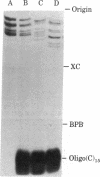
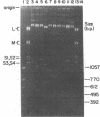
Abstract
Genome double-stranded RNAs isolated from purified human reovirus (serotype 3) and rotavirus (Wa strain) were modified at the 3' termini by addition of oligo(C) approximately 15 with T4 RNA ligase. These RNAs were transcribed into cDNA by oligo(dG)-primed reverse transcriptase and cloned after insertion into pBR322 at the Pst I site. Hybridization of plasmid-transformed Escherichia coli RR1 colonies with 32P-labeled viral genome RNAs demonstrated the presence of DNA clones representative of each of the 10 reovirus RNAs and 10 of the 11 constituent segments of the rotavirus genome. Analyses of the size and terminal nucleotide sequences of insert DNAs indicated that some clones contained a full-length copy of the virus genome segment. The complete nucleotide sequence of rotavirus genome segment 11 double-stranded RNA was obtained by using this procedure. It provides a general method for cloning double-stranded RNAs and also nonpolyadenylylated single-stranded RNAs.
Full text
PDF
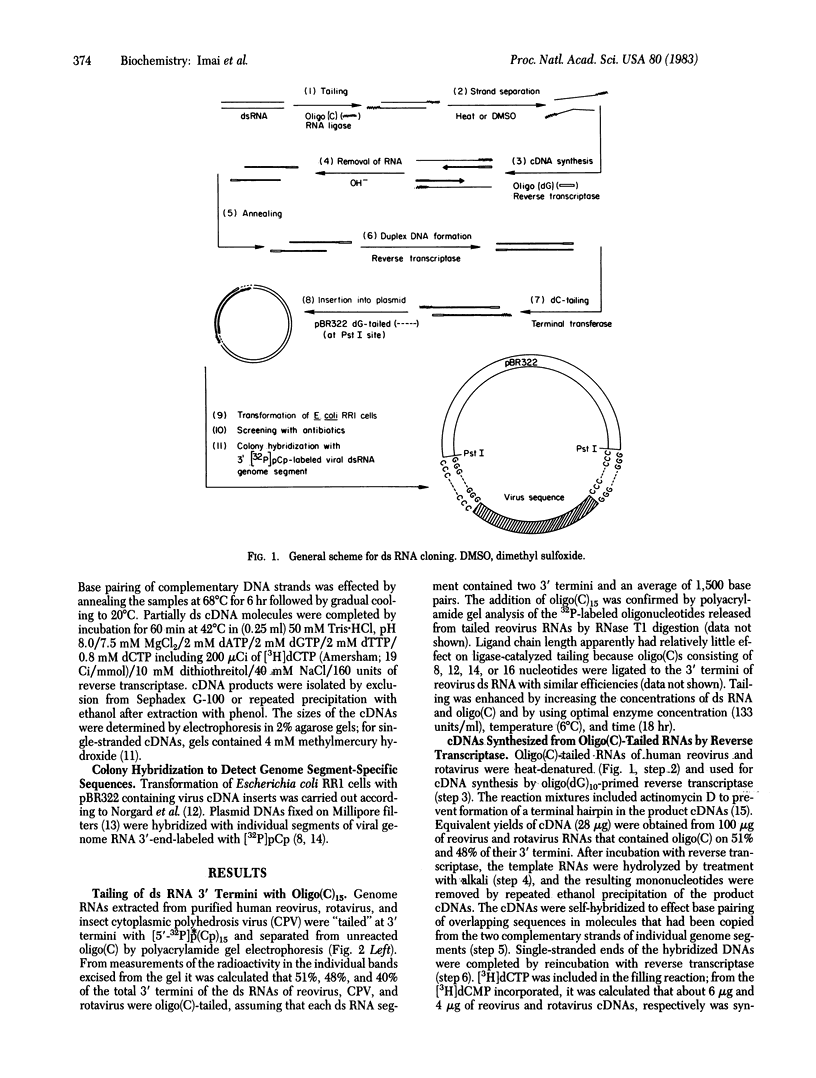
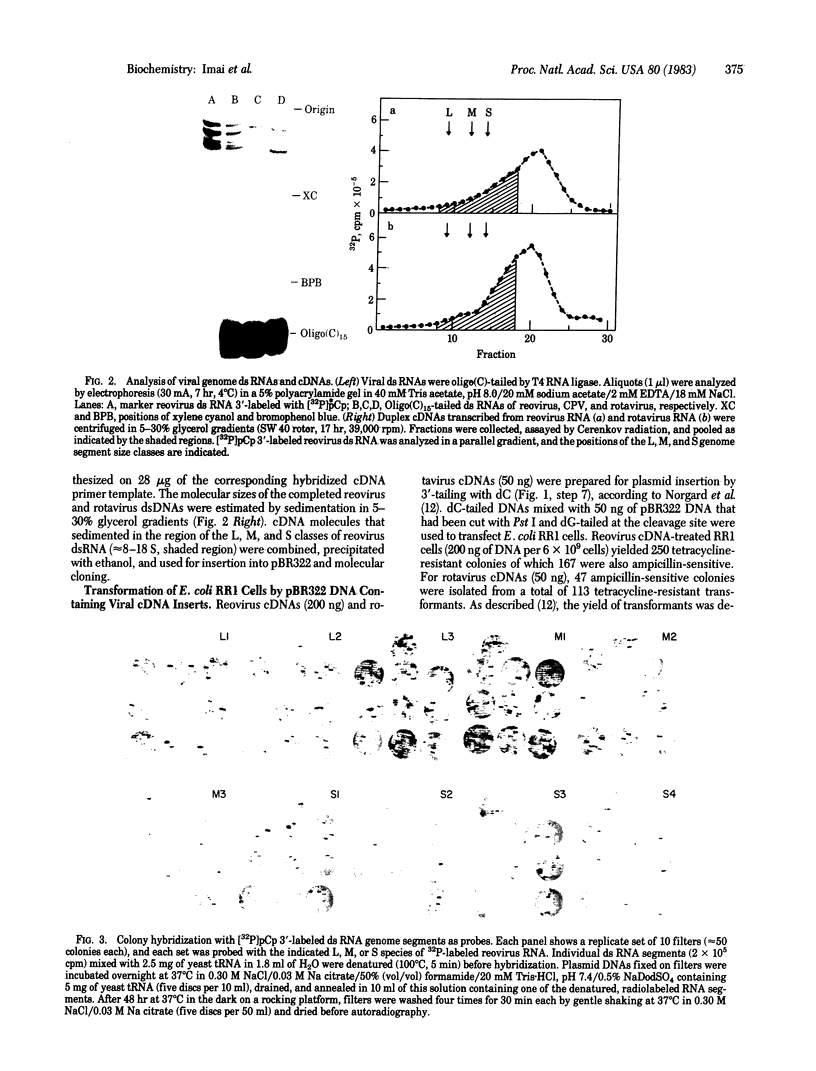

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bailey J. M., Davidson N. Methylmercury as a reversible denaturing agent for agarose gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1976 Jan;70(1):75–85. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(76)80049-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buck K. W. Replication of double-stranded RNA in particles of Penicillium stoloniferum virus S. Nucleic Acids Res. 1975 Oct;2(10):1889–1902. doi: 10.1093/nar/2.10.1889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darzynkiewicz E., Shatkin A. J. Assignment of reovirus mRNA ribosome binding sites to virion genome segments by nucleotide sequence analyses. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jan 25;8(2):337–350. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.2.337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald M., Shenk T. The sequence 5'-AAUAAA-3'forms parts of the recognition site for polyadenylation of late SV40 mRNAs. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):251–260. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90521-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuichi Y. Allosteric stimulatory effect of S-adenosylmethionine on the RNA polymerase in cytoplasmic polyhedrosis virus. A model for the positive control of eukaryotic transcription. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 10;256(1):483–493. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Wallis J. Colony hybridization. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:379–389. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68027-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iba H., Watanabe T., Emori Y., Okada Y. Three double-stranded RNA genome segments of bacteriophage phi 6 have homologous terminal sequences. FEBS Lett. 1982 May 3;141(1):111–115. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80027-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joklik W. K. Structure and function of the reovirus genome. Microbiol Rev. 1981 Dec;45(4):483–501. doi: 10.1128/mr.45.4.483-501.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klenow H., Overgaard-Hansen K., Patkar S. A. Proteolytic cleavage fo native DNA polymerase into two different catalytic fragments. Influence of assay condtions on the change of exonuclease activity and polymerase activity accompanying cleavage. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Oct 14;22(3):371–381. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01554.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuchino Y., Nishimura S., Smith R. E., Furuichi Y. Homologous Terminal Sequences in the Double-Stranded RNA Genome Segments of Cytoplasmic Polyhedrosis Virus of the Silkworm Bombyx mori. J Virol. 1982 Nov;44(2):538–543. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.2.538-543.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mertens P. P., Jamieson P. B., Dobos P. In vitro RNA synthesis by infectious pancreatic necrosis virus-associated RNA polymerase. J Gen Virol. 1982 Mar;59(Pt 1):47–56. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-59-1-47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers J. C., Dobkin C., Spiegelman S. RNA primer used in synthesis of anticomplementary DNA by reverse transcriptase of avian myeloblastosis virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1316–1320. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norgard M. V., Keem K., Monahan J. J. Factors affecting the transformation of Escherichia coli strain chi1776 by pBR322 plasmid DNA. Gene. 1978 Jul;3(4):279–292. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(78)90038-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roychoudhury R., Jay E., Wu R. Terminal labeling and addition of homopolymer tracts to duplex DNA fragments by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Apr;3(4):863–877. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.4.863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. E., Morgan M. A., Furuichi Y. Separation of the plus and minus strands of cytoplasmic polyhedrosis virus and human reovirus double-stranded genome RNAs by gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Oct 24;9(20):5269–5286. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.20.5269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinschneider A., Fraenkel-Conrat H. Studies of nucleotide sequences in tobacco mosaic virus ribonucleic acid. IV. Use of aniline in stepwise degradation. Biochemistry. 1966 Aug;5(8):2735–2743. doi: 10.1021/bi00872a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood H. A. Viruses with double-stranded RNA genomes. J Gen Virol. 1973 Jun;20(Suppl):61–85. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-20-Supplement-61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]