Abstract
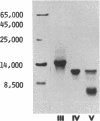
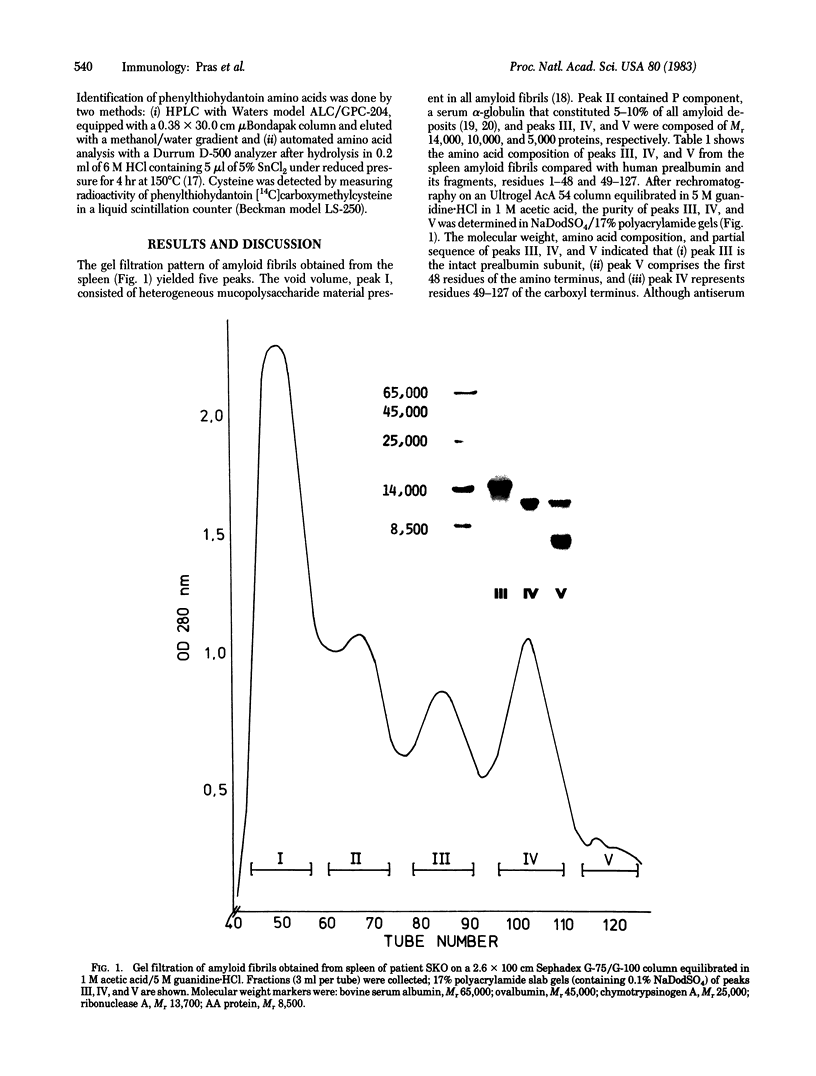
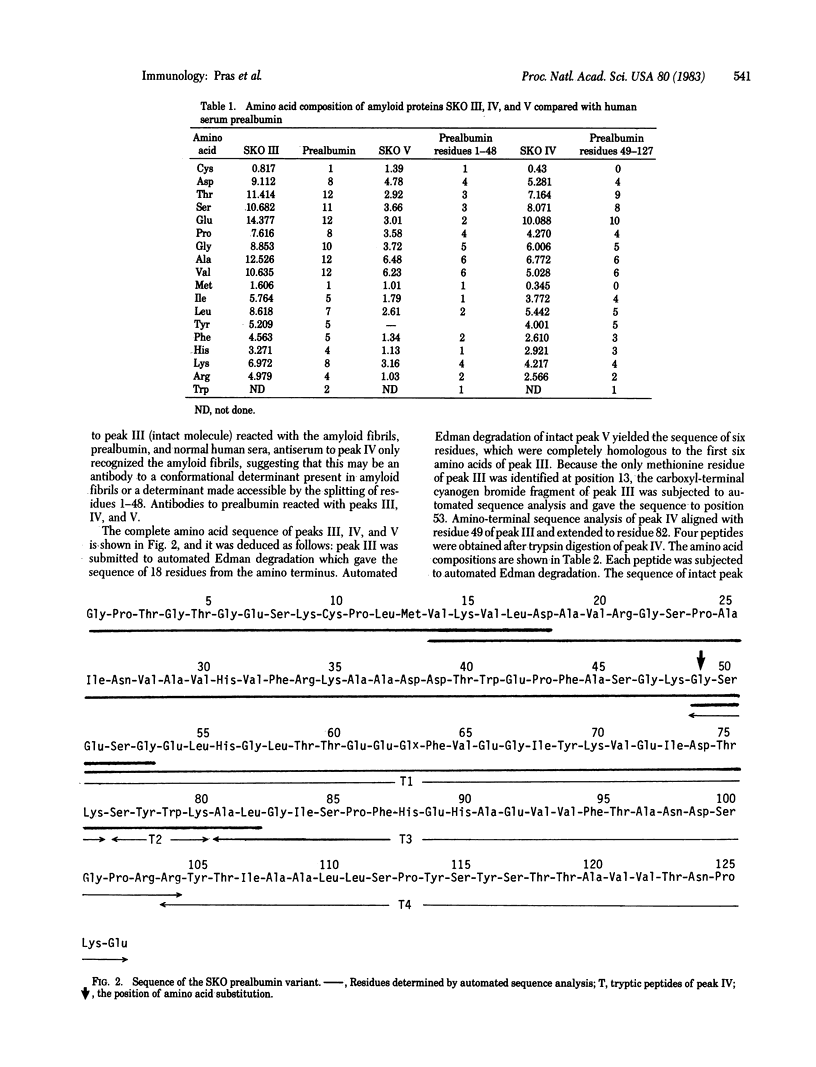
The complete amino acid sequence of three related amyloid proteins (Mr 14,000, 10,000, and 5,000) derived from tissues of a Jewish patient who suffered from a variant of familial polyneuropathic amyloidosis was determined. The protein, which contains 127 residues, is identical to a human serum prealbumin subunit. Only one amino acid substitution, glycine for threonine, was detected at position 49, where enzymatic cleavage occurred, yielding Mr 5,000 and 10,000 fragments which represent the amino terminus (residues 1-48) and carboxyl terminus (residues 49-127) of the molecule, respectively. Thus, a prealbumin variant and its fragments constitute the amyloid fibrils in a heredofamilial amyloidosis syndrome of dominant inheritance.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anders R. F., Natvig J. B., Michaelsen T. E., Husby G. Isolation and characterization of amyloid-related serum protein SAA as a low molecular weight protein. Scand J Immunol. 1975;4(4):397–401. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1975.tb02642.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrade C., Araki S., Block W. D., Cohen A. S., Jackson C. E., Kuroiwa Y., Nissim J., Sohar E., McKusick V. A., Van Allen M. W. Hereditary amyloidosis. Arthritis Rheum. 1970 Nov-Dec;13(6):902–915. doi: 10.1002/art.1780130622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake C. C., Geisow M. J., Oatley S. J., Rérat B., Rérat C. Structure of prealbumin: secondary, tertiary and quaternary interactions determined by Fourier refinement at 1.8 A. J Mol Biol. 1978 May 25;121(3):339–356. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90368-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake C. C., Oatley S. J. Protein-DNA and protein-hormone interactions in prealbumin: a model of the thyroid hormone nuclear receptor? Nature. 1977 Jul 14;268(5616):115–120. doi: 10.1038/268115a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa P. P., Figueira A. S., Bravo F. R. Amyloid fibril protein related to prealbumin in familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4499–4503. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frangione B., Milstein C., Franklin E. C. Chemical typing of immunoglobulins. Nature. 1969 Jan 11;221(5176):149–151. doi: 10.1038/221149a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frangione B., Rosenwasser E., Penefsky H. S., Pullman M. E. Amino acid sequence of the protein inhibitor of mitochondrial adenosine triphosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7403–7407. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frangione B., Rosenwasser E., Prelli F., Franklin E. C. Primary structure of human gamma 3 immunoglobulin deletion mutant: gamma 3 heavy-chain disease protein Wis. Biochemistry. 1980 Sep 2;19(18):4304–4308. doi: 10.1021/bi00559a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenner G. G., Terry W., Harada M., Isersky C., Page D. Amyloid fibril proteins: proof of homology with immunoglobulin light chains by sequence analyses. Science. 1971 Jun 11;172(3988):1150–1151. doi: 10.1126/science.172.3988.1150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Husby G., Natvig J. B. A serum component related to nonimmunoglobulin amyloid protein AS, a possible precursor of the fibrils. J Clin Invest. 1974 Apr;53(4):1054–1061. doi: 10.1172/JCI107642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanda Y., Goodman D. S., Canfield R. E., Morgan F. J. The amino acid sequence of human plasma prealbumin. J Biol Chem. 1974 Nov 10;249(21):6796–6805. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin M., Franklin E. C., Frangione B., Pras M. The amino acid sequence of a major nonimmunoglobulin component of some amyloid fibrils. J Clin Invest. 1972 Oct;51(10):2773–2776. doi: 10.1172/JCI107098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niall H. D. Automated Edman degradation: the protein sequenator. Methods Enzymol. 1973;27:942–1010. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(73)27039-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepys M. B., Dash A. C. Isolation of amyloid P component (protein AP) from normal serum as a calcium-dependent binding protein. Lancet. 1977 May 14;1(8020):1029–1031. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)91260-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pras M., Franklin E. C., Prelli F., Frangione B. A variant of prealbumin from amyloid fibrils in familial polyneuropathy of Jewish origin. J Exp Med. 1981 Sep 1;154(3):989–993. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.3.989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pras M., Schubert M., Zucker-Franklin D., Rimon A., Franklin E. C. The characterization of soluble amyloid prepared in water. J Clin Invest. 1968 Apr;47(4):924–933. doi: 10.1172/JCI105784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner M., Cohen A. S. The prealbumin nature of the amyloid protein in familial amyloid polyneuropathy (FAP)-swedish variety. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Apr 30;99(4):1326–1332. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)90764-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]