Abstract
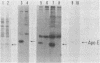
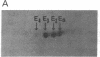
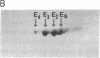
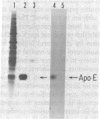
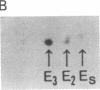
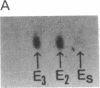
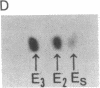
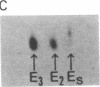
Human tissues were incubated in vitro with radiolabeled amino acids to determine whether plasma apolipoproteins are synthesized in human kidney. Subsequently, tissue extracts were screened with antisera directed against apolipoprotein E (apo E), apolipoprotein B (apo B), apolipoprotein AI (apo AI), and bulk apolipoproteins of high density lipoprotein (HDL). Newly synthesized apo E, but not apo AI or apo B, was identified in kidney and adrenal cortex. Estimates of relative rates of apo E synthesis in vitro suggest that a substantial portion of adrenal and kidney protein synthesis is committed to apo E synthesis. The relative rate of apo E synthesis was 4-6 times greater in kidney cortex than in kidney medulla. Analysis of immunoreactive apo E showed that kidney and adrenal apo E species have the same electrophoretic mobility in NaDodSO4/polyacrylamide gels as does plasma apo E. Further characterization by high resolution two-dimensional gel analysis indicated that the isoforms of newly synthesized kidney and adrenal apo E correspond to specific isoforms of plasma apo E. These findings suggest that apolipoproteins arising from peripheral tissues may play an important role in lipid transport and metabolism.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bersot T. P., Mahley R. W., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Interaction of swine lipoproteins with the low density lipoprotein receptor in human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1976 Apr 25;251(8):2395–2398. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blue M. L., Protter A. A., Williams D. L. Biosynthesis of apolipoprotein B in rooster kidney, intestine, and liver. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 10;255(21):10048–10051. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blum C. B., Aron L., Sciacca R. Radioimmunoassay studies of human apolipoprotein E. J Clin Invest. 1980 Dec;66(6):1240–1250. doi: 10.1172/JCI109975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blum C. B., Levy R. I., Eisenberg S., Hall M., 3rd, Goebel R. H., Berman M. High density lipoprotein metabolism in man. J Clin Invest. 1977 Oct;60(4):795–807. doi: 10.1172/JCI108833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capony F., Williams D. L. Apolipoprotein B of avian very low density lipoprotein: characteristics of its regulation in nonstimulated and estrogen-stimulated rooster. Biochemistry. 1980 May 13;19(10):2219–2226. doi: 10.1021/bi00551a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curry M. D., McConathy W. J., Alaupovic P., Ledford J. H., Popović M. Determination of human apolipoprotein E by electroimmunoassay. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Aug 9;439(2):413–425. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(76)90078-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glickman R. M., Green P. H. The intestine as a source of apolipoprotein A1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jun;74(6):2569–2573. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.6.2569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAVEL R. J., EDER H. A., BRAGDON J. H. The distribution and chemical composition of ultracentrifugally separated lipoproteins in human serum. J Clin Invest. 1955 Sep;34(9):1345–1353. doi: 10.1172/JCI103182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hui D. Y., Innerarity T. L., Mahley R. W. Lipoprotein binding to canine hepatic membranes. Metabolically distinct apo-E and apo-B,E receptors. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 10;256(11):5646–5655. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Innerarity T. L., Mahley R. W. Enhanced binding by cultured human fibroblasts of apo-E-containing lipoproteins as compared with low density lipoproteins. Biochemistry. 1978 Apr 18;17(8):1440–1447. doi: 10.1021/bi00601a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Innerarity T. L., Pitas R. E., Mahley R. W. Binding of arginine-rich (E) apoprotein after recombination with phospholipid vesicles to the low density lipoprotein receptors of fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 25;254(10):4186–4190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kushwaha R. S., Hazzard W. R., Wahl P. W., Hoover J. J. Type III hyperlipoproteinemia: diagnosis in whole plasma by apolipoprotein-E immunoassay. Ann Intern Med. 1977 Nov;87(5):509–516. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-87-5-509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahley R. W., Innerarity T. L., Bersot T. P., Lipson A., Margolis S. Alterations in human high-density lipoproteins, with or without increased plasma-cholesterol, induced by diets high in cholesterol. Lancet. 1978 Oct 14;2(8094):807–809. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)92588-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahley R. W., Innerarity T. L. Interaction of canine and swine lipoproteins with the low density lipoprotein receptor of fibroblasts as correlated with heparin/manganese precipitability. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jun 10;252(11):3980–3986. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahley R. W., Innerarity T. L., Weisgraber K. B., Oh S. Y. Altered metabolism (in vivo and in vitro) of plasma lipoproteins after selective chemical modification of lysine residues of the apoproteins. J Clin Invest. 1979 Sep;64(3):743–750. doi: 10.1172/JCI109518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahley R. W., Weisgraber K. H., Innerarity T. Atherogenic hyperlipoproteinemia induced by cholesterol feeding the Patas monkey. Biochemistry. 1976 Jul 13;15(14):2979–2985. doi: 10.1021/bi00659a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahley R. W., Weisgraber K. H., Innerarity T., Brewer H. B., Jr, Assmann G. Swine lipoproteins and atherosclerosis. Changes in the plasma lipoproteins and apoproteins induced by cholesterol feeding. Biochemistry. 1975 Jul;14(13):2817–2823. doi: 10.1021/bi00684a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahley R. W., Weisgraber K. H., Innerarity T. Canine lipoproteins and atherosclerosis. II. Characterization of the plasma lipoproteins associated with atherogenic and nonatherogenic hyperlipidemia. Circ Res. 1974 Nov;35(5):722–733. doi: 10.1161/01.res.35.5.722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morganroth J., Levy R. I., Fredrickson D. S. The biochemical, clinical, and genetic features of type III hyperlipoproteinemia. Ann Intern Med. 1975 Feb;82(2):158–174. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-82-2-158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rachmilewitz D., Albers J. J., Saunders D. R., Fainaru M. Apoprotein synthesis by human duodenojejunal mucosa. Gastroenterology. 1978 Oct;75(4):677–682. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rachmilewitz D., Fainaru M. Apolipoprotein A-I synthesis and secretion by cultured human intestinal mucosa. Metabolism. 1979 Jul;28(7):739–743. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(79)90179-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rash J. M., Rothblat G. H., Sparks C. E. Lipoprotein apolipoprotein synthesis by human hepatoma cells in culture. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Nov 23;666(2):294–298. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(81)90120-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherrill B. C., Innerarity T. L., Mahley R. W. Rapid hepatic clearance of the canine lipoproteins containing only the E apoprotein by a high affinity receptor. Identity with the chylomicron remnant transport process. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 10;255(5):1804–1807. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utermann G., Vogelberg K. H., Steinmetz A., Schoenborn W., Pruin N., Jaeschke M., Hees M., Canzler H. Polymorphism of apolipoprotein E. II. Genetics of hyperlipoproteinemia type III. Clin Genet. 1979 Jan;15(1):37–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. L. Apoproteins of avian very low density lipoprotein: demonstration of a single high molecular weight apoprotein. Biochemistry. 1979 Mar 20;18(6):1056–1063. doi: 10.1021/bi00573a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Windmueller H. G., Levy R. I. Production of beta-lipoprotein by intestine in the rat. J Biol Chem. 1968 Sep 25;243(18):4878–4884. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu A. L., Windmueller H. G. Identification of circulating apolipoproteins synthesized by rat small intestine in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 25;253(8):2525–2528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu A. L., Windmueller H. G. Relative contributions by liver and intestine to individual plasma apolipoproteins in the rat. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 10;254(15):7316–7322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zannis V. I., Breslow J. L. Characterization of a unique human apolipoprotein E variant associated with type III hyperlipoproteinemia. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 10;255(5):1759–1762. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zannis V. I., Breslow J. L. Human very low density lipoprotein apolipoprotein E isoprotein polymorphism is explained by genetic variation and posttranslational modification. Biochemistry. 1981 Feb 17;20(4):1033–1041. doi: 10.1021/bi00507a059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zannis V. I., Breslow J. L., SanGiacomo T. R., Aden D. P., Knowles B. B. Characterization of the major apolipoproteins secreted by two human hepatoma cell lines. Biochemistry. 1981 Dec 8;20(25):7089–7096. doi: 10.1021/bi00528a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zannis V. I., Breslow J. L., Utermann G., Mahley R. W., Weisgraber K. H., Havel R. J., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S., Schonfeld G., Hazzard W. R. Proposed nomenclature of apoE isoproteins, apoE genotypes, and phenotypes. J Lipid Res. 1982 Aug;23(6):911–914. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zannis V. I., Kurnit D. M., Breslow J. L. Hepatic apo-A-I and apo-E and intestinal apo-A-I are synthesized in precursor isoprotein forms by organ cultures of human fetal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jan 10;257(1):536–544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]