Abstract
This paper reports the antigenicity of the fusion region of the influenza virus hemagglutinin (HA). Two peptides, comprising the fusion region (residues 1-11 of the HA2 part of HA) of strain A and strain B influenza virus, were synthesized and their abilities to bind rabbit, goat, and human anti-influenza antibodies were determined. In addition, 30 anti-HA monoclonal antibodies were examined for their ability to bind the synthetic peptides. In quantitative immunoadsorbent titrations, the two peptides bound considerable amounts of antibodies in rabbit and goat antisera against virus or HA of the A or B strain as well as in several human sera from patients recovering from influenza A. Of the 30 anti-HA monoclonal antibodies, 5 bound completely and 4 bound partially to the peptides. Antibodies were raised in rabbits against the peptides by immunizing with peptide-bovine serum albumin conjugates or with the free peptides. Anti-peptide antibodies were bound by HA and by the intact virus of the respective strain. However, these antisera failed to exhibit significant virus neutralizing activity. In contrast, the monoclonal antibodies that reacted with these peptides inhibited viral infectivity. The results clearly show that residues 1-11 of HA2 represent an important antigenic site on influenza virus.
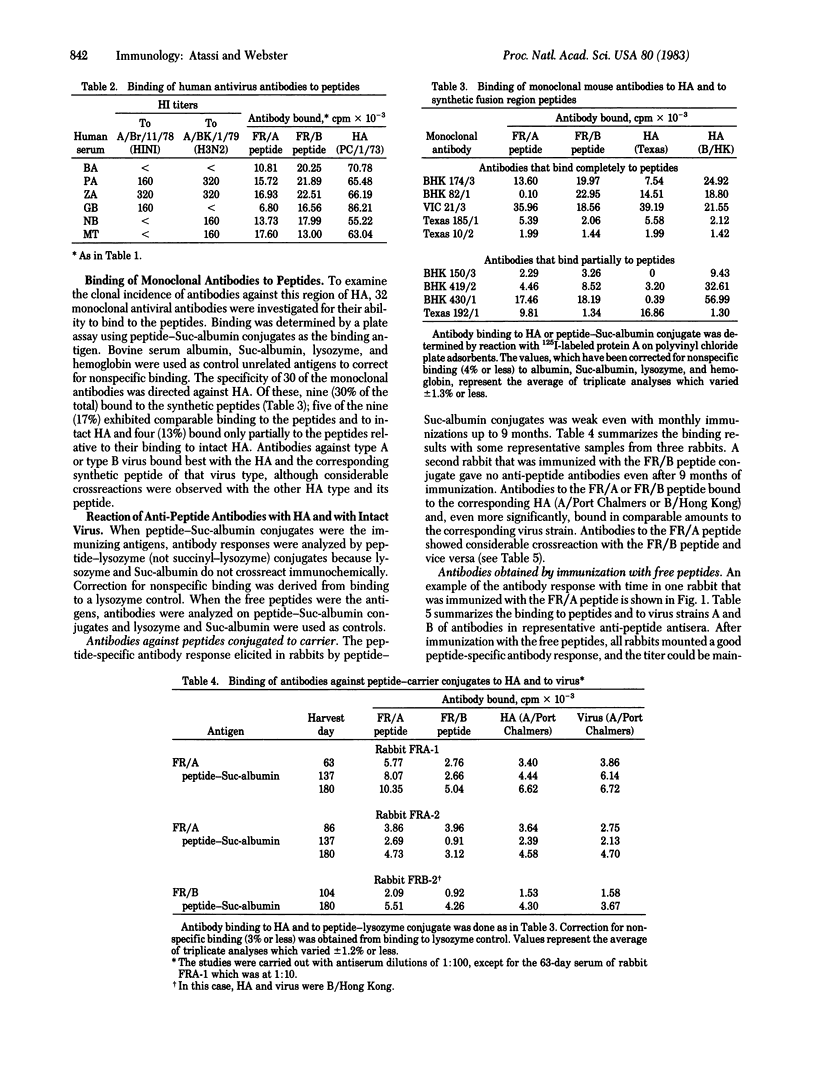
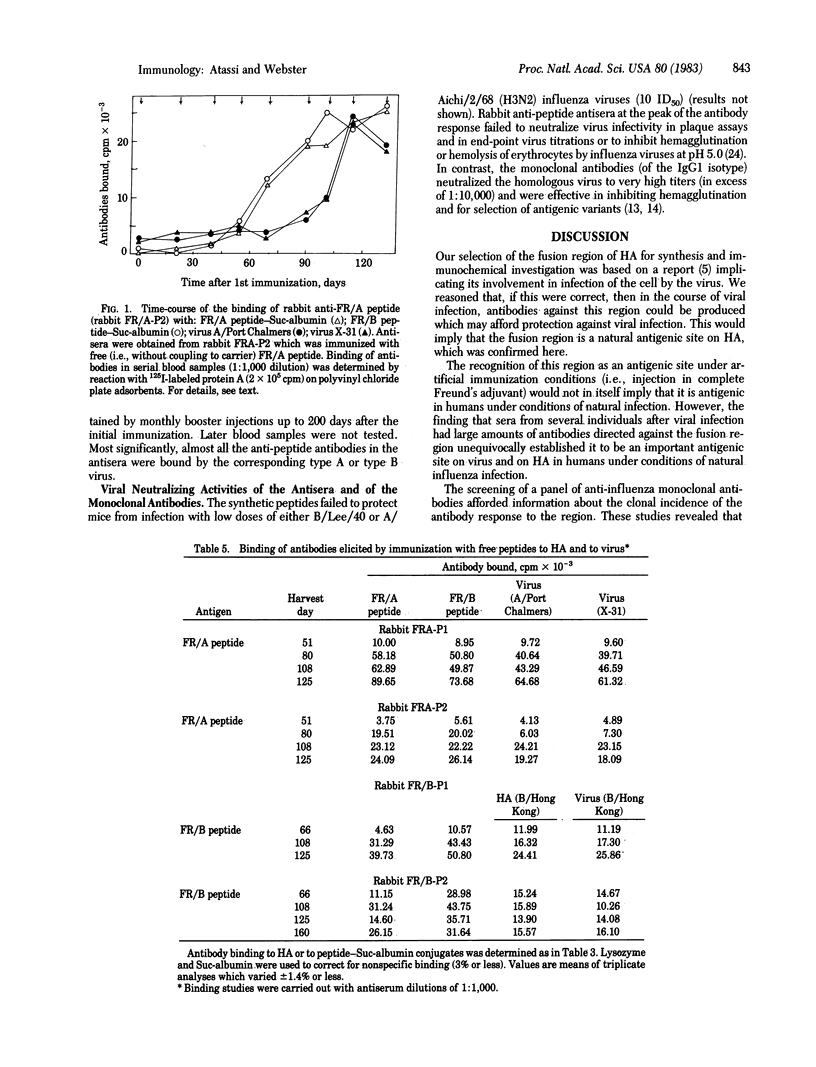
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atassi M. Z. Antigenic structure of myoglobin: the complete immunochemical anatomy of a protein and conclusions relating to antigenic structures of proteins. Immunochemistry. 1975 May;12(5):423–438. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(75)90010-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atassi M. Z., Kazim A. L., Sakata S. High yield coupling of peptides to protein carriers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Sep 29;670(2):300–302. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(81)90025-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atassi M. Z., Lee C. L. Boundary refinement of the lysozyme antigenic site around the disulphide bond 6-127 (site 1) by 'surface-simulation' synthesis. Biochem J. 1978 May 1;171(2):419–427. doi: 10.1042/bj1710419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atassi M. Z., Lee C. L., Pai R. C. Enzymic and immunochemical properties of lysozyme. XVI. A novel synthetic approach to an antigenic reactive site by direct linkage of the relevant conformationally adjacent residues constituting the site. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Apr 14;427(2):745–751. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(76)90219-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atassi M. Z., Lee C. L. The precise and entire antigenic structure of native lysozyme. Biochem J. 1978 May 1;171(2):429–434. doi: 10.1042/bj1710429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atassi M. Z. Precise determination of the entire antigenic structure of lysozyme: molecular features of protein antigenic structures and potential of "surface-simulation" synthesis--a powerful new concept for protein binding sites. Immunochemistry. 1978 Dec;15(12):909–936. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(78)90126-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atassi M. Z., Smith J. A. A proposal for the nomenclature of antigenic sites in peptides and proteins. Immunochemistry. 1978 Aug;15(8):609–610. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(78)90016-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown L. E., Ward C. W., Jackson D. C. Antigenic determinants of influenza virus hemagglutinin--IX. The carbohydrate side chains from an Asian strain. Mol Immunol. 1982 Feb;19(2):329–338. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(82)90347-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Prediction of protein conformation. Biochemistry. 1974 Jan 15;13(2):222–245. doi: 10.1021/bi00699a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green N., Alexander H., Olson A., Alexander S., Shinnick T. M., Sutcliffe J. G., Lerner R. A. Immunogenic structure of the influenza virus hemagglutinin. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):477–487. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90202-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER W. M., GREENWOOD F. C. Preparation of iodine-131 labelled human growth hormone of high specific activity. Nature. 1962 May 5;194:495–496. doi: 10.1038/194495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopp T. P., Woods K. R. Prediction of protein antigenic determinants from amino acid sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3824–3828. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazim A. L., Atassi M. Z. Structurally inherent antigenic sites. Localization of the antigenic sites of the alpha-chain of human haemoglobin in three host species by a comprehensive synthetic approach. Biochem J. 1982 Apr 1;203(1):201–208. doi: 10.1042/bj2030201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koketsu J., Atassi M. Z. Immunochemistry of sperm-whale myoglobin. 18. Accurate delineation of the single reactive region in sequence 120-153 by study of synthetic peptides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Dec 6;328(2):289–302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koketsu J., Atassi M. Z. Immunochemistry of sperm-whale myoglobin. XVI. Accurate delineation of the single region in sequence 1-55 by immunochemical studies of synthetic peptides. Some conclusions concerning antigenic structures of proteins. Immunochemistry. 1974 Jan;11(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(74)90335-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Derivation of specific antibody-producing tissue culture and tumor lines by cell fusion. Eur J Immunol. 1976 Jul;6(7):511–519. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830060713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laver W. G., Air G. M., Dopheide T. A., Ward C. W. Amino acid sequence changes in the haemagglutinin of A/Hong Kong (H3N2) influenza virus during the period 1968--77. Nature. 1980 Jan 31;283(5746):454–457. doi: 10.1038/283454a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laver W. G., Webster R. G. Studies on the origin of pandemic influenza. 3. Evidence implicating duck and equine influenza viruses as possible progenitors of the Hong Kong strain of human influenza. Virology. 1973 Feb;51(2):383–391. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90437-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. L., Atassi M. Z. Enzymic and immunochemical properties of lysozyme. Accurate definition of the antigenic site around the disulphide bridge 30-115 (site 3) by 'surface-simulation' synthesis. Biochem J. 1977 Dec 1;167(3):571–581. doi: 10.1042/bj1670571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. L., Atassi M. Z. Enzymic and immunochemical properties of lysozyme. XIX. Definition of the direction and conformational restrictions of the antigenic site around the disulfide bonds 64-80 and 76-94 (site 2) by 'surface-simulation' synthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Dec 20;495(2):354–368. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(77)90391-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenard J., Miller D. K. pH-dependent hemolysis by influenza, Semliki, Forest virus, and Sendai virus. Virology. 1981 Apr 30;110(2):479–482. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90079-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- March S. C., Parikh I., Cuatrecasas P. A simplified method for cyanogen bromide activation of agarose for affinity chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1974 Jul;60(1):149–152. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90139-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller G. M., Shapira M., Arnon R. Anti-influenza response achieved by immunization with a synthetic conjugate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):569–573. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakata S., Atassi M. Z. Immune recognition of serum albumin--XIII. Autoreactivity with rabbit serum albumin of rabbit antibodies against bovine or human serum albumins and autoimmune recognition of rabbit serum albumin. Mol Immunol. 1981 Nov;18(11):961–967. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(81)90113-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakata S., Atassi M. Z. Immunochemistry of serum albumin. VI. A dynamic approach to the immunochemical cross reactions of proteins using serum albumins from various species as models. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Feb 26;576(2):322–332. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(79)90407-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheid A., Choppin P. W. Identification of biological activities of paramyxovirus glycoproteins. Activation of cell fusion, hemolysis, and infectivity of proteolytic cleavage of an inactive precursor protein of Sendai virus. Virology. 1974 Feb;57(2):475–490. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90187-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobita K., Sugiura A., Enomote C., Furuyama M. Plaque assay and primary isolation of influenza A viruses in an established line of canine kidney cells (MDCK) in the presence of trypsin. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1975 Dec 30;162(1):9–14. doi: 10.1007/BF02123572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twining S. S., Atassi M. Z. Use of immunoadsorbents for the study of antibody binding to sperm whale myoglobin and its synthetic antigenic sites. J Immunol Methods. 1979;30(2):139–151. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(79)90088-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twining S. S., Lehmann H., Atassi M. Z. The antibody response to myoglobin is independent of the immunized species. Analysis in terms of replacements in the antigenic sites and in environmental residues of the cross-reactions of fifteen myoglobins with sperm-whale myoglobin antisera raised in different species. Biochem J. 1980 Dec 1;191(3):681–697. doi: 10.1042/bj1910681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster R. G., Berton M. T. Analysis of antigenic drift in the haemagglutinin molecule of influenza B virus with monoclonal antibodies. J Gen Virol. 1981 Jun;54(Pt 2):243–251. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-54-2-243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster R. G., Hinshaw V. S., Laver W. G. Selection and analysis of antigenic variants of the neuraminidase of N2 influenza viruses with monoclonal antibodies. Virology. 1982 Feb;117(1):93–104. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90510-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster R. G., Laver W. G., Air G. M., Schild G. C. Molecular mechanisms of variation in influenza viruses. Nature. 1982 Mar 11;296(5853):115–121. doi: 10.1038/296115a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster R. G., Laver W. G. Determination of the number of nonoverlapping antigenic areas on Hong Kong (H3N2) influenza virus hemagglutinin with monoclonal antibodies and the selection of variants with potential epidemiological significance. Virology. 1980 Jul 15;104(1):139–148. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90372-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley D. C., Wilson I. A., Skehel J. J. Structural identification of the antibody-binding sites of Hong Kong influenza haemagglutinin and their involvement in antigenic variation. Nature. 1981 Jan 29;289(5796):373–378. doi: 10.1038/289373a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson I. A., Skehel J. J., Wiley D. C. Structure of the haemagglutinin membrane glycoprotein of influenza virus at 3 A resolution. Nature. 1981 Jan 29;289(5796):366–373. doi: 10.1038/289366a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young C. R., Atassi M. Z. Antibodies to sperm-whale myoglobin evoked by free synthetic peptides of an antigenic site. Immunol Commun. 1982;11(1):9–16. doi: 10.3109/08820138209050719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



