Abstract
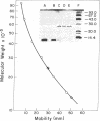
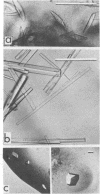
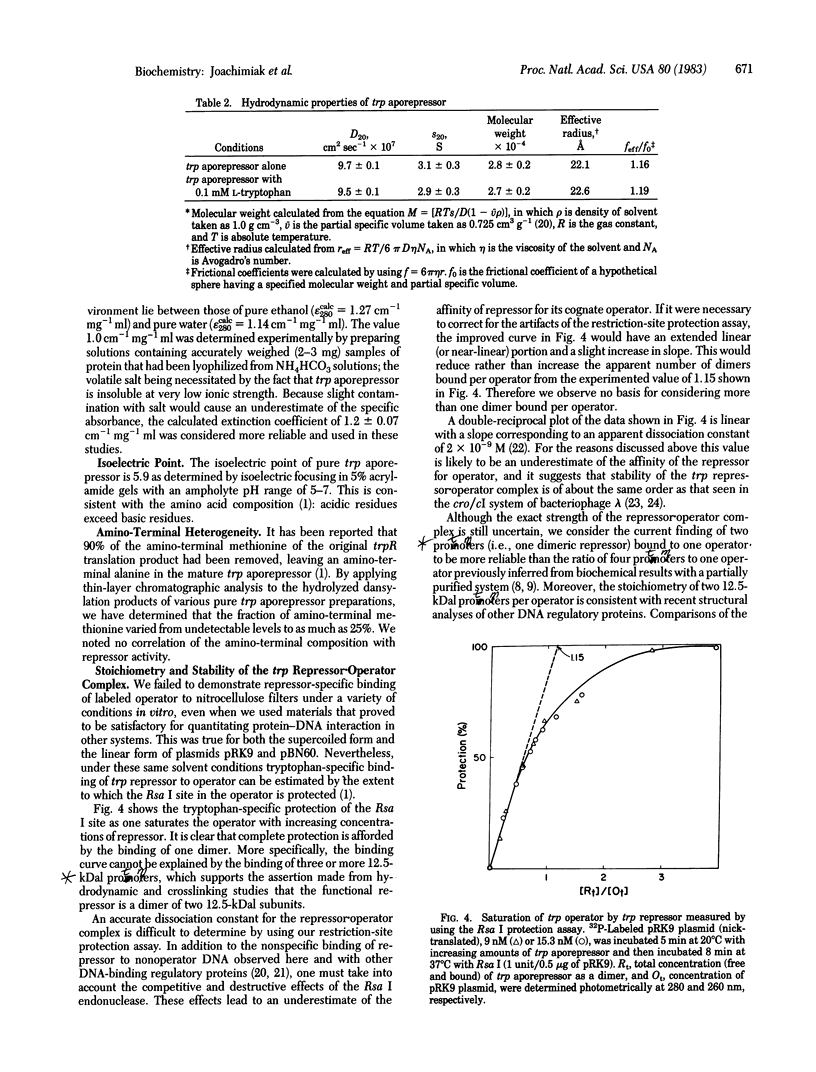
We have isolated homogeneous trp aporepressor from an overproducing strain of Escherichia coli carrying a plasmid containing trpR preceded by tandem trp operon promoters. Dye-affinity and ion-exchange chromatography were used in conjunction with a gel electrophoresis assay in which the repressor, when bound to the trp operator, protects an Rsa I restriction site from endonuclease cleavage. Crystals suitable for x-ray diffraction studies were grown from a variety of concentrated salt solutions. Hydrodynamic properties and electrophoretic analysis of unmodified and covalently crosslinked aporepressor show that the free aporepressor has an isoelectric point of 5.9 and is a dimer containing two identical 12.5-kilodalton subunits in the presence or absence of L-tryptophan. The repressor . operator complex binds poorly to nitrocellulose filters, but restriction-site protection studies indicate that, in the presence of tryptophan, one dimer is bound to the operator site with an apparent dissociation constant less than 2 X 10(-9) M. Preliminary equilibrium dialysis experiments suggest that tryptophan binds to the aporepressor with a dissociation constant of 1.6 X 10(-5) M.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson W. F., Ohlendorf D. H., Takeda Y., Matthews B. W. Structure of the cro repressor from bacteriophage lambda and its interaction with DNA. Nature. 1981 Apr 30;290(5809):754–758. doi: 10.1038/290754a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett G. N., Yanofsky C. Sequence analysis of operator constitutive mutants of the tryptophan operon of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1978 May 15;121(2):179–192. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(78)80004-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg O. G., Winter R. B., von Hippel P. H. Diffusion-driven mechanisms of protein translocation on nucleic acids. 1. Models and theory. Biochemistry. 1981 Nov 24;20(24):6929–6948. doi: 10.1021/bi00527a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunsalus R. P., Yanofsky C. Nucleotide sequence and expression of Escherichia coli trpR, the structural gene for the trp aporepressor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7117–7121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunsalus R. P., Zurawski G., Yanofsky C. Structural and functional analysis of cloned deoxyribonucleic acid containing the trpR-thr region of the Escherichia coli chromosome. J Bacteriol. 1979 Oct;140(1):106–113. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.1.106-113.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helling R. B., Goodman H. M., Boyer H. W. Analysis of endonuclease R-EcoRI fragments of DNA from lambdoid bacteriophages and other viruses by agarose-gel electrophoresis. J Virol. 1974 Nov;14(5):1235–1244. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.5.1235-1244.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. D., Poteete A. R., Lauer G., Sauer R. T., Ackers G. K., Ptashne M. lambda Repressor and cro--components of an efficient molecular switch. Nature. 1981 Nov 19;294(5838):217–223. doi: 10.1038/294217a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson C. D., Adolph K., Rosa J. J., Hall M. D., Sigler P. B. Crystallographic study of formylmethionine tRNA from baker's yeast. Nature. 1970 Jun 27;226(5252):1246–1247. doi: 10.1038/2261246a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley R. L., Yanofsky C. Trp aporepressor production is controlled by autogenous regulation and inefficient translation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(10):3120–3124. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.10.3120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly R. B., Cozzarelli N. R., Deutscher M. P., Lehman I. R., Kornberg A. Enzymatic synthesis of deoxyribonucleic acid. XXXII. Replication of duplex deoxyribonucleic acid by polymerase at a single strand break. J Biol Chem. 1970 Jan 10;245(1):39–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klotz I. M., Hunston D. L. Properties of graphical representations of multiple classes of binding sites. Biochemistry. 1971 Aug 3;10(16):3065–3069. doi: 10.1021/bi00792a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay D. B., Steitz T. A. Structure of catabolite gene activator protein at 2.9 A resolution suggests binding to left-handed B-DNA. Nature. 1981 Apr 30;290(5809):744–749. doi: 10.1038/290744a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merril C. R., Switzer R. C., Van Keuren M. L. Trace polypeptides in cellular extracts and human body fluids detected by two-dimensional electrophoresis and a highly sensitive silver stain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4335–4339. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlendorf D. H., Anderson W. F., Fisher R. G., Takeda Y., Matthews B. W. The molecular basis of DNA-protein recognition inferred from the structure of cro repressor. Nature. 1982 Aug 19;298(5876):718–723. doi: 10.1038/298718a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheim D. S., Bennett G. N., Yanofsky C. Escherichia coli RNA polymerase and trp repressor interaction with the promoter-operator region of the tryptophan operon of Salmonella typhimurium. J Mol Biol. 1980 Dec 5;144(2):133–142. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90029-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabo C. O., Lewis M. The operator-binding domain of lambda repressor: structure and DNA recognition. Nature. 1982 Jul 29;298(5873):443–447. doi: 10.1038/298443a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabo C. O., Lewis M. The operator-binding domain of lambda repressor: structure and DNA recognition. Nature. 1982 Jul 29;298(5873):443–447. doi: 10.1038/298443a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roeder W., Somerville R. L. Cloning the trpR gene. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Nov;176(3):361–368. doi: 10.1007/BF00333098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. K., Squires C. L., Yanofsky C., Yang H. L., Zubay G. Regulation of in vitro transcription of the tryptophan operon by purified RNA polymerase in the presence of partially purified repressor and tryptophan. Nat New Biol. 1973 Oct 3;245(144):133–137. doi: 10.1038/newbio245133a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. K., Yanofsky C. Interaction of the operator of the tryptophan operon with repressor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Aug;71(8):3134–3138. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.8.3134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauer R. T., Yocum R. R., Doolittle R. F., Lewis M., Pabo C. O. Homology among DNA-binding proteins suggests use of a conserved super-secondary structure. Nature. 1982 Jul 29;298(5873):447–451. doi: 10.1038/298447a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steitz T. A., Ohlendorf D. H., McKay D. B., Anderson W. F., Matthews B. W. Structural similarity in the DNA-binding domains of catabolite gene activator and cro repressor proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(10):3097–3100. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.10.3097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda Y., Folkmanis A., Echols H. Cro regulatory protein specified by bacteriophage lambda. Structure, DNA-binding, and repression of RNA synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Sep 10;252(17):6177–6183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGEL H. J., BONNER D. M. Acetylornithinase of Escherichia coli: partial purification and some properties. J Biol Chem. 1956 Jan;218(1):97–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winter R. B., Berg O. G., von Hippel P. H. Diffusion-driven mechanisms of protein translocation on nucleic acids. 3. The Escherichia coli lac repressor--operator interaction: kinetic measurements and conclusions. Biochemistry. 1981 Nov 24;20(24):6961–6977. doi: 10.1021/bi00527a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanofsky C. Tryptophan biosynthesis in Escherichia coli. Genetic determination of the proteins involved. JAMA. 1971 Nov 15;218(7):1026–1035. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zubay G., Morse D. E., Schrenk W. J., Miller J. H. Detection and isolation of the repressor protein for the tryptophan operon of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 May;69(5):1100–1103. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.5.1100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurawski G., Gunsalus R. P., Brown K. D., Yanofsky C. Structure and regulation of aroH, the structural gene for the tryptophan-repressible 3-deoxy-D-arabino-heptulosonic acid-7-phosphate synthetase of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jan 5;145(1):47–73. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90334-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]