Abstract
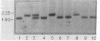
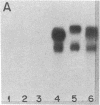
We have used plasmid pMK908, whose cDNA insert corresponds to an androgen-inducible RNA from mouse kidney, as a probe to study both the complementary genomic DNA and the encoded RNA sequences in several inbred strains of mice. A polymorphism in the 908 structural gene, revealed by Southern blotting of HindIII-generated DNA fragments, was found to map near the Gpi-1 and Tam-1 loci on chromosome 7. The 908 structural gene has been termed RP2. The 908 RNAs constitute a sequence-related group displaying extensive size heterogeneity. This heterogeneity, reflected in the size distribution of the RNA on electrophoretic blots, is controlled by a genetic site that is tightly linked to RP2. Thus, associated with polymorphism at RP2 is a change in the molecular size pattern of encoded transcripts.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alwine J. C., Kemp D. J., Stark G. R. Method for detection of specific RNAs in agarose gels by transfer to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and hybridization with DNA probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5350–5354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bardin C. W., Catterall J. F. Testosterone: a major determinant of extragenital sexual dimorphism. Science. 1981 Mar 20;211(4488):1285–1294. doi: 10.1126/science.7010603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett K. L., Lalley P. A., Barth R. K., Hastie N. D. Mapping the structural genes coding for the major urinary proteins in the mouse: combined use of recombinant inbred strains and somatic cell hybrids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1220–1224. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger F. G., Breen G. A., Paigen K. Genetic determination of the developmental program for mouse liver beta-galactosidase: involvement of sites proximate to and distant from the structural gene. Genetics. 1979 Aug;92(4):1187–1203. doi: 10.1093/genetics/92.4.1187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger F. G., Gross K. W., Watson G. Isolation and characterization of a DNA sequence complementary to an androgen-inducible messenger RNA from mouse kidney. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 10;256(13):7006–7013. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson M., Botstein D. Two differentially regulated mRNAs with different 5' ends encode secreted with intracellular forms of yeast invertase. Cell. 1982 Jan;28(1):145–154. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90384-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derman E., Krauter K., Walling L., Weinberger C., Ray M., Darnell J. E., Jr Transcriptional control in the production of liver-specific mRNAs. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):731–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90436-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Early P., Rogers J., Davis M., Calame K., Bond M., Wall R., Hood L. Two mRNAs can be produced from a single immunoglobulin mu gene by alternative RNA processing pathways. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):313–319. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90617-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hastie N. D., Held W. A., Toole J. J. Multiple genes coding for the androgen-regulated major urinary proteins of the mouse. Cell. 1979 Jun;17(2):449–457. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90171-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heilig R., Perrin F., Gannon F., Mandel J. L., Chambon P. The ovalbumin gene family: structure of the X gene and evolution of duplicated split genes. Cell. 1980 Jul;20(3):625–637. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90309-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J., Flavell R. A. A physical map of the DNA regions flanking the rabbit beta-globin gene. Cell. 1977 Oct;12(2):429–439. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90119-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labarca C., Paigen K. MRNA-directed synthesis of catalytically active mouse beta-glucuronidase in Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4462–4465. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orkin S. H., Kazazian H. H., Jr, Antonarakis S. E., Goff S. C., Boehm C. D., Sexton J. P., Waber P. G., Giardina P. J. Linkage of beta-thalassaemia mutations and beta-globin gene polymorphisms with DNA polymorphisms in human beta-globin gene cluster. Nature. 1982 Apr 15;296(5858):627–631. doi: 10.1038/296627a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paigen K. Acid hydrolases as models of genetic control. Annu Rev Genet. 1979;13:417–466. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.13.120179.002221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld M. G., Lin C. R., Amara S. G., Stolarsky L., Roos B. A., Ong E. S., Evans R. M. Calcitonin mRNA polymorphism: peptide switching associated with alternative RNA splicing events. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):1717–1721. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.1717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setzer D. R., McGrogan M., Nunberg J. H., Schimke R. T. Size heterogeneity in the 3' end of dihydrofolate reductase messenger RNAs in mouse cells. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(2 Pt 2):361–370. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90346-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setzer D. R., McGrogan M., Schimke R. T. Nucleotide sequence surrounding multiple polyadenylation sites in the mouse dihydrofolate reductase gene. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 10;257(9):5143–5147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skow L. C. Genetic variation at a locus (TAM-1) for submaxillary gland protease in the mouse and its location on chromosome No. 7. Genetics. 1978 Dec;90(4):713–724. doi: 10.1093/genetics/90.4.713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swank R. T., Brandt E. J. Turnover of kidney beta-glucuronidase in normal and Chédiak-Higashi (beige) mice. Am J Pathol. 1978 Sep;92(3):755–772. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swank R. T., Paigen K., Davey R., Chapman V., Labarca C., Watson G., Ganschow R., Brandt E. J., Novak E. Genetic regulation of mammalian glucuronidase. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1978;34:401–436. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571134-0.50015-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szoka P. R., Gallagher J. F., Held W. A. In vitro synthesis and characterization of precursors to the mouse major urinary proteins. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 25;255(4):1367–1373. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor B. A., Meier H. Mapping the adrenal lipid depletion gene of the AKR/J mouse strain. Genet Res. 1975 Dec;26(3):307–312. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300016104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traina V. L., Taylor B. A., Cohen J. C. Genetic mapping of endogenous mouse mammary tumor viruses: locus characterization, segregation, and chromosomal distribution. J Virol. 1981 Dec;40(3):735–744. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.3.735-744.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood A. W., Taylor B. A. Genetic regulation of coumarin hydroxylase activity in mice. Evidence for single locus control on chromosome. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 10;254(13):5647–5651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Hagenbüchle O., Schibler U. A single mouse alpha-amylase gene specifies two different tissue-specific mRNAs. Cell. 1981 Feb;23(2):451–458. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90140-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]