Abstract
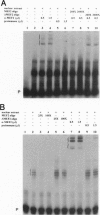
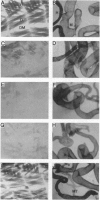
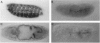
MEF2 (myocyte-specific enhancer factor 2) is a MADS box transcription factor that is thought to be a key regulator of myogenesis in vertebrates. Mutations in the Drosophila homologue of the mef2 gene indicate that it plays a key role in regulating myogenesis in Drosophila. We show here that the Drosophila tropomyosin I (TmI) gene is a target gene for mef2 regulation. The TmI gene contains a proximal and a distal muscle enhancer within the first intron of the gene. We show that both enhancers contain a MEF2 binding site and that a mutation in the MEF2 binding site of either enhancer significantly reduces reporter gene expression in embryonic, larval, and adult somatic body wall muscles of transgenic flies. We also show that a high level of proximal enhancer-directed reporter gene expression in somatic muscles requires the cooperative activity of MEF2 and a cis-acting muscle activator region located within the enhancer. Thus, mef2 null mutant embryos show a significant reduction but not an elimination of TmI expression in the body wall myoblasts and muscle fibers that are present. Surprisingly, there is little effect in these mutants on TmI expression in developing visceral muscles and dorsal vessel (heart), despite the fact that MEF2 is expressed in these muscles in wild-type embryos, indicating that TmI expression is regulated differently in these muscles. Taken together, our results show that mef2 is a positive regulator of tropomyosin gene transcription that is necessary but not sufficient for high level expression in somatic muscle of the embryo, larva, and adult.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bour B. A., O'Brien M. A., Lockwood W. L., Goldstein E. S., Bodmer R., Taghert P. H., Abmayr S. M., Nguyen H. T. Drosophila MEF2, a transcription factor that is essential for myogenesis. Genes Dev. 1995 Mar 15;9(6):730–741. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.6.730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coen E. S., Meyerowitz E. M. The war of the whorls: genetic interactions controlling flower development. Nature. 1991 Sep 5;353(6339):31–37. doi: 10.1038/353031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cserjesi P., Lilly B., Hinkley C., Perry M., Olson E. N. Homeodomain protein MHox and MADS protein myocyte enhancer-binding factor-2 converge on a common element in the muscle creatine kinase enhancer. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jun 17;269(24):16740–16745. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmondson D. G., Olson E. N. Helix-loop-helix proteins as regulators of muscle-specific transcription. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 15;268(2):755–758. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein H. F., Bernstein S. I. Genetic approaches to understanding muscle development. Dev Biol. 1992 Dec;154(2):231–244. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(92)90064-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gossett L. A., Kelvin D. J., Sternberg E. A., Olson E. N. A new myocyte-specific enhancer-binding factor that recognizes a conserved element associated with multiple muscle-specific genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):5022–5033. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.5022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gremke L., Lord P. C., Sabacan L., Lin S. C., Wohlwill A., Storti R. V. Coordinate regulation of Drosophila tropomyosin gene expression is controlled by multiple muscle-type-specific positive and negative enhancer elements. Dev Biol. 1993 Oct;159(2):513–527. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1993.1260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang J., Kosman D., Ip Y. T., Levine M. The dorsal morphogen gradient regulates the mesoderm determinant twist in early Drosophila embryos. Genes Dev. 1991 Oct;5(10):1881–1891. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.10.1881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaushal S., Schneider J. W., Nadal-Ginard B., Mahdavi V. Activation of the myogenic lineage by MEF2A, a factor that induces and cooperates with MyoD. Science. 1994 Nov 18;266(5188):1236–1240. doi: 10.1126/science.7973707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li H., Capetanaki Y. An E box in the desmin promoter cooperates with the E box and MEF-2 sites of a distal enhancer to direct muscle-specific transcription. EMBO J. 1994 Aug 1;13(15):3580–3589. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06665.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichter J. B., Storti R. V. In vitro transcription analysis of the Drosophila tropomyosin and other muscle genes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Mar 26;1088(3):419–424. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(91)90135-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilly B., Galewsky S., Firulli A. B., Schulz R. A., Olson E. N. D-MEF2: a MADS box transcription factor expressed in differentiating mesoderm and muscle cell lineages during Drosophila embryogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jun 7;91(12):5662–5666. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.12.5662. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilly B., Zhao B., Ranganayakulu G., Paterson B. M., Schulz R. A., Olson E. N. Requirement of MADS domain transcription factor D-MEF2 for muscle formation in Drosophila. Science. 1995 Feb 3;267(5198):688–693. doi: 10.1126/science.7839146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michael S. F. Mutagenesis by incorporation of a phosphorylated oligo during PCR amplification. Biotechniques. 1994 Mar;16(3):410–412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michelson A. M., Abmayr S. M., Bate M., Arias A. M., Maniatis T. Expression of a MyoD family member prefigures muscle pattern in Drosophila embryos. Genes Dev. 1990 Dec;4(12A):2086–2097. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.12a.2086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naidu P. S., Ludolph D. C., To R. Q., Hinterberger T. J., Konieczny S. F. Myogenin and MEF2 function synergistically to activate the MRF4 promoter during myogenesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 May;15(5):2707–2718. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.5.2707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen H. T., Bodmer R., Abmayr S. M., McDermott J. C., Spoerel N. A. D-mef2: a Drosophila mesoderm-specific MADS box-containing gene with a biphasic expression profile during embryogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Aug 2;91(16):7520–7524. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.16.7520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien M. A., Roberts M. S., Taghert P. H. A genetic and molecular analysis of the 46C chromosomal region surrounding the FMRFamide neuropeptide gene in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1994 May;137(1):121–137. doi: 10.1093/genetics/137.1.121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson E. N., Klein W. H. bHLH factors in muscle development: dead lines and commitments, what to leave in and what to leave out. Genes Dev. 1994 Jan;8(1):1–8. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parmacek M. S., Ip H. S., Jung F., Shen T., Martin J. F., Vora A. J., Olson E. N., Leiden J. M. A novel myogenic regulatory circuit controls slow/cardiac troponin C gene transcription in skeletal muscle. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Mar;14(3):1870–1885. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.3.1870. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson B. M., Walldorf U., Eldridge J., Dübendorfer A., Frasch M., Gehring W. J. The Drosophila homologue of vertebrate myogenic-determination genes encodes a transiently expressed nuclear protein marking primary myogenic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3782–3786. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz J. R., Tansey T., Gremke L., Storti R. V. A muscle-specific intron enhancer required for rescue of indirect flight muscle and jump muscle function regulates Drosophila tropomyosin I gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):1901–1911. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.1901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz-Sommer Z., Huijser P., Nacken W., Saedler H., Sommer H. Genetic Control of Flower Development by Homeotic Genes in Antirrhinum majus. Science. 1990 Nov 16;250(4983):931–936. doi: 10.1126/science.250.4983.931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spradling A. C., Rubin G. M. Transposition of cloned P elements into Drosophila germ line chromosomes. Science. 1982 Oct 22;218(4570):341–347. doi: 10.1126/science.6289435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tautz D., Pfeifle C. A non-radioactive in situ hybridization method for the localization of specific RNAs in Drosophila embryos reveals translational control of the segmentation gene hunchback. Chromosoma. 1989 Aug;98(2):81–85. doi: 10.1007/BF00291041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]