Abstract
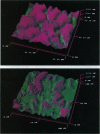
Leaf surfaces provide the ecologically relevant landscapes to those organisms that encounter or colonize the leaf surface. Leaf surface topography directly affects microhabitat availability for colonizing microbes, microhabitat quality and acceptability for insects, and the efficacy of agricultural spray applications. Prior detailed mechanistic studies that examined particular fungi-plant and pollinator-plant interactions have demonstrated the importance of plant surface topography or roughness in determining the outcome of the interactions. Until now, however, it has not been possible to measure accurately the topography--i.e., the three-dimensional structure--of such leaf surfaces or to record precise changes in patterns of leaf surface elevation over time. Using contact mode atomic force microscopy, we measured three-dimensional coordinates of upper leaf surfaces of Vaccinium macrocarpon (cranberry), a perennial plant, on leaves of two age classes. We then produced topographic maps of these leaf surfaces, which revealed striking differences between age classes of leaves: old leaves have much rougher surfaces than those of young leaves. Atomic force microscope measurements were analyzed by lag (1) autocorrelation estimates of leaf surfaces by age class. We suggest that the changes in topography result from removal of epicuticular lipids and that the changes in leaf surface topography influence phylloplane ecology. Visualizing and mapping leaf surfaces permit detailed investigations into leaf surface-mediated phenomena, improving our understanding of phylloplane interactions.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Hoch H. C., Staples R. C., Whitehead B., Comeau J., Wolf E. D. Signaling for growth orientation and cell differentiation by surface topography in uromyces. Science. 1987 Mar 27;235(4796):1659–1662. doi: 10.1126/science.235.4796.1659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kevan P. G., Lane M. A. Flower petal microtexture is a tactile cue for bees. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4750–4752. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]