Abstract
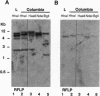
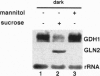
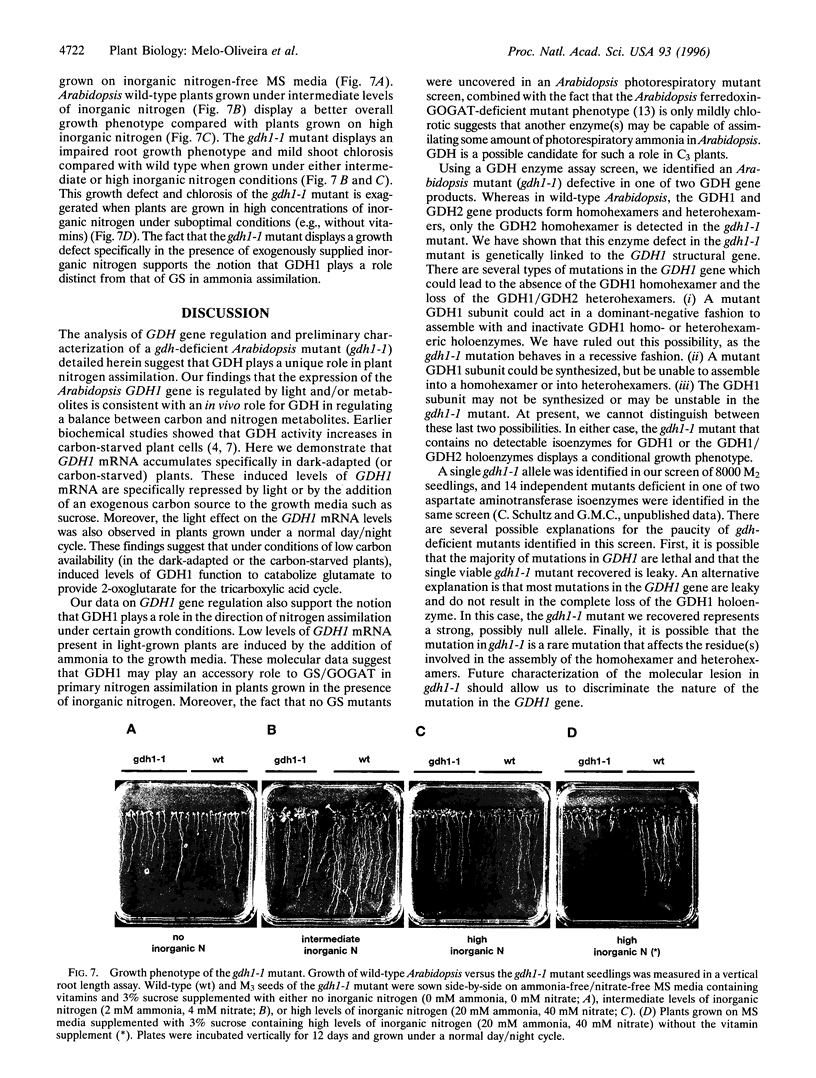
Glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH) is ubiquitous to all organisms, yet its role in higher plants remains enigmatic. To better understand the role of GDH in plant nitrogen metabolism, we have characterized an Arabidopsis mutant (gdh1-1) defective in one of two GDH gene products and have studied GDH1 gene expression. GDH1 mRNA accumulates to highest levels in dark-adapted or sucrose-starved plants, and light or sucrose treatment each repress GDH1 mRNA accumulation. These results suggest that the GDH1 gene product functions in the direction of glutamate catabolism under carbon-limiting conditions. Low levels of GDH1 mRNA present in leaves of light-grown plants can be induced by exogenously supplied ammonia. Under such conditions of carbon and ammonia excess, GDH1 may function in the direction of glutamate biosynthesis. The Arabidopsis gdh-deficient mutant allele gdh1-1 cosegregates with the GDH1 gene and behaves as a recessive mutation. The gdh1-1 mutant displays a conditional phenotype in that seedling growth is specifically retarded on media containing exogenously supplied inorganic nitrogen. These results suggest that GDH1 plays a nonredundant role in ammonia assimilation under conditions of inorganic nitrogen excess. This notion is further supported by the fact that the levels of mRNA for GDH1 and chloroplastic glutamine synthetase (GS2) are reciprocally regulated by light.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amuro N., Yamaura M., Goto Y., Okazaki T. Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequence of the cDNA for human liver glutamate dehydrogenase precursor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 May 16;152(3):1395–1400. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80440-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell C. J., Ecker J. R. Assignment of 30 microsatellite loci to the linkage map of Arabidopsis. Genomics. 1994 Jan 1;19(1):137–144. doi: 10.1006/geno.1994.1023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benachenhou N., Baldacci G. The gene for a halophilic glutamate dehydrogenase: sequence, transcription analysis and phylogenetic implications. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 Dec;230(3):345–352. doi: 10.1007/BF00280290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botstein D., White R. L., Skolnick M., Davis R. W. Construction of a genetic linkage map in man using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Am J Hum Genet. 1980 May;32(3):314–331. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britton K. L., Baker P. J., Rice D. W., Stillman T. J. Structural relationship between the hexameric and tetrameric family of glutamate dehydrogenases. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Nov 1;209(3):851–859. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb17357.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cock J. M., Kim K. D., Miller P. W., Hutson R. G., Schmidt R. R. A nuclear gene with many introns encoding ammonium-inducible chloroplastic NADP-specific glutamate dehydrogenase(s) in Chlorella sorokiniana. Plant Mol Biol. 1991 Nov;17(5):1023–1044. doi: 10.1007/BF00037142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faure J. D., Jullien M., Caboche M. Zea3: a pleiotropic mutation affecting cotyledon development, cytokinin resistance and carbon-nitrogen metabolism. Plant J. 1994 Apr;5(4):481–491. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.1994.5040481.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finckh U., Lingenfelter P. A., Myerson D. Producing single-stranded DNA probes with the Taq DNA polymerase: a high yield protocol. Biotechniques. 1991 Jan;10(1):35-6, 38-9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam H. M., Peng S. S., Coruzzi G. M. Metabolic regulation of the gene encoding glutamine-dependent asparagine synthetase in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiol. 1994 Dec;106(4):1347–1357. doi: 10.1104/pp.106.4.1347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lea P. J., Miflin B. J. Alternative route for nitrogen assimilation in higher plants. Nature. 1974 Oct 18;251(5476):614–616. doi: 10.1038/251614a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magalhães J. R., Ju G. C., Rich P. J., Rhodes D. Kinetics of NH(4) Assimilation in Zea mays: Preliminary Studies with a Glutamate Dehydrogenase (GDH1) Null Mutant. Plant Physiol. 1990 Oct;94(2):647–656. doi: 10.1104/pp.94.2.647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magasanik B. Genetic control of nitrogen assimilation in bacteria. Annu Rev Genet. 1982;16:135–168. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.16.120182.001031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moye W. S., Amuro N., Rao J. K., Zalkin H. Nucleotide sequence of yeast GDH1 encoding nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate-dependent glutamate dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 15;260(14):8502–8508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakai K., Kanehisa M. A knowledge base for predicting protein localization sites in eukaryotic cells. Genomics. 1992 Dec;14(4):897–911. doi: 10.1016/S0888-7543(05)80111-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman T., de Bruijn F. J., Green P., Keegstra K., Kende H., McIntosh L., Ohlrogge J., Raikhel N., Somerville S., Thomashow M. Genes galore: a summary of methods for accessing results from large-scale partial sequencing of anonymous Arabidopsis cDNA clones. Plant Physiol. 1994 Dec;106(4):1241–1255. doi: 10.1104/pp.106.4.1241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olszańska-Skorek T., Mazurowa A., Pełczynska I. Agregacja krwinek płytkowych u chorych z chorobá wieńcowa serca po dozylnym podaniu dipyridamolu. Pol Arch Med Wewn. 1981 Oct;66(4):277–280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterman T. K., Goodman H. M. The glutamine synthetase gene family of Arabidopsis thaliana: light-regulation and differential expression in leaves, roots and seeds. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 Nov;230(1-2):145–154. doi: 10.1007/BF00290662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajasekhar V. K., Gowri G., Campbell W. H. Phytochrome-mediated light regulation of nitrate reductase expression in squash cotyledons. Plant Physiol. 1988 Oct;88(2):242–244. doi: 10.1104/pp.88.2.242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson S. A., Slade A. P., Fox G. G., Phillips R., Ratcliffe R. G., Stewart G. R. The role of glutamate dehydrogenase in plant nitrogen metabolism. Plant Physiol. 1991 Feb;95(2):509–516. doi: 10.1104/pp.95.2.509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakakibara H., Fujii K., Sugiyama T. Isolation and characterization of a cDNA that encodes maize glutamate dehydrogenase. Plant Cell Physiol. 1995 Jul;36(5):789–797. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.pcp.a078823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valle F., Becerril B., Chen E., Seeburg P., Heyneker H., Bolivar F. Complete nucleotide sequence of the glutamate dehydrogenase gene from Escherichia coli K-12. Gene. 1984 Feb;27(2):193–199. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90140-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincentz M., Moureaux T., Leydecker M. T., Vaucheret H., Caboche M. Regulation of nitrate and nitrite reductase expression in Nicotiana plumbaginifolia leaves by nitrogen and carbon metabolites. Plant J. 1993 Feb;3(2):315–324. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313x.1993.tb00183.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallsgrove R. M., Turner J. C., Hall N. P., Kendall A. C., Bright S. W. Barley mutants lacking chloroplast glutamine synthetase-biochemical and genetic analysis. Plant Physiol. 1987 Jan;83(1):155–158. doi: 10.1104/pp.83.1.155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]