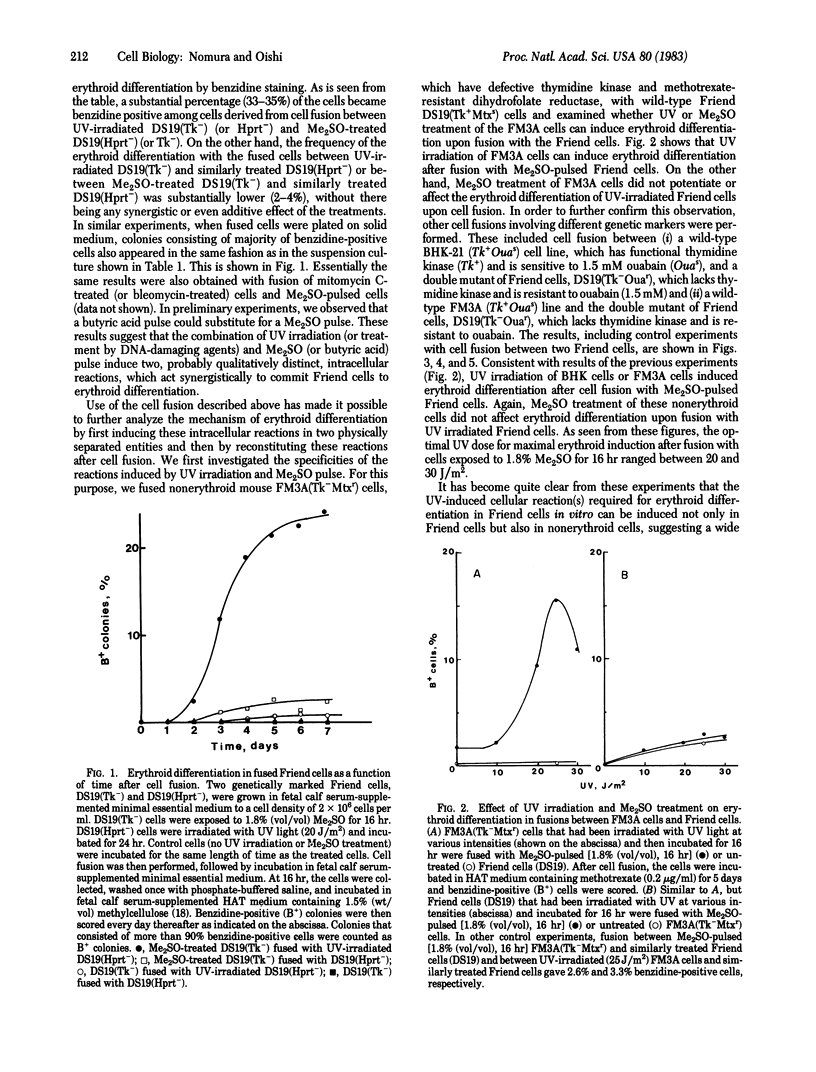
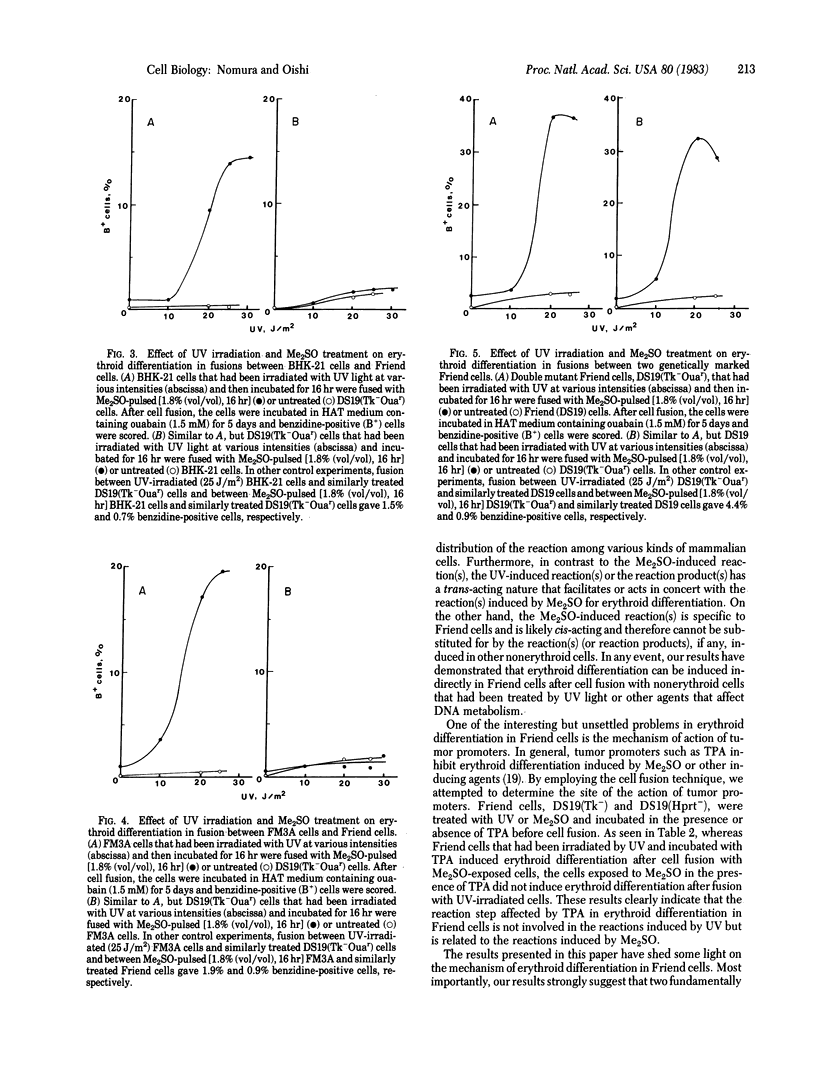
Abstract
The mechanism of in vitro erythroid differentiation in mouse Friend cells was studied by employing cell fusion between two genetically marked Friend cells and other nonerythroid cells, including BHK (baby hamster kidney) and FM3A (mouse mammary gland) cells. We were able to induce erythroid differentiation indirectly by fusing Friend cells that had been exposed briefly to dimethyl sulfoxide prior to fusion with nonerythroid cells that had been treated with ultraviolet light (or other DNA-damaging agents). The results suggest that two distinct reactions are involved in erythroid differentiation in Friend cells in vitro. One reaction, originating from the damaged DNA (or inhibition of DNA replication as a consequence), exhibits an inducible nature, is nonspecific to Friend cells, and is trans-acting. The other reaction is specific to Friend cells and most likely is cis-acting. We also present evidence from the cell fusion experiments that a typical tumor promoter, 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol 13-acetate, inhibits erythroid differentiation by affecting the latter reaction. The biological significance of these findings is discussed.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ebert P. S., Wars I., Buell D. N. Erythroid differentiation in cultured Friend leukemia cells treated with metabolic inhibitors. Cancer Res. 1976 May;36(5):1809–1813. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flintoff W. F., Davidson S. V., Siminovitch L. Isolation and partial characterization of three methotrexate-resistant phenotypes from Chinese hamster ovary cells. Somatic Cell Genet. 1976 May;2(3):245–261. doi: 10.1007/BF01538963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friend C., Patuleia M. C., De Harven E. Erythrocytic maturation in vitro of murine (Friend) virus-induced leukemic cells. Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 1966 Sep;22:505–522. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friend C., Scher W., Holland J. G., Sato T. Hemoglobin synthesis in murine virus-induced leukemic cells in vitro: stimulation of erythroid differentiation by dimethyl sulfoxide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Feb;68(2):378–382. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.2.378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabat D., Sherton C. C., Evans L. H., Bigley R., Koler R. D. Synthesis of erythrocyte-specific proteins in cultured friend leukemia cells. Cell. 1975 Jul;5(3):331–338. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90109-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leder A., Leder P. Butyric acid, a potent inducer of erythroid differentiation in cultured erythroleukemic cells. Cell. 1975 Jul;5(3):319–322. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90107-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLeod D. L., Shreeve M. M., Axelrad A. A. Improved plasma culture system for production of erythrocytic colonies in vitro: quantitative assay method for CFU-E. Blood. 1974 Oct;44(4):517–534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano N. Establishment of cell lines in vitro from a mammary ascites tumor of mouse and biological properties of the established lines in a serum containing medium. Tohoku J Exp Med. 1966 Jan 25;88(1):69–84. doi: 10.1620/tjem.88.69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orkin S. H., Harosi F. I., Leder P. Differentiation in erythroleukemic cells and their somatic hybrids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):98–102. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.98. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orkin S. H., Swan D., Leder P. Differential expression of alpha- and beta-globin genes during differentiation of cultured erythroleukemic cells. J Biol Chem. 1975 Nov 25;250(22):8753–8760. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pontecorvo G. Production of mammalian somatic cell hybrids by means of polyethylene glycol treatment. Somatic Cell Genet. 1975 Oct;1(4):397–400. doi: 10.1007/BF01538671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuben R. C., Wife R. L., Breslow R., Rifkind R. A., Marks P. A. A new group of potent inducers of differentiation in murine erythroleukemia cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Mar;73(3):862–866. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.3.862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross J., Ikawa Y., Leder P. Globin messenger-RNA induction during erythroid differentiation of cultured leukemia cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Dec;69(12):3620–3623. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.12.3620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scher W., Friend C. Breakage of DNA and alterations in folded genomes by inducers of differentiation in Friend erythroleukemic cells. Cancer Res. 1978 Mar;38(3):841–849. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugano H., Furusawa M., Kawaguchi T., Ikawa Y. Enhancement of erythrocytic maturation of Friend virus-induced leukemia cells in vivo. Bibl Haematol. 1973;39:943–954. doi: 10.1159/000427927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi E., Yamada M., Saito M., Kuboyama M., Ogasa K. Differentiation of cultured Friend leukemia cells induced by short-chain fatty acids. Gan. 1975 Oct;66(5):577–580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terada M., Nudel U., Fibach E., Rifkind R. A., Marks P. A. Changes in DNA associated with induction of erythroid differentiation by dimethyl sulfoxide in murine erythroleukemia cells. Cancer Res. 1978 Mar;38(3):835–840. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witkin E. M. Ultraviolet mutagenesis and inducible DNA repair in Escherichia coli. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Dec;40(4):869–907. doi: 10.1128/br.40.4.869-907.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamasaki H., Fibach E., Nudel U., Weinstein I. B., Rifkind R. A., Marks P. A. Tumor promoters inhibit spontaneous and induced differentiation of murine erythroleukemia cells in culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3451–3455. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



