Abstract
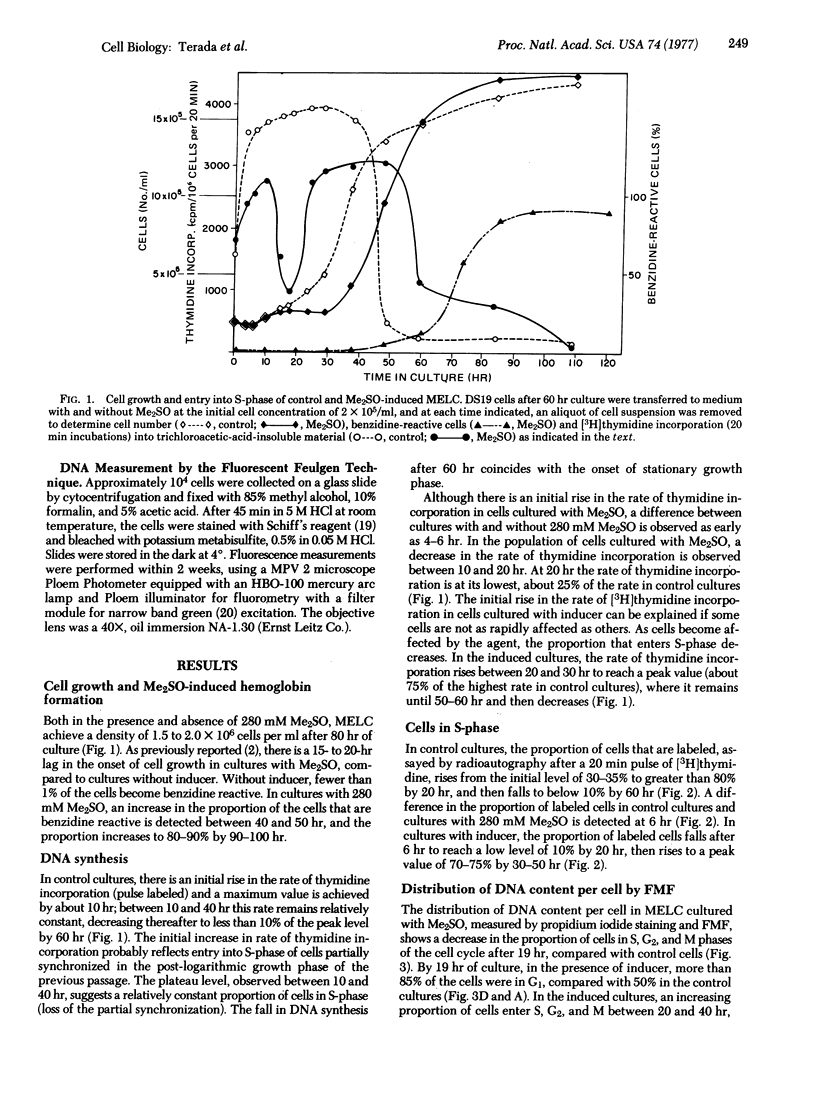
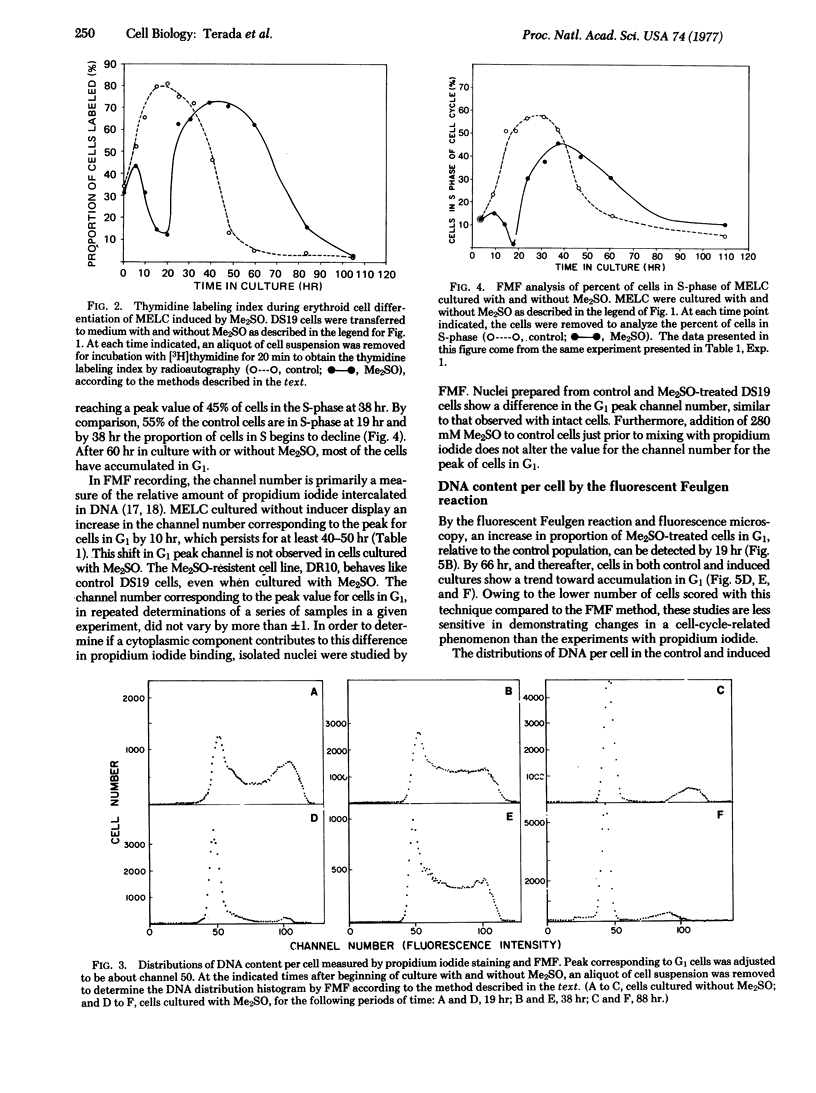
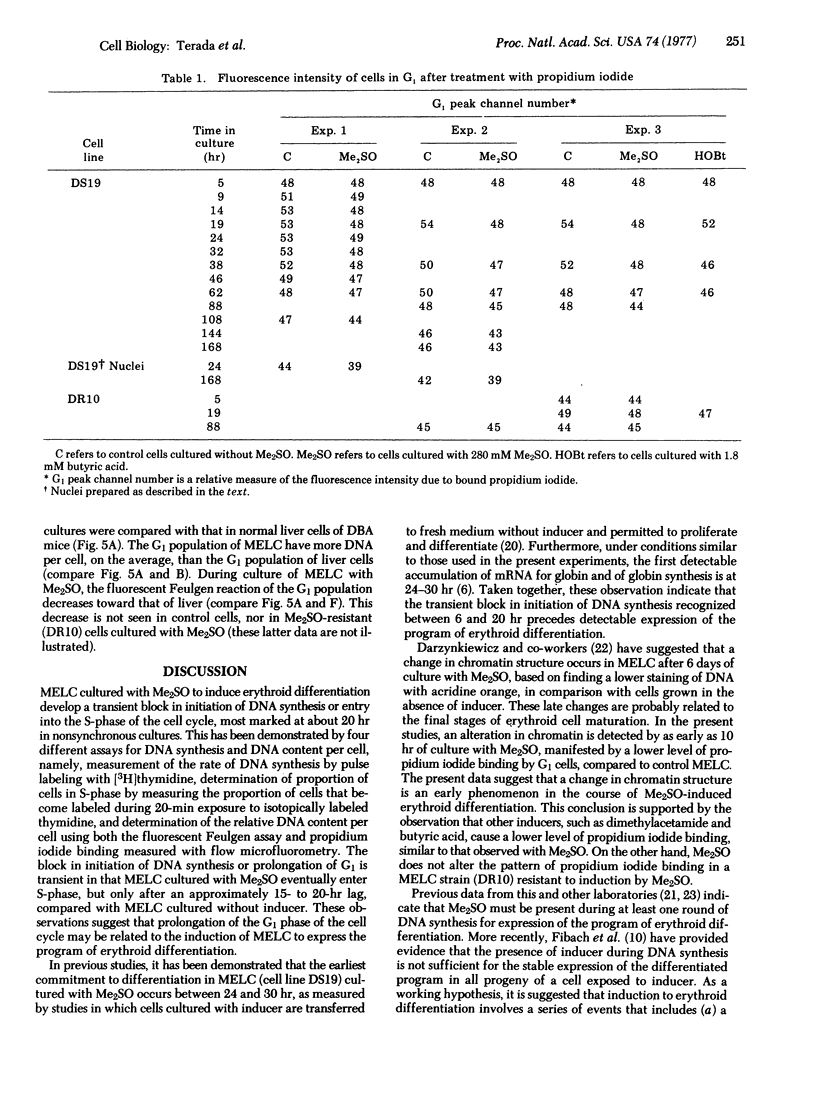
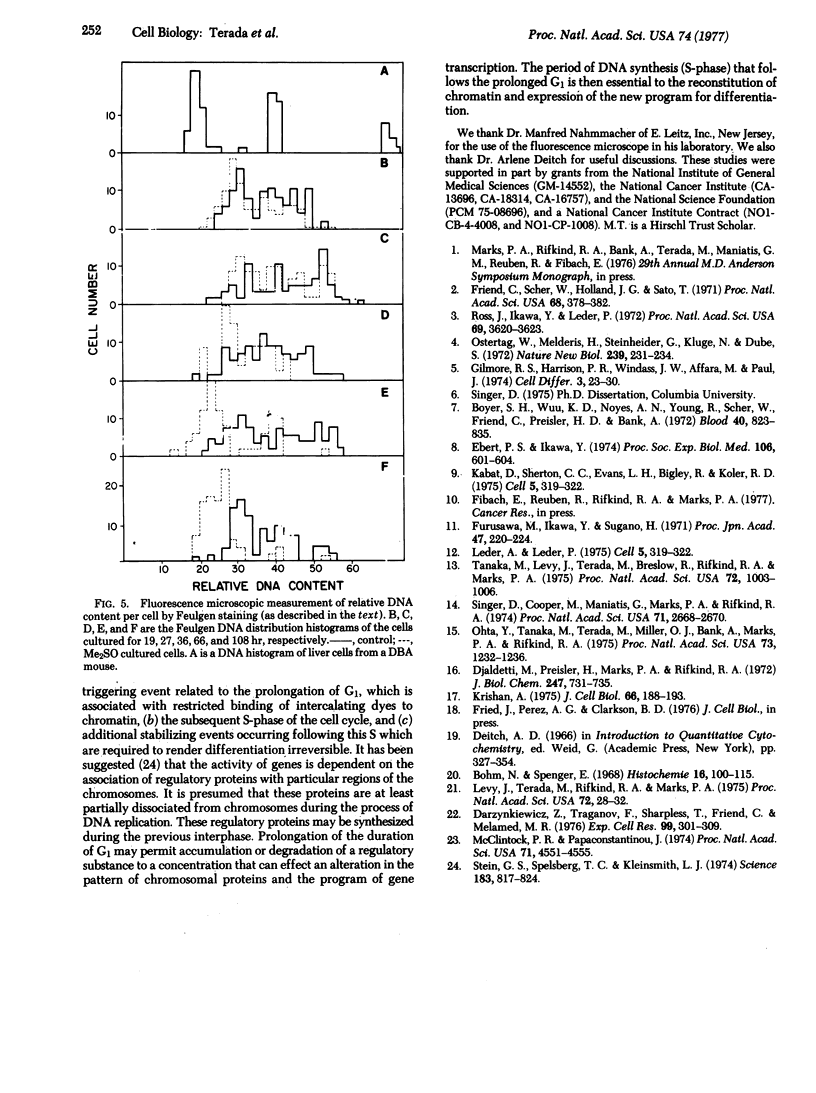
The murine erythroleukemia cell (MELC) line in suspension culture can be induced to differentiate to erythroid cells by various compounds, including dimethyl sulfoxide (Me2SO). Analysis of the cell cycle, during differentiation induced by Me2SO, using thymidine incorporation, thymidine labeling index, and relative DNA content per cell as measured by flow microfluorometry, demonstrates a transient inhibition of entry of cells into S-phase of the cell cycle which is detected as early as 5 hr and is maximal about 20 hr after beginning of nonsynchronous cultures. Furthermore, in the presence of Me2SO there is restricted binding of the intercalating dye propidium iodide to chromatin from MELC in G1 phase of the cell cycle, as early as 10 hr of culture. This restricted binding of propidium iodide to chromatin is observed in MELC cultured with other inducing agents, such as butyric acid and dimethyl-acetamide, but is not detected with an Me2SO-resistant cell line cultured with Me2SO.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boyer S. H., Wuu K. D., Noyes A. N., Young R., Scher W., Friend C., Preisler H. D., Bank A. Hemoglobin biosynthesis in murine virus-induced leukemic cells in vitro: structure and amounts of globin chains produced. Blood. 1972 Dec;40(6):823–835. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhm N., Sprenger E. Fluorescence cytophotometry: a valuable method for the quantitative determination of nuclear Feulgen-DNA. Histochemie. 1968;16(2):100–118. doi: 10.1007/BF00280607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darzynkiewicz Z., Tragnos F., Sharpless T., Friend C., Melamed M. R. Nuclear chromatin changes during erythroid differentiation of friend virus induced leukemic cells. Exp Cell Res. 1976 May;99(2):301–309. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(76)90587-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Djaidetti M., Preisler H., Marks P. A., Rifkind R. A. Erythropoietin effects on fetal mouse erythroid cells. II. Nucleic acid synthesis and the erythropoietin-sensitive cell. J Biol Chem. 1972 Feb 10;247(3):731–735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebert P. S., Ikawa Y. Induction of delta-aminolevulinic acid synthetase during erythroid differentiation of cultured leukemia cells. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1974 Jun;146(2):601–604. doi: 10.3181/00379727-146-38155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friend C., Scher W., Holland J. G., Sato T. Hemoglobin synthesis in murine virus-induced leukemic cells in vitro: stimulation of erythroid differentiation by dimethyl sulfoxide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Feb;68(2):378–382. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.2.378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison P. R., Gilmour R. S., Affara N. A., Conkie D., Paul J. Globin messenger RNA synthesis and processing during haemoglobin induction in Friend cells. II. Evidence for post-transcriptional control in clone 707. Cell Differ. 1974 Jun;3(1):23–30. doi: 10.1016/0045-6039(74)90037-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishan A. Rapid flow cytofluorometric analysis of mammalian cell cycle by propidium iodide staining. J Cell Biol. 1975 Jul;66(1):188–193. doi: 10.1083/jcb.66.1.188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leder A., Leder P. Butyric acid, a potent inducer of erythroid differentiation in cultured erythroleukemic cells. Cell. 1975 Jul;5(3):319–322. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90107-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy J., Terada M., Rifkind R. A., Marks P. A. Induction of erythroid differentiation by dimethylsulfoxide in cells infected with Friend virus: relationship to the cell cycle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):28–32. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.28. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClintock P. R., Papaconstantinou J. Regulation of hemoglobin synthesis in a murine erythroblastic leukemic cell: the requirement for replication to induce hemoglobin synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Nov;71(11):4551–4555. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.11.4551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohta Y., Tanaka M., Terada M., Miller O. J., Bank A., Marks P., Rifkind R. A. Erythroid cell differentiation: murine erythroleukemia cell variant with unique pattern of induction by polar compounds. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Apr;73(4):1232–1236. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.4.1232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostertag W., Melderis H., Steinheider G., Kluge N., Dube S. Synthesis of mouse haemoglobin and globin mRNA in leukaemic cell cultures. Nat New Biol. 1972 Oct 25;239(95):231–234. doi: 10.1038/newbio239231a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross J., Ikawa Y., Leder P. Globin messenger-RNA induction during erythroid differentiation of cultured leukemia cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Dec;69(12):3620–3623. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.12.3620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer D., Cooper M., Maniatis G. M., Marks P. A., Rifkind R. A. Erythropoietic differentiation in colonies of cells transformed by Friend virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jul;71(7):2668–2670. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.7.2668. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein G. S., Spelsberg T. C., Kleinsmith L. J. Nonhistone chromosomal proteins and gene regulation. Science. 1974 Mar 1;183(4127):817–824. doi: 10.1126/science.183.4127.817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka M., Levy J., Terada M., Breslow R., Rifkind R. A., Marks P. A. Induction of erythroid differentiation in murine virus infected eythroleukemia cells by highly polar compounds. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1003–1006. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



