Abstract
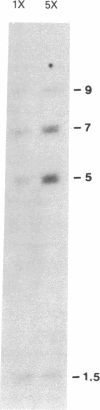
We have obtained a cDNA clone encoding most of human X-linked 3-phosphoglycerate kinase (PGK; ATP:3-phospho-D-glycerate 1-phosphotransferase, EC 2.7.2.3). Total mRNA was prepared from human adenocarcinoma-derived cell line LS174T and used for cDNA preparation. Double-stranded cDNA was inserted, after tailing with oligo(dC), into the plasmid vector pBR327 and cloned in Escherichia coli K-12. Transformants were screened by colony hybridization with a mixture of 32P-labeled oligodeoxyribonucleotides. A pool of hexadecamers complementary to all 32 possible sequences encoding amino acids 291-296 of X-linked PGK was used for the initial screen. One clone among 2,500 gave a strong positive signal. Plasmid DNA from this clone was purified and characterized by hybridization first to the hexadecamer probe mixture and then to an undecamer probe consisting of a mixture of four sequences. The cloned fragment hybridizes preferentially to DNA from human cells with five X chromosomes. DNA sequence analysis has established that the 1.2-kilobase-pair fragment encodes PGK from amino acid 121 through the COOH terminus.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banks R. D., Blake C. C., Evans P. R., Haser R., Rice D. W., Hardy G. W., Merrett M., Phillips A. W. Sequence, structure and activity of phosphoglycerate kinase: a possible hinge-bending enzyme. Nature. 1979 Jun 28;279(5716):773–777. doi: 10.1038/279773a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennand J., Chinault A. C., Konecki D. S., Melton D. W., Caskey C. T. Cloned cDNA sequences of the hypoxanthine/guanine phosphoribosyltransferase gene from a mouse neuroblastoma cell line found to have amplified genomic sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):1950–1954. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comb M., Seeburg P. H., Adelman J., Eiden L., Herbert E. Primary structure of the human Met- and Leu-enkephalin precursor and its mRNA. Nature. 1982 Feb 25;295(5851):663–666. doi: 10.1038/295663a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daskal I., Ramirez S. A., Ballal R. N., Spohn W. H., Wu B., Busch H. Detergent lysis for isolation of intact polysomes of Nivikoff hepatoma ascites cells. Cancer Res. 1976 Mar;36(3):1026–1034. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson R. P., Kramer J. M., Rittenhouse J., Salkeld A. Quantitation of mRNAs during mouse spermatogenesis: protamine-like histone and phosphoglycerate kinase-2 mRNAs increase after meiosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):6086–6090. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.6086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujii H., Yoshida A. Molecular abnormality of phosphoglycerate kinase-Uppsala associated with chronic nonspherocytic hemolytic anemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5461–5465. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartler S. M., Andina R. J. Mammalian X-chromosome inactivation. Adv Hum Genet. 1976;7:99–140. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4757-0659-8_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gergen J. P., Stern R. H., Wensink P. C. Filter replicas and permanent collections of recombinant DNA plasmids. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Dec 20;7(8):2115–2136. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.8.2115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goeddel D. V., Shepard H. M., Yelverton E., Leung D., Crea R., Sloma A., Pestka S. Synthesis of human fibroblast interferon by E. coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Sep 25;8(18):4057–4074. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.18.4057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goeddel D. V., Yelverton E., Ullrich A., Heyneker H. L., Miozzari G., Holmes W., Seeburg P. H., Dull T., May L., Stebbing N. Human leukocyte interferon produced by E. coli is biologically active. Nature. 1980 Oct 2;287(5781):411–416. doi: 10.1038/287411a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harpold M. M., Dobner P. R., Evans R. M., Bancroft F. C. Construction and identification by positive hybridization-translation of a bacterial plasmid containing a rat growth hormone structural gene sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Jun;5(6):2039–2053. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.6.2039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang I. Y., Fujii H., Yoshida A. Structure and function of normal and variant human phosphoglycerate kinase. Hemoglobin. 1980;4(5-6):601–609. doi: 10.3109/03630268008997730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang I. Y., Welch C. D., Yoshida A. Complete amino acid sequence of human phosphoglycerate kinase. Cyanogen bromide peptides and complete amino acid sequence. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 10;255(13):6412–6420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ish-Horowicz D., Burke J. F. Rapid and efficient cosmid cloning. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):2989–2998. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.2989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itakura K., Riggs A. D. Chemical DNA synthesis and recombinant DNA studies. Science. 1980 Sep 19;209(4463):1401–1405. doi: 10.1126/science.6106285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jolly D. J., Esty A. C., Bernard H. U., Friedmann T. Isolation of a genomic clone partially encoding human hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(16):5038–5041. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.16.5038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakidani H., Furutani Y., Takahashi H., Noda M., Morimoto Y., Hirose T., Asai M., Inayama S., Nakanishi S., Numa S. Cloning and sequence analysis of cDNA for porcine beta-neo-endorphin/dynorphin precursor. Nature. 1982 Jul 15;298(5871):245–249. doi: 10.1038/298245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manteuil S., Hamer D. H., Thomas C. A., Jr Regular arrangement of restriction sites in Drosophila DNA. Cell. 1975 Aug;5(4):413–422. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90060-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin G. R. X-chromosome inactivation in mammals. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):721–724. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90432-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahon A., Fosten M., Monk M. Random X-chromosome inactivation in female primordial germ cells in the mouse. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1981 Aug;64:251–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Crea R., Seeburg P. H. A system for shotgun DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 24;9(2):309–321. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.2.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyoshi K., Miyake T., Hozumi T., Itakura K. Solid-phase synthesis of polynucleotides. II. Synthesis of polythymidylic acids by the block coupling phosphotriester method. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Nov 25;8(22):5473–5489. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.22.5473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norgard M. V. Rapid and simple removal of contaminating RNA from plasmid DNA without the use of RNase. Anal Biochem. 1981 May 1;113(1):34–42. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90040-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pegoraro B., Lee C. Y. Purification and characterization of two isozymes of 3-phosphoglycerate kinase from the mouse. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Feb 10;522(2):423–433. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(78)90075-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persico M. G., Toniolo D., Nobile C., D'Urso M., Luzzatto L. cDNA sequences of human glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase cloned in pBR322. Nature. 1981 Dec 24;294(5843):778–780. doi: 10.1038/294778a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reyes A. A., Johnson M. J., Schöld M., Ito H., Ike Y., Morin C., Itakura K., Wallace R. B. Identification of an H-2Kb-related molecule by molecular cloning. Immunogenetics. 1981;14(5):383–392. doi: 10.1007/BF00373318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggs A. D. X inactivation, differentiation, and DNA methylation. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1975;14(1):9–25. doi: 10.1159/000130315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez R. L., West R. W., Heyneker H. L., Bolivar F., Boyer H. W. Characterizing wild-type and mutant promoters of the tetracycline resistance gene in pBR313. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jul 25;6(10):3267–3287. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.10.3267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roychoudhury R., Wu R. Terminal transferase-catalyzed addition of nucleotides to the 3' termini of DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):43–62. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65009-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlaeger R., Hoffmann D., Hilz H. Polyribosomes in tumor cells during induction of ribonuclease by cytostatic treatment. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1969 Aug;350(8):1017–1022. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1969.350.2.1017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shively J. E. Sequence determinations of proteins and peptides at the nanomole and subnanomole level with a modified spinning cup sequenator. Methods Enzymol. 1981;79(Pt B):31–48. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(81)79011-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer R. H., Penman S. Messenger RNA in HeLa cells: kinetics of formation and decay. J Mol Biol. 1973 Aug 5;78(2):321–334. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90119-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soberon X., Covarrubias L., Bolivar F. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. IV. Deletion derivatives of pBR322 and pBR325. Gene. 1980 May;9(3-4):287–305. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90328-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suggs S. V., Wallace R. B., Hirose T., Kawashima E. H., Itakura K. Use of synthetic oligonucleotides as hybridization probes: isolation of cloned cDNA sequences for human beta 2-microglobulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6613–6617. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tom B. H., Rutzky L. P., Jakstys M. M., Oyasu R., Kaye C. I., Kahan B. D. Human colonic adenocarcinoma cells. I. Establishment and description of a new line. In Vitro. 1976 Mar;12(3):180–191. doi: 10.1007/BF02796440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. B., Johnson M. J., Hirose T., Miyake T., Kawashima E. H., Itakura K. The use of synthetic oligonucleotides as hybridization probes. II. Hybridization of oligonucleotides of mixed sequence to rabbit beta-globin DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Feb 25;9(4):879–894. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.4.879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. B., Schold M., Johnson M. J., Dembek P., Itakura K. Oligonucleotide directed mutagenesis of the human beta-globin gene: a general method for producing specific point mutations in cloned DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Aug 11;9(15):3647–3656. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.15.3647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]