Abstract
Purpose.
To define the phenotype and location of antigen-presenting cells (APCs) in normal donor human corneas, and to assess the response of APC to herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) infection.
Methods.
Donor human corneal tissue was analyzed by fluorescence confocal microscopy and flow cytometry to determine the phenotype and location of tissue-resident APCs. Confocal fluorescence microscopy was also utilized to investigate the response of corneal resident APCs to ex vivo infection with HSV-1.
Results.
CD11c+ dendritic cells (DCs) and CD207+ Langerhans cells (LCs) were situated predominantly in the basal epithelium and CD68+ macrophages in the anterior stroma of human corneas. The majority of DCs expressed major histocompatibility complex class II. Corneal resident APCs colocalized with HSV-1-infected corneal cells within 8 to 16 hours of ex vivo infection.
Conclusions.
The stratification of APCs found in human corneas is very similar to that previously reported in mice, confirming the relevance of murine models for the study of corneal APCs. Furthermore, corneal resident APCs are capable of rapidly mobilizing to the site of trauma and HSV-1 infection within the cornea.
Keywords: human, cornea, antigen-presenting cells, dendritic cells, Langerhans cells
Dendritic cells (DCs) and Langerhans cells were found predominantly in the basal epithelium and macrophages in the anterior stroma of human corneas. Most DCs expressed major histocompatibility complex class II. Corneal resident antigen-presenting cells responded rapidly to ex vivo HSV-1 infection.
Introduction
Maintaining corneal clarity is essential for unaltered vision. Inflammation, reflecting both innate and adaptive immunity, is a major antagonist of tissue clarity, but also an essential component of tissue protection and eradication of infection. Both innate and adaptive immune responses are initiated by antigen presenting cells (APCs). Dendritic cells (DCs) and macrophages can serve as potent APCs but can also inhibit adaptive immunity.1 Until recently, maintenance of corneal clarity was thought to be attributable, at least in part, to a lack of resident APCs capable of initiating inflammatory responses. However, evidence has emerged demonstrating a unique stratification of APCs within the normal murine cornea.2 CD11c+ DCs are found in the basal layer of the murine corneal epithelium, with a subpopulation expressing the CD207+ Langerhans cell (LC) marker, and many expressing major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II.2-5 CD11c-expressing cells,5–7 as well as a population of monocyte-derived cells,2,8 also reside in the corneal stroma.
MHC class II–expressing cells were identified in the human corneal basal epithelium and stroma nearly three decades ago.9–11 These cells have traditionally been referred to as either DCs or LCs, given their dendritic morphology; however, relatively few studies have investigated the phenotype of corneal APC. More recently, Yamagami et al. have identified CD11c+ myeloid-derived DCs within the human basal epithelium12 and CD11c+ CD11b+ CD14+ bone marrow-derived cells throughout the peripheral stroma and within the anterior central stroma.13 A separate study identified Langerin+ CD1a+ LCs in the peripheral epithelium and anterior stroma.14 While the function of corneal APCs remains incompletely understood, fully defining the APC populations and their locations in normal human corneas is an essential first step in understanding how these cells might contribute to immune protection and immunopathology.
Materials and Methods
Human Corneal Tissue
Approval from the University of Pittsburgh Committee for Oversight of Research and Clinical Training Involving Decedents was obtained. Whole human donor corneas were obtained from the Center for Organ Recovery and Education in organ culture chambers containing storage medium (Optisol GS; Bausch & Lomb, Inc., Rochester, NY) and donor corneoscleral rims were obtained after corneal transplant surgery in their original organ culture chambers containing storage medium. Corneas from 10 donors were analyzed by confocal microscopy. An additional three donors were included for flow cytometric analysis. Three additional donors were used for HSV infection experiments. The age of donors ranged from 21 to 79 years. The time between incubation of corneal tissue in storage medium (Bausch & Lomb, Inc.) and fixation ranged from 11.6 to 47.15 hours.
Preparation of Tissue for Fluorescence Immunohistochemistry
The corneal tissue was fixed upon receipt, cut into small pie pieces, and stained in a similar manner to that previously described for murine corneas.2 For intracellular staining, tissue was fixed in a cell fixation and permeabilization kit (Fix/Perm; Becton, Dickinson & Company, Franklin Lakes, NJ) followed by incubation with the indicated antibodies diluted in buffer solution (Perm/Wash; Becton, Dickinson & Company) for 6 hours. Antibodies against the following surface antigens were used: CD45 (clone HI30, 1:10 dilution; Becton, Dickinson & Company); CD11c (clone B-ly6, 1:5 dilution; Becton, Dickinson & Company); HLA-DR (clone G46-6, 1:5 dilution; Becton, Dickinson & Company). Antibodies against the following intracellular antigens were used: CD68 (clone Y1/82A, 1:20 dilution; Becton, Dickinson & Company) and CD207 (Langerin, clone 929F3.01, 0.02 μg/μL; Dendritics, Lyon, France).
Confocal Microscopy
Images were acquired by sequential scanning to avoid fluorescence crossover on a confocal microscope (Olympus FluoView ×1000; Olympus Corporation of the Americas, Center Valley, PA). Z stacks were acquired at Nyquist sampling frequency. All image reconstructions were made using microscope automation and image analysis software (MetaMorph version 7.5.4.0; Molecular Devices, Sunnyvale, CA). The number of APCs were manually counted using microscope automation and image analysis software (Molecular Devices) in random ×20 or ×40 fields of the central, paracentral, and peripheral regions of the cornea as previously defined.14 For consistency, the number of cells was counted in the anterior 31 μm of stroma in each sample.
Flow Cytometry
Flow cytometry was performed in a similar manner to that previously described for murine corneas.15 Briefly, human corneal tissue was dissected and incubated for 2 hours in collagenase blend type L (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO) at a concentration of 10 mg/mL followed by trituration with a micropipette. The fluorochrome-conjugated antibodies used to stain the single cell suspension are listed above. Data were collected on a cytometer and analyzed by laboratory software (FACSAria and FACSDiva; BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA).
HSV-1 Infection of Human Corneal Tissue Ex Vivo
The peripheral cornea of corneoscleral rims obtained after corneal transplant surgery was abraded with a 30-gauge needle and 1 × 105 plaque forming units of a transgenic HSV-1 that expresses enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP) from the viral ICP0 promoter (pICP0-EGFP HSV-1)16 was applied to the scarified area. The tissue was incubated for 1 hour at 37°C, extensively washed, and further cultured for various times (time points of 4, 8, and 16 hours were used), at which point the tissue was fixed, stained, and imaged as above.
Statistical Analysis
ANOVA with Bonferroni posttest was performed using graphing software (GraphPad Prism; GraphPad Software, Inc., La Jolla, CA). P values < 0.05 were considered significant.
Results
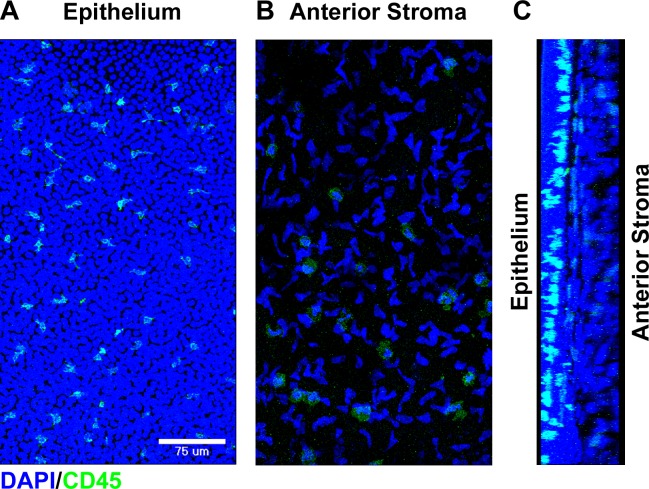
Dendritiform CD45+ bone marrow-derived cells were observed in the basal layer of the human corneal epithelium extending cellular process toward the ocular surface (Figs. 1A, 1C). A population of CD45+ cells was also seen in the anterior stroma (Figs. 1B, 1C). Compared with the CD45+ cells in the basal epithelium, those in the anterior stroma appeared rounder and flatter and lacked the extensive dendritic processes.
Figure 1.
Bone marrow–derived cells within the normal human cornea. Fresh donor human corneal tissue was fixed, and whole mounts were stained with the indicated markers prior to confocal imaging. Compressed images of z-stacks in the xy plane from the peripheral corneal epithelium (A) and anterior stroma (B) showing staining for DAPI (blue) and CD45 (green). (C) Cross-sectional reconstruction in the yz plane (epithelium on the left and anterior stroma on the right) of the peripheral cornea showing staining for DAPI (blue) and CD45 (green).
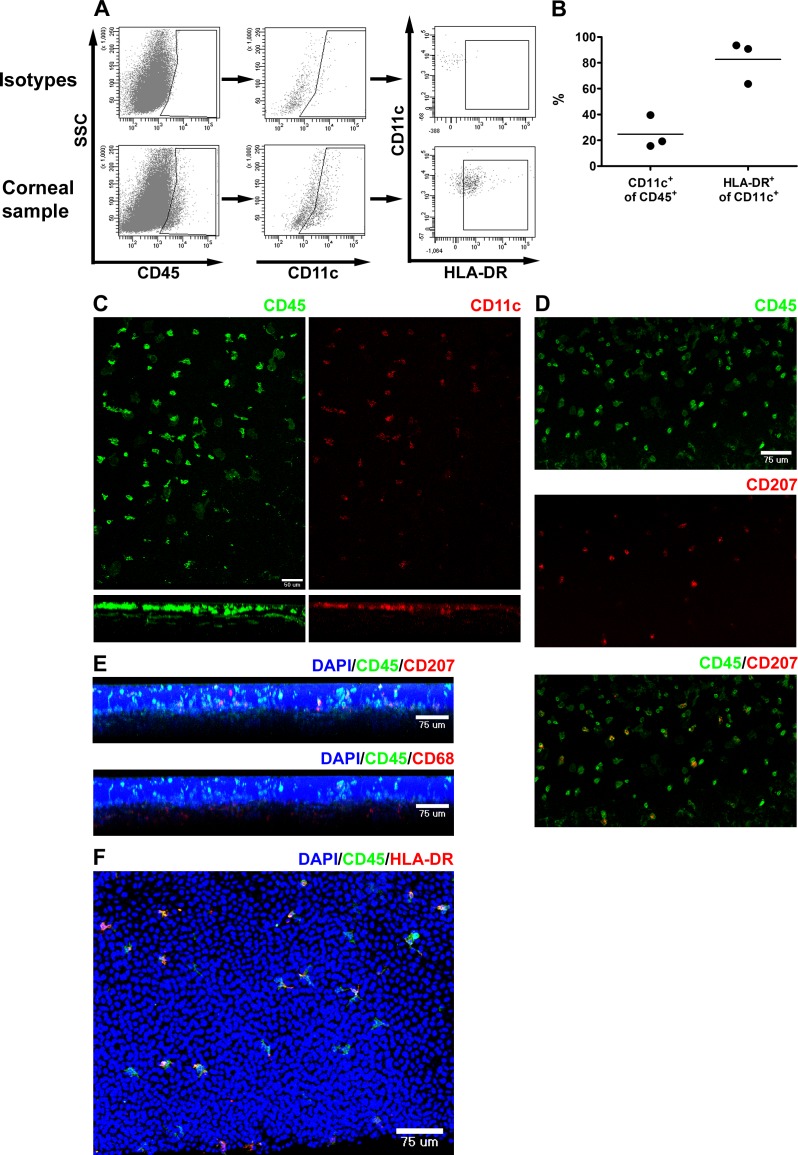
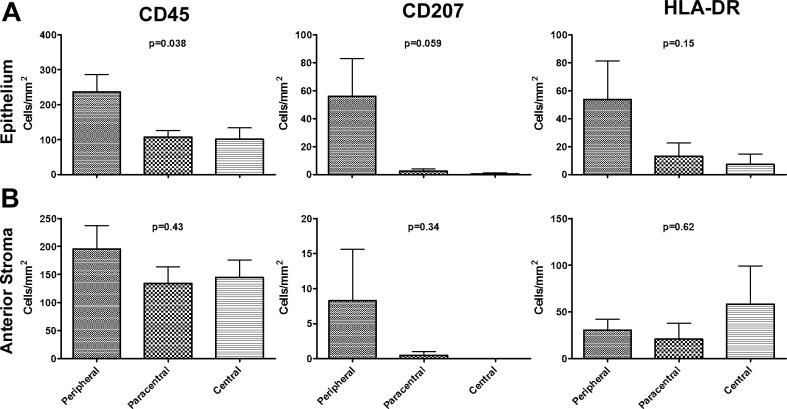
Flow cytometric analysis of dispersed corneal cells revealed that approximately a quarter of the CD45+ cells were CD11c+ dendritic cells, and the majority of DCs expressed MHC class II (Figs. 2A, 2B). Confocal microscopic analysis showed that DCs were situated in the basal aspect of the epithelium as well as in the peripheral anterior stroma (Fig. 2C). Langerin (CD207+) cells, likely representing LCs, were essentially confined to the basal epithelium of the peripheral cornea (Figs. 2D, 2E, 3), while CD68+ macrophages were identified mostly within the anterior stroma (Fig. 2D). A substantial portion of the CD45+ cells expressed MHC class II (HLA-DR) on at least a portion of their dendrites (Fig. 2F). There was a trend toward decreased density of CD45+, CD207+, and HLA-DR+ cells from peripheral to central epithelium (Fig. 3A). The densities of CD45+ and HLA-DR+ cells were relatively constant from peripheral to central anterior stroma (Fig. 3B). In the anterior stroma, very few LCs were identified peripherally and none centrally.
Figure 2.
Phenotype of APC within the normal human cornea. (A, B) Fresh donor human corneal tissue was dispersed with collagenase prior to flow cytometric analysis. (A) Dot plots showing gating strategy to identify CD45+, CD11c+, and HLA-DR+ cells. SSC, side scatter. (B) Graph showing percent of CD45+ leukocytes that are CD11c+ (DC: left) and percent of CD11c+ DCs that are HLA-DR+ (right: n = 3). (C–F) Fresh donor human corneal tissue was fixed, and whole mounts were stained with the indicated markers prior to confocal imaging. (C) Top: Compressed image of z-stack in the xy plane from the peripheral cornea showing staining for CD45 (left: green) and CD11c (right: red). Bottom: Cross-sectional reconstructions in the xz plane (below the corresponding image in xy) were made using microscope automation and image analysis software (Molecular Devices; epithelium toward the top). (D) Compressed image of z-stack in the xy plane from the peripheral cornea showing staining for CD45 (top: green); CD207 (middle: red); and composite (bottom). (E) Cross-sectional reconstructions in the xz plane (epithelium toward the top) showing staining for DAPI, CD45, CD207 (top), and CD68 (bottom). (F) Compressed image of z-stack in the xy plane from the peripheral cornea showing staining for DAPI, CD45, and HLA-DR.
Figure 3.
Density of APCs within the normal human cornea. Single plane images were created from stacks acquired with a ×20 or ×40 objective through the entire epithelium or the anterior 31 μm of stroma using microscope automation and image analysis software (Molecular Devices). The indicated cell types were manually counted with image analysis software (Molecular Devices). Plots of the density of CD45+ (left), CD207+ (middle), and HLA-DR+ (right) in the central (3-mm diameter); paracentral (2-mm ring around central); and peripheral (beyond paracentral to limbus) regions of the human corneal epithelium (A) and the anterior 31 μm of stroma (B). Values were zero where no bars are seen. P values calculated by ANOVA using graphing software (GraphPad Software, Inc.; n = 5–8 corneas per group). Posttest analysis did not reveal significant differences between any two groups for CD45 in the epithelium.
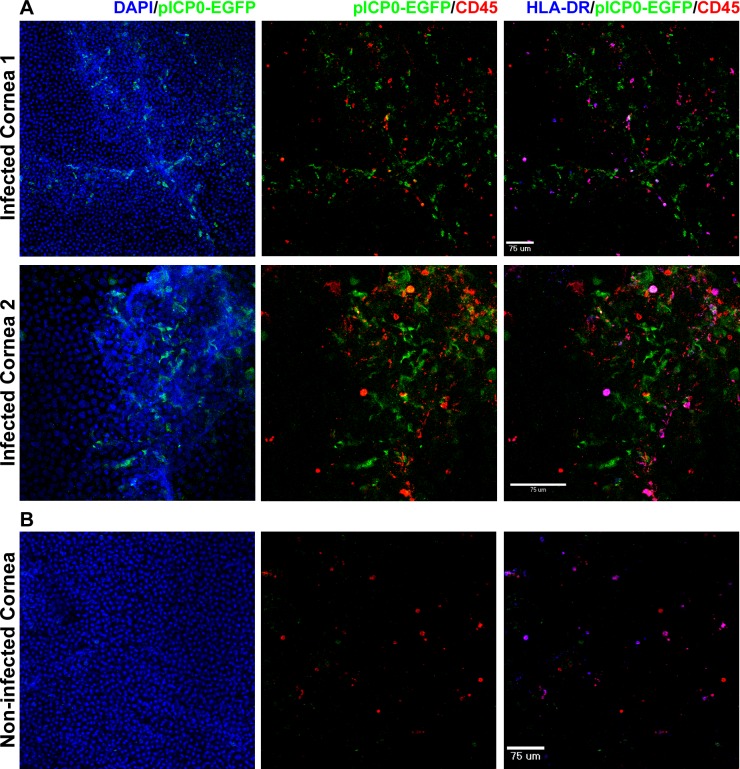
In an ex vivo corneal tissue HSV-1 infection model, EGFP expression was seen in epithelial cells in the areas of scarification 4 to 8 hours following infection with pICP0-EGFP HSV-1. By 16 hours postinfection, HLA-DR+ APC were heavily aggregated in areas of HSV-1 infection, and a small proportion of HLA-DR+ cells expressed EGFP, indicating direct infection of APCs by HSV-1 (Fig. 4A). Control tissue that was not scarified or infected revealed intact corneal epithelium and a relatively even distribution of APCs (Fig. 4B).
Figure 4.
HSV-1 infection of the corneal epithelium induces migration of tissue-resident APCs. (A) The epithelium of human corneal tissue was scarified and pICP0-EGFP HSV-1 RE applied. The tissue was incubated at 37°C for 1 hour and then washed extensively. The tissue was placed in fresh media and further cultured for various times (16 hours depicted in the figure). The tissue was then fixed and stained with the indicated markers prior to confocal imaging. Compressed images of z-stacks in the xy plane from the peripheral epithelium and anterior stroma of two separate corneas are shown. Epithelial scarification and infection lead to disruption of the normal anterior corneal architecture as assessed by DAPI staining. APCs were found throughout the remaining epithelium and anterior stroma. Data are representative of three separate corneas. (B) Tissue that was not scarified or infected but otherwise treated as above served as control. Compressed image of a z-stack in the xy plane from the peripheral epithelium is shown.
Discussion
Defining the local APC population within the cornea is important for understanding how immune responses are initiated at the ocular surface in response to trauma, infection, or transplantation. Here, we demonstrate a unique stratification of APCs within the normal human cornea with DCs and LCs situated predominantly in the basal epithelium and macrophages in the anterior stroma. These findings are strikingly similar to the distribution of APCs previously described in mice, confirming the relevance of the murine model for study of corneal APCs. Furthermore, these results support and extend the findings of previous studies utilizing epithelial sheets or frozen sections of human corneas for assessment of bone marrow-derived cells.12,14,17
In vivo confocal microscopy (IVCM) has become an increasingly utilized clinical tool to evaluate the ocular surface.18–21 While this technology provides excellent morphologic analysis of corneal cells, phenotypic information is lacking. Often cells that have a dendritic appearance on IVCM are labeled as DCs or LCs without phenotypic analysis. Our study confirms that DCs and LCs indeed reside in the human corneal basal epithelium and anterior stroma and are likely the source of cells seen on IVCM.
Our study is limited by the range of donor ages and lengths of time the tissue was stored in media (Bausch & Lomb, Inc.) prior to fixation, both external factors that could not be controlled. The range of patient ages in our study is similar to that reported in a previous study investigating human corneal APCs,17 and no correlation was found between patient age and APC density (data not shown). A previous report demonstrated a reduction in the density of human corneal APCs over time while tissue was stored in media (Bausch & Lomb, Inc.) at 31°C, with the largest decline occurring between 3 and 7 days.22 In our study, all samples were fixed within 2 days of storage, and all tissue was kept at 4°C at all times until fixation in an attempt to minimize any decline in APC density.
The function of corneal APCs remains an area of active investigation. In a murine model of HSV-1 corneal infection, it was recently shown that corneal resident or early responding blood-derived DCs react rapidly to HSV-1 infection and are required to attract natural killer cells and inflammatory monocytes to the site of viral infection within the cornea.15 In the current study utilizing ex vivo cultures of isolated human corneal tissue, corneal resident MHC class II+ APCs migrated to the site of epithelial trauma and HSV-1 infection within 8 to 16 hours of HSV-1 infection. This finding demonstrates that corneal resident APCs are capable of rapidly recognizing and mobilizing to corneal trauma and HSV-1 infection. It is possible that scarification alone may have caused APC migration. While infrequent, some APCs were directly infected by HSV-1 as evidenced by viral gene expression within these cells. Whether HSV-1–infected APCs are capable of transit to draining lymph nodes for priming of the adaptive immune response or if they are retained within the cornea for restimulation of infiltrating T cells requires further investigation.
Until recently, corneal immune privilege was attributed in part to a lack of functional APCs within the cornea. Several studies in mice have now shown distinct subsets of APC that are stratified throughout the naïve cornea.2–7 The current study demonstrates a similar stratification of APCs in normal human donor corneas confirming the relevance of the murine model for investigation of corneal APCs. Furthermore, using an ex vivo HSV-1 infection model of corneal tissue, we demonstrate that APCs resident within the cornea are capable of mobilizing to the site of scarification and viral infection. These findings provide the basis for future studies investigating how corneal APCs contribute to immune protection and immunopathology.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Kira Lathrop, MS (Department of Ophthalmology), for assistance with imaging experiments.
Supported in part through National Institutes of Health Grants R01EY010359 and P30EY08098, as well as unrestricted grants from Research to Prevent Blindness and the Eye and Ear Foundation of Pittsburgh (RLH). The authors alone are responsible for the content and writing of the paper.
Disclosure: J.E. Knickelbein, None; K.-A. Buela, None; R.L. Hendricks, None
References
- 1. Steinman RM. Dendritic cells: understanding immunogenicity. Eur J Immunol. 2007; 37 (suppl 1): S53–S60 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Knickelbein JE, Watkins SC, McMenamin PG, Hendricks RL. Stratification of antigen-presenting cells within the normal cornea. Ophthalmol Eye Dis. 2009; 1: 45–54 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Hamrah P, Zhang Q, Liu Y, Dana MR. Novel characterization of MHC class II-negative population of resident corneal Langerhans cell-type dendritic cells. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2002; 43: 639–646 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Lee EJ, Rosenbaum JT, Planck SR. Epifluorescence intravital microscopy of murine corneal dendritic cells. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010; 51: 2101–2108 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Hattori T, Chauhan SK, Lee H, et al. Characterization of Langerin-expressing dendritic cell subsets in the normal cornea. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011; 52: 4598–4604 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Hamrah P, Liu Y, Zhang Q, Dana MR. The corneal stroma is endowed with a significant number of resident dendritic cells. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2003; 44: 581–589 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Nakamura T, Ishikawa F, Sonoda KH, et al. Characterization and distribution of bone marrow-derived cells in mouse cornea. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2005; 46: 497–503 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Brissette-Storkus CS, Reynolds SM, Lepisto AJ, Hendricks RL. Identification of a novel macrophage population in the normal mouse corneal stroma. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2002; 43: 2264–2271 [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Pels E, van der Gaag R. HLA-A,B,C, and HLA-DR antigens and dendritic cells in fresh and organ culture preserved corneas. Cornea. 1984; 3: 231–239 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Treseler PA, Foulks GN, Sanfilippo F. The expression of HLA antigens by cells in the human cornea. Am J Ophthalmol. 1984; 98: 763–772 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Whitsett CF, Stulting RD. The distribution of HLA antigens on human corneal tissue. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1984; 25: 519–524 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Yamagami S, Yokoo S, Usui T, Yamagami H, Amano S, Ebihara N. Distinct populations of dendritic cells in the normal human donor corneal epithelium. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2005; 46: 4489–4494 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Yamagami S, Ebihara N, Usui T, Yokoo S, Amano S. Bone marrow-derived cells in normal human corneal stroma. Arch Ophthalmol. 2006; 124: 62–69 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Mayer WJ, Mackert MJ, Kranebitter N, et al. Distribution of antigen presenting cells in the human cornea: correlation of in vivo confocal microscopy and immunohistochemistry in different pathologic entities. Curr Eye Res. 2012; 37: 1012–1018 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Frank GM, Buela KA, Maker DM, Harvey SA, Hendricks RL. Early responding dendritic cells direct the local NK response to control herpes simplex virus 1 infection within the cornea. J Immunol. 2012; 188: 1350–1359 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Decman V, Kinchington PR, Harvey SA, Hendricks RL. Gamma interferon can block herpes simplex virus type 1 reactivation from latency, even in the presence of late gene expression. J Virol. 2005; 79: 10339–10347 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Mayer WJ, Irschick UM, Moser P, et al. Characterization of antigen-presenting cells in fresh and cultured human corneas using novel dendritic cell markers. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2007; 48: 4459–4467 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Cruzat A, Pavan-Langston D, Hamrah P. In vivo confocal microscopy of corneal nerves: analysis and clinical correlation. Semin Ophthalmol. 2010; 25: 171–177 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Kumar RL, Cruzat A, Hamrah P. Current state of in vivo confocal microscopy in management of microbial keratitis. Semin Ophthalmol. 2010; 25: 166–170 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Alhatem A, Cavalcanti B, Hamrah P. In vivo confocal microscopy in dry eye disease and related conditions. Semin Ophthalmol. 2012; 27: 138–148 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Shukla AN, Cruzat A, Hamrah P. Confocal microscopy of corneal dystrophies. Semin Ophthalmol. 2012; 27: 107–116 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Ardjomand N, Berghold A, Reich ME. Loss of corneal Langerhans cells during storage in organ culture medium, Optisol and McCarey-Kaufman medium. Eye (Lond). 1998; 12: 134–138 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]