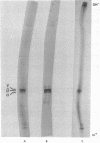
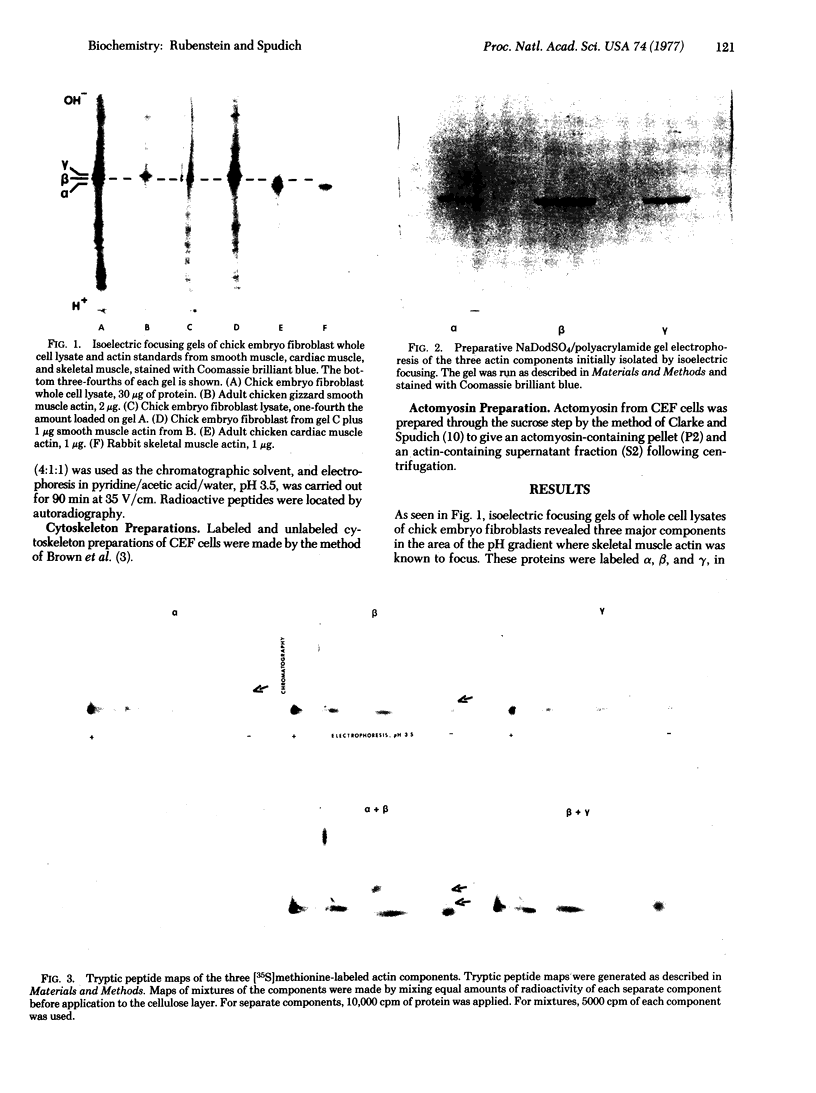
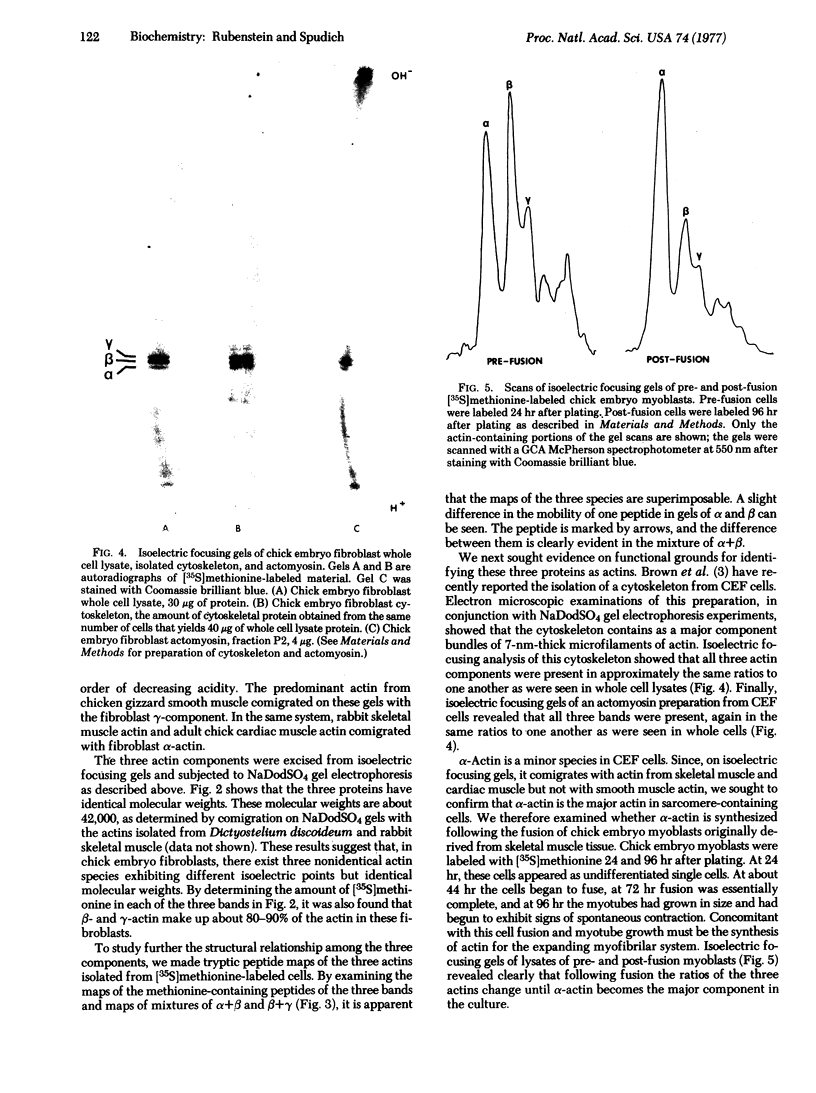
Secondary chick embryo fibroblasts contain three distinct actin species--alpha, beta, and lambda, in the approximate ratio of 1:6:3--with the same molecular weights but different isoelectric points. The most acidic of these components, alpha, comigrates on isoelectric focusing gels with the major actin of cardiac and skeletal muscle, while lambda, the most basic of the actins, comigrates with smooth muscle actin. The three components have overlapping methionine-containing tryptic peptides. All three actins are found to be present in actomyosin and cytoskeleton preparations from chick embryo fibroblasts. Identification of alpha-actin as the major actin from sarcomere-containing cells is confirmed by comparing embryonic chicken pre- and post-fusion myoblast cultures. Following myoblast fusion, the relative amount of alpha-actin increases until it changes from a minor actin component to the predominant actin species in the culture.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bremel R. D. Myosin linked calcium regulation in vertebrate smooth muscle. Nature. 1974 Nov 29;252(5482):405–407. doi: 10.1038/252405a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke M., Spudich J. A. Biochemical and structural studies of actomyosin-like proteins from non-muscle cells. Isolation and characterization of myosin from amoebae of Dictyostelium discoideum. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jun 25;86(2):209–222. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90013-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins J. H., Elzinga M. The primary structure of actin from rabbit skeletal muscle. Completion and analysis of the amino acid sequence. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 10;250(15):5915–5920. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kempe T. D., Gee D. M., Hathaway G. M., Noltman E. A. Subunit and peptide compositions of yeast phosphoglucose isomerase isoenzymes. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 25;249(14):4625–4633. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarides E., Burridge K. Alpha-actinin: immunofluorescent localization of a muscle structural protein in nonmuscle cells. Cell. 1975 Nov;6(3):289–298. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90180-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarides E. Tropomyosin antibody: the specific localization of tropomyosin in nonmuscle cells. J Cell Biol. 1975 Jun;65(3):549–561. doi: 10.1083/jcb.65.3.549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard T. D., Weihing R. R. Actin and myosin and cell movement. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1974 Jan;2(1):1–65. doi: 10.3109/10409237409105443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poste G., Papahadjopoulos D., Nicolson G. L. Local anesthetics affect transmembrane cytoskeletal control of mobility and distribution of cell surface receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4430–4434. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger J. W. Presence of actin during chromosomal movement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2451–2455. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich J. A., Watt S. The regulation of rabbit skeletal muscle contraction. I. Biochemical studies of the interaction of the tropomyosin-troponin complex with actin and the proteolytic fragments of myosin. J Biol Chem. 1971 Aug 10;246(15):4866–4871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storti R. V., Rich A. Chick cytoplasmic actin and muscle actin have different structural genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2346–2350. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whalen R. G., Butler-Browne G. S., Gros F. Protein synthesis and actin heterogeneity in calf muscle cells in culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jun;73(6):2018–2022. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.6.2018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]