Abstract
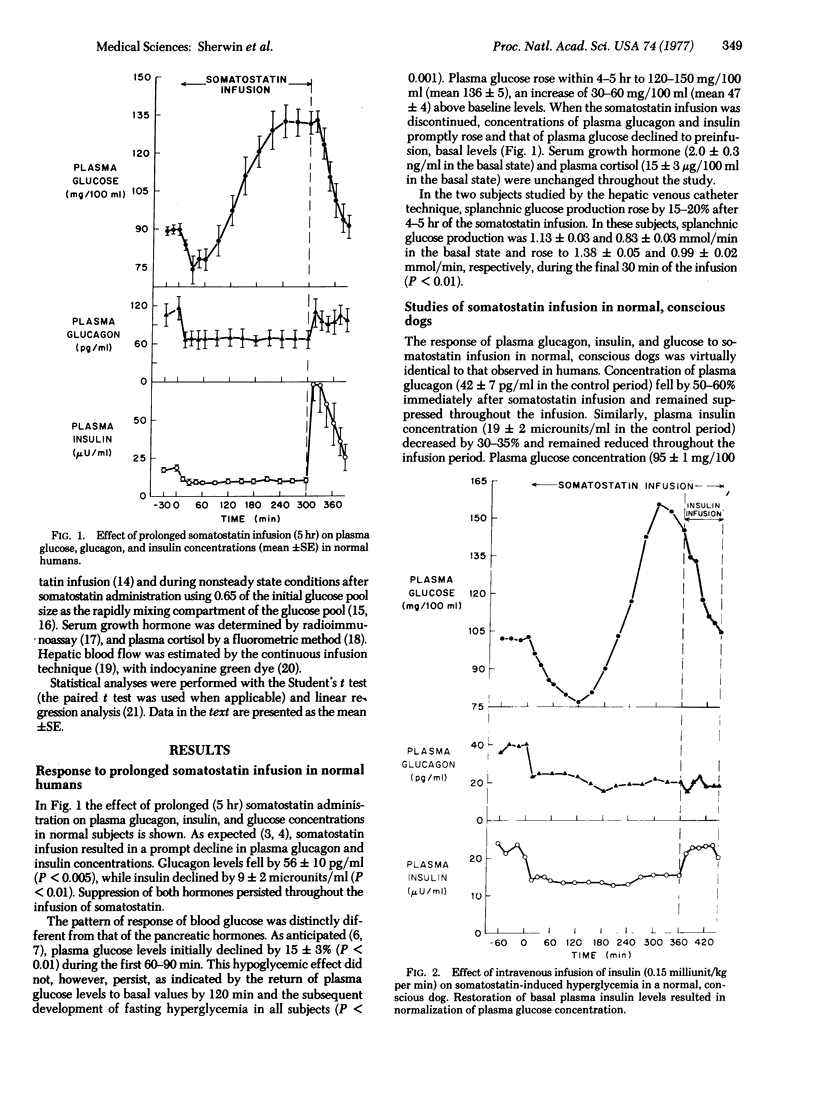
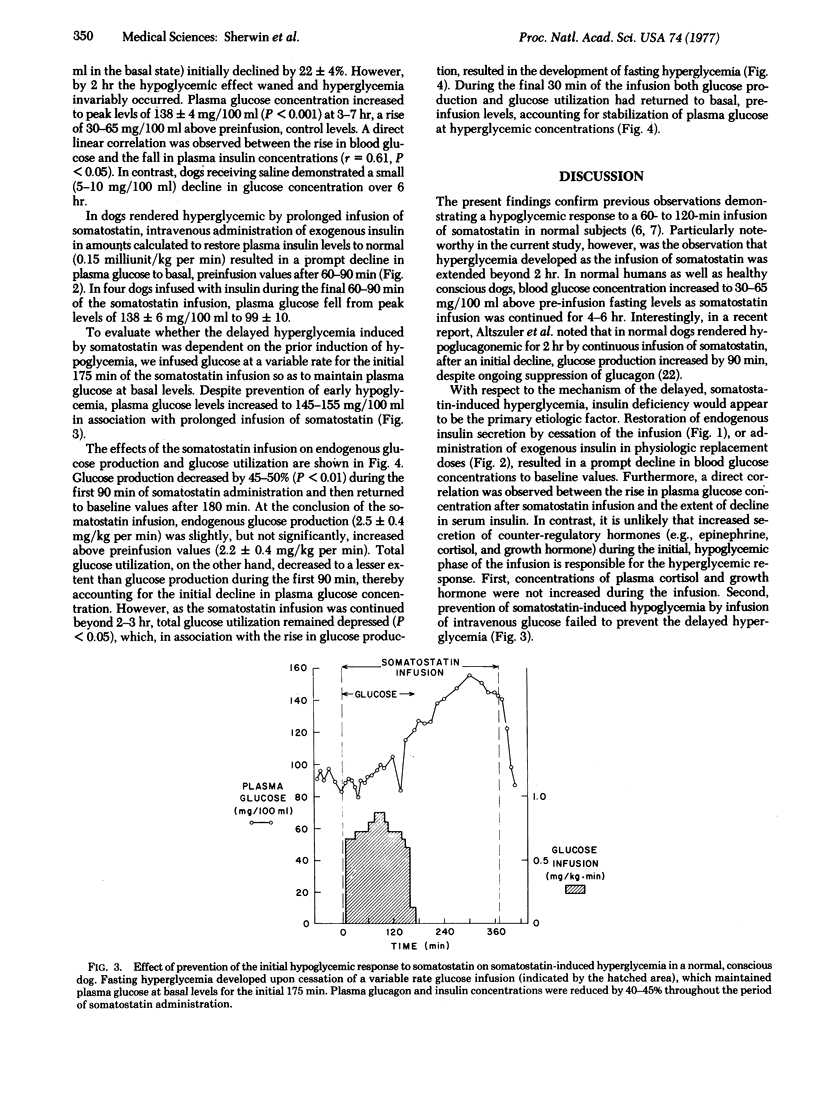
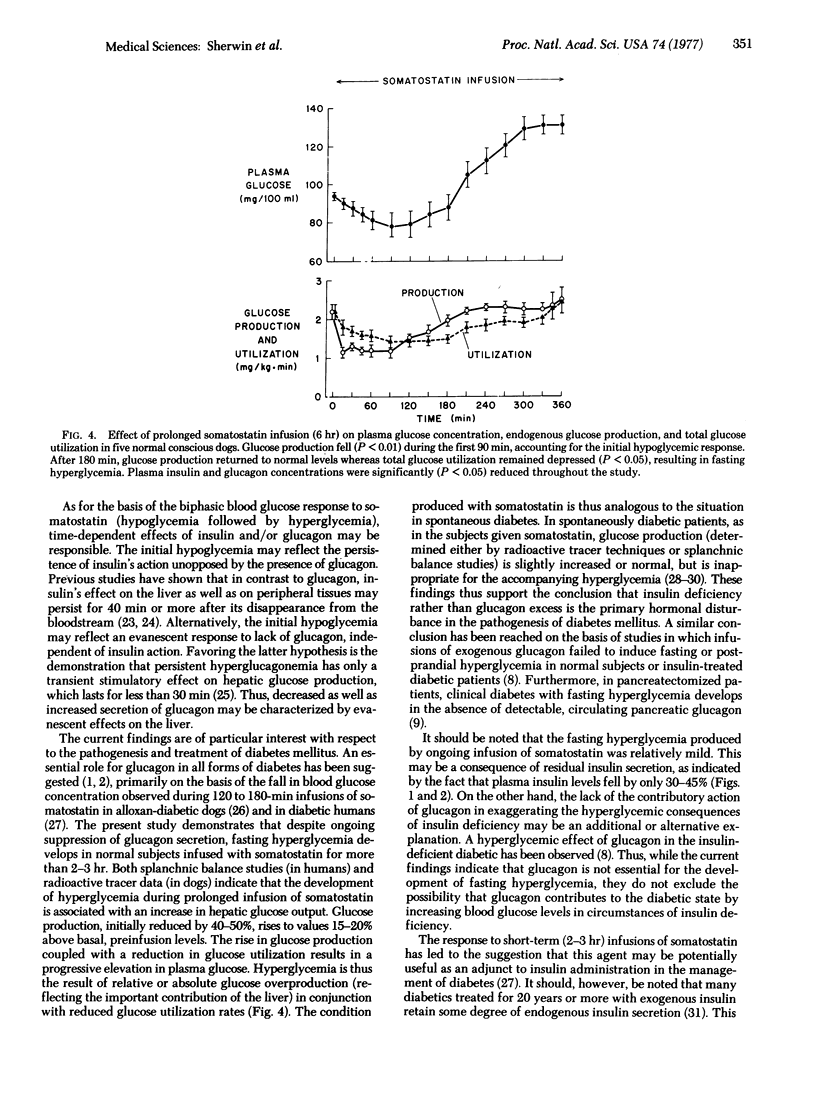
Somatostatin was infused for 5-8 hr into five normal men and eleven normal, conscious dogs. This infusion resulted in a persistent decline in plasma glucagon (40-60%) and insulin (30-45%). Plasma gluccose fell 15-25% during the initial 1-2 hr, but subsequently rose to hyperglycemic levels (130-155 mg/100ml) by 3-6 hr, despite persistent hypoglucagonemia. Glucose production initially declined by 40-50%, but later rose to levels 15-20% above basal rates while peripheral glucose utilization fell to levels 20-30% below basal, thereby accounting for hyperglycemia. Infusion of exogenous insulin so as to restore plasma insulin to preinfusion values or cessation of the somatostatin infusion with restoration of endogenous insulin secretion resulted in a prompt reduction of plasma glucose to baseline values. Prevention of the initial somatostatin-induced hypoglycemic response by intravenous infusion of glucose failed to prevent the delayed hyperglycemia. We conclude that somatostatin caused only transient hypoglycemia in normal subjects and that hyperglycemia eventually developes as a consequence of insulin deficiency. These data indicate that basal glucagon secretion is not essential for the development of fasting hyperglycemia and support the conclusion that insulin deficiency rather than glucagon excess is the primary factor responsible for abnormal glucose homeostasis in the diabetic.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alberti K. G., Christensen N. J., Christensen S. E., Hansen A. P., Iversen J., Lundbaek K., Seyer-Hansen K., Orskov H. Inhibition of insulin secretion by somatostatin. Lancet. 1973 Dec 8;2(7841):1299–1301. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)92873-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alford F. P., Bloom S. R., Nabarro J. D., Hall R., Besser G. M., Coy D. H., Kastin A. J., Schally A. V. Glucagon control of fasting glucose in man. Lancet. 1974 Oct 26;2(7887):974–977. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)92071-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altszuler N., Barkai A., Bjerknes C., Gottlieb B., Steele R. Glucose turnover values in the dog obtained with various species of labeled glucose. Am J Physiol. 1975 Dec;229(6):1662–1667. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1975.229.6.1662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altszuler N., Gottlieb B., Hampshire J. Interaction of somatostatin, glucagon, and insulin on hepatic glucose output in the normal dog. Diabetes. 1976 Feb;25(2):116–121. doi: 10.2337/diab.25.2.116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes A. J., Bloom S. R. Pancreatectomised man: A model for diabetes without glucagon. Lancet. 1976 Jan 31;1(7953):219–221. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)91339-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Block M. B., Mako M. E., Steiner D. F., Rubenstein A. H. Circulating C-peptide immunoreactivity. Studies in normals and diabetic patients. Diabetes. 1972 Oct;21(10):1013–1026. doi: 10.2337/diab.21.10.1013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brazeau P., Vale W., Burgus R., Ling N., Butcher M., Rivier J., Guillemin R. Hypothalamic polypeptide that inhibits the secretion of immunoreactive pituitary growth hormone. Science. 1973 Jan 5;179(4068):77–79. doi: 10.1126/science.179.4068.77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAESAR J., SHALDON S., CHIANDUSSI L., GUEVARA L., SHERLOCK S. The use of indocyanine green in the measurement of hepatic blood flow and as a test of hepatic function. Clin Sci. 1961 Aug;21:43–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowan J. S., Hetenyi G., Jr Glucoregulatory responses in normal and diabetic dogs recorded by a new tracer method. Metabolism. 1971 Apr;20(4):360–372. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(71)90098-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobbs R., Sakurai H., Sasaki H., Faloona G., Valverde I., Baetens D., Orci L., Unger R. Glucagon: role in the hyperglycemia of diabetes mellitus. Science. 1975 Feb 14;187(4176):544–547. doi: 10.1126/science.1089999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felig P., Wahren J., Hendler R. Influence of physiologic hyperglucagonemia on basal and insulin-inhibited splanchnic glucose output in normal man. J Clin Invest. 1976 Sep;58(3):761–765. doi: 10.1172/JCI108523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felig P., Wahren J. Influence of endogenous insulin secretion on splanchnic glucose and amino acid metabolism in man. J Clin Invest. 1971 Aug;50(8):1702–1711. doi: 10.1172/JCI106659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forbath N., Hetenyi G., Jr Glucose dynamics in normal subjects and diabetic patients before and after a glucose load. Diabetes. 1966 Nov;15(11):778–789. doi: 10.2337/diab.15.11.778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerich J. E., Lorenzi M., Hane S., Gustafson G., Guillemin R., Forsham P. H. Evidence for a physiologic role of pancreatic glucagon in human glucose homeostasis: studies with somatostatin. Metabolism. 1975 Feb;24(2):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(75)90018-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerich J. E., Lorenzi M., Schneider V., Karam J. H., Rivier J., Guillemin R., Forsham P. H. Effects of somatostatin on plasma glucose and glucagon levels in human diabetes mellitus. Pathophysiologic and therapeutic implications. N Engl J Med. 1974 Sep 12;291(11):544–547. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197409122911102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Insel P. A., Liljenquist J. E., Tobin J. D., Sherwin R. S., Watkins P., Andres R., Berman M. Insulin control of glucose metabolism in man: a new kinetic analysis. J Clin Invest. 1975 May;55(5):1057–1066. doi: 10.1172/JCI108006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koerker D. J., Ruch W., Chideckel E., Palmer J., Goodner C. J., Ensinck J., Gale C. C. Somatostatin: hypothalamic inhibitor of the endocrine pancreas. Science. 1974 Apr 26;184(4135):482–484. doi: 10.1126/science.184.4135.482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MYERS J. D. Net splanchnic glucose production in normal man and in various disease states. J Clin Invest. 1950 Nov;29(11):1421–1429. doi: 10.1172/JCI102380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radziuk J., Norwich K. H., Vranic M. Measurement and validation of nonsteady turnover rates with applications to the inulin and glucose systems. Fed Proc. 1974 Jul;33(7):1855–1864. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosselin G., Assan R., Yalow R. S., Berson S. A. Separation of antibody-bound and unbound peptide hormones labelled with iodine-131 by talcum powder and precipitated silica. Nature. 1966 Oct 22;212(5060):355–357. doi: 10.1038/212355a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEELE R., WALL J. S., DE BODO R. C., ALTSZULER N. Measurement of size and turnover rate of body glucose pool by the isotope dilution method. Am J Physiol. 1956 Sep;187(1):15–24. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1956.187.1.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherwin R. S., Fisher M., Hendler R., Felig P. Hyperglucagonemia and blood glucose regulation in normal, obese and diabetic subjects. N Engl J Med. 1976 Feb 26;294(9):455–461. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197602262940901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherwin R. S., Kramer K. J., Tobin J. D., Insel P. A., Liljenquist J. E., Berman M., Andres R. A model of the kinetics of insulin in man. J Clin Invest. 1974 May;53(5):1481–1492. doi: 10.1172/JCI107697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger R. H., Orci L. The essential role of glucagon in the pathogenesis of diabetes mellitus. Lancet. 1975 Jan 4;1(7897):14–16. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)92375-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger R. H. The Banting Memorial Lecture 1975. Diabetes and the alpha cell. Diabetes. 1976 Feb;25(2):136–151. doi: 10.2337/diab.25.2.136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahren J., Felig P., Cerasi E., Luft R. Splanchnic and peripheral glucose and amino acid metabolism in diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest. 1972 Jul;51(7):1870–1878. doi: 10.1172/JCI106989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise J. K., Hendler R., Felig P. Influence of glucocorticoids on glucagon secretion and plasma amino acid concentrations in man. J Clin Invest. 1973 Nov;52(11):2774–2782. doi: 10.1172/JCI107473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]