Abstract
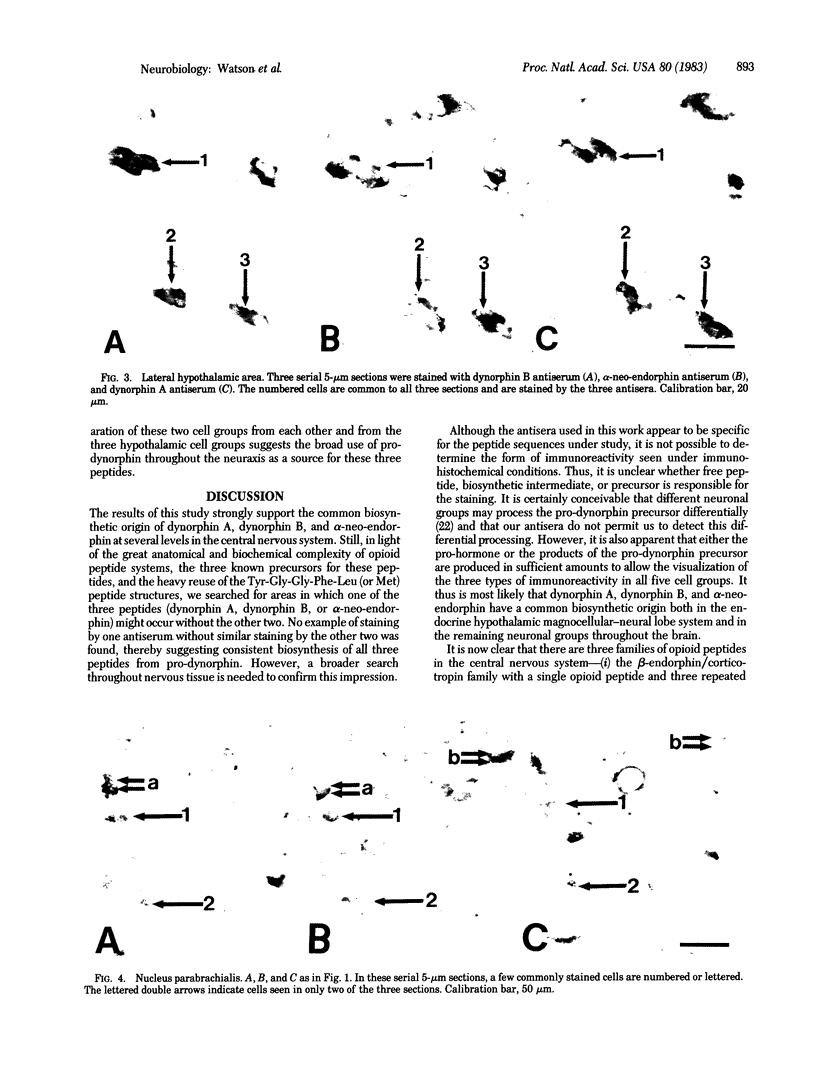
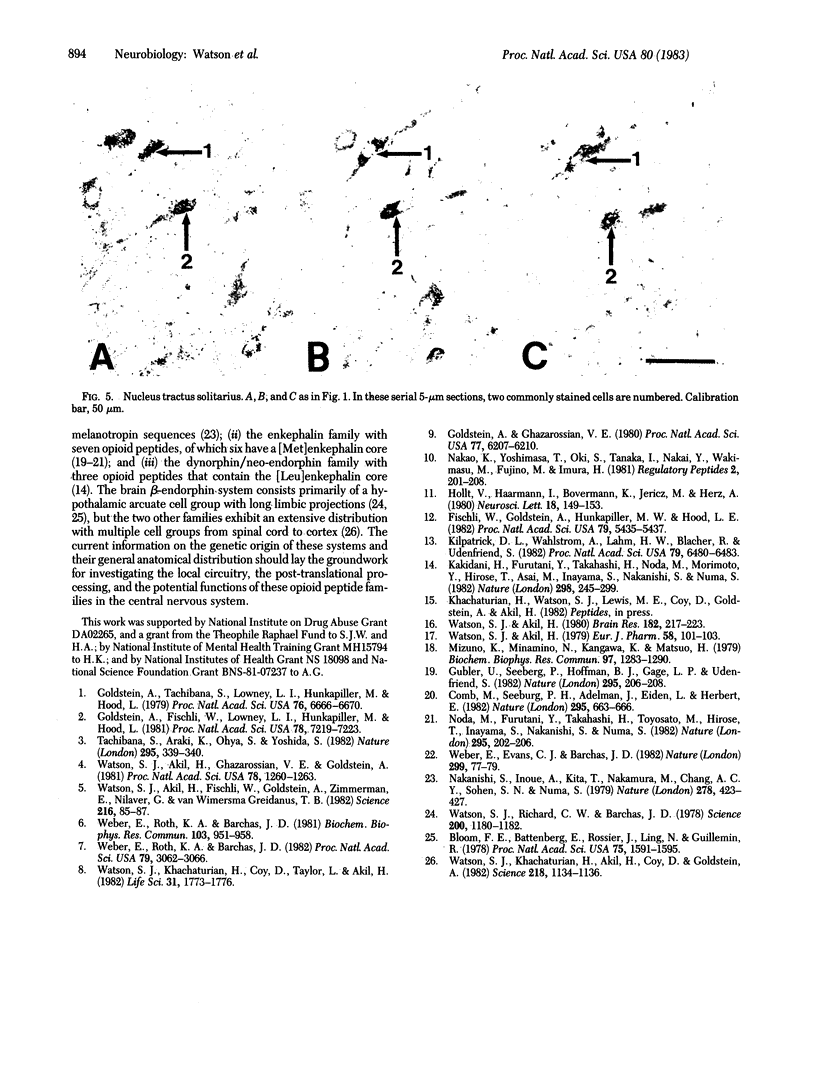
It is known that the opioid peptide dynorphin A has a broad distribution throughout the neuraxis. Recent biochemical studies have extended the sequence of dynorphin A by 15 amino acids to include another [Leu]enkephalin-containing peptide known as dynorphin B. These sequence data have been validated by the elucidation of the structure of the hypothalamic mRNA coding for alpha- and beta-neo-endorphin, dynorphin A, and dynorphin B. Using specific antisera directed against each of the three opioid peptides, we have studied their cellular distribution in rat brain. Their distribution patterns are extremely similar, if not identical. Furthermore, all three peptide immunoreactivities can be localized to the same cells in five nuclear groups throughout the brainstem--the supraoptic nucleus, the paraventricular nucleus, a group of cells in the lateral hypothalamic area, the nucleus parabrachialis, and the nucleus tractus solitarius. The sequence of a common precursor for dynorphin A, B, and alpha- and beta-neo-endorphin was deduced from hypothalamic mRNA. The ability to localize all three peptides together within cells in widely placed nuclei strongly supports the use of the same biosynthetic precursor for the neo-endorphin and dynorphin peptides in other parts of the central nervous system as well.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bloom F., Battenberg E., Rossier J., Ling N., Guillemin R. Neurons containing beta-endorphin in rat brain exist separately from those containing enkephalin: immunocytochemical studies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1591–1595. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comb M., Seeburg P. H., Adelman J., Eiden L., Herbert E. Primary structure of the human Met- and Leu-enkephalin precursor and its mRNA. Nature. 1982 Feb 25;295(5851):663–666. doi: 10.1038/295663a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischli W., Goldstein A., Hunkapiller M. W., Hood L. E. Isolation and amino acid sequence analysis of a 4,000-dalton dynorphin from porcine pituitary. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(17):5435–5437. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.17.5435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein A., Fischli W., Lowney L. I., Hunkapiller M., Hood L. Porcine pituitary dynorphin: complete amino acid sequence of the biologically active heptadecapeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):7219–7223. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.7219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein A., Ghazarossian V. E. Immunoreactive dynorphin in pituitary and brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):6207–6210. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.6207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein A., Tachibana S., Lowney L. I., Hunkapiller M., Hood L. Dynorphin-(1-13), an extraordinarily potent opioid peptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6666–6670. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Seeburg P., Hoffman B. J., Gage L. P., Udenfriend S. Molecular cloning establishes proenkephalin as precursor of enkephalin-containing peptides. Nature. 1982 Jan 21;295(5846):206–208. doi: 10.1038/295206a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höllt V., Haarmann I., Bovermann K., Jerlicz M., Herz A. Dynorphin-related immunoreactive peptides in rat brain and pituitary. Neurosci Lett. 1980 Jun;18(2):149–153. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(80)90318-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakidani H., Furutani Y., Takahashi H., Noda M., Morimoto Y., Hirose T., Asai M., Inayama S., Nakanishi S., Numa S. Cloning and sequence analysis of cDNA for porcine beta-neo-endorphin/dynorphin precursor. Nature. 1982 Jul 15;298(5871):245–249. doi: 10.1038/298245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilpatrick D. L., Wahlstrom A., Lahm H. W., Blacher R., Udenfriend S. Rimorphin, a unique, naturally occurring [Leu]enkephalin-containing peptide found in association with dynorphin and alpha-neo-endorphin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6480–6483. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuno K., Minamino N., Kangawa K., Matsuo H. A new family of endogenous "big" Met-enkephalins from bovine adrenal medulla: purification and structure of docosa- (BAM-22P) and eicosapeptide (BAM-20P) with very potent opiate activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Dec 31;97(4):1283–1290. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(80)80005-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakanishi S., Inoue A., Kita T., Nakamura M., Chang A. C., Cohen S. N., Numa S. Nucleotide sequence of cloned cDNA for bovine corticotropin-beta-lipotropin precursor. Nature. 1979 Mar 29;278(5703):423–427. doi: 10.1038/278423a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakao K., Yoshimasa T., Oki S., Tanaka I., Nakai Y., Wakimasu M., Fujino M., Imura H. Presence of dynorphin-like immunoreactivity in rat pituitary gland and hypothalamus. Regul Pept. 1981 Jun;2(3):201–208. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(81)90014-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Furutani Y., Takahashi H., Toyosato M., Hirose T., Inayama S., Nakanishi S., Numa S. Cloning and sequence analysis of cDNA for bovine adrenal preproenkephalin. Nature. 1982 Jan 21;295(5846):202–206. doi: 10.1038/295202a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tachibana S., Araki K., Ohya S., Yoshida S. Isolation and structure of dynorphin, an opioid peptide, from porcine duodenum. Nature. 1982 Jan 28;295(5847):339–340. doi: 10.1038/295339a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson S. J., Akil H., Fischli W., Goldstein A., Zimmerman E., Nilaver G., van wimersma Griedanus T. B. Dynorphin and vasopressin: common localization in magnocellular neurons. Science. 1982 Apr 2;216(4541):85–87. doi: 10.1126/science.6121376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson S. J., Akil H., Ghazarossian V. E., Goldstein A. Dynorphin immunocytochemical localization in brain and peripheral nervous system: preliminary studies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1260–1263. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson S. J., Akil H. The presence of two alpha-MSH positive cell groups in rat hypothalamus. Eur J Pharmacol. 1979 Sep 1;58(1):101–103. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(79)90351-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson S. J., Akil H. alpha-MSH in rat brain: occurrence within and outside of beta-endorphin neurons. Brain Res. 1980 Jan 20;182(1):217–223. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)90849-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson S. J., Khachaturian H., Akil H., Coy D. H., Goldstein A. Comparison of the distribution of dynorphin systems and enkephalin systems in brain. Science. 1982 Dec 10;218(4577):1134–1136. doi: 10.1126/science.6128790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson S. J., Khachaturian H., Coy D., Taylor L., Akil H. Dynorphin is located throughout the CNS and is often co-localized with alpha-neo-endorphin. Life Sci. 1982 Oct 18;31(16-17):1773–1776. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(82)90207-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson S. J., Richard C. W., 3rd, Barchas J. D. Adrenocorticotropin in rat brain: immunocytochemical localization in cells and axons. Science. 1978 Jun 9;200(4346):1180–1182. doi: 10.1126/science.206967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber E., Evans C. J., Barchas J. D. Predominance of the amino-terminal octapeptide fragment of dynorphin in rat brain regions. Nature. 1982 Sep 2;299(5878):77–79. doi: 10.1038/299077a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber E., Roth K. A., Barchas J. D. Colocalization of alpha-neo-endorphin and dynorphin immunoreactivity in hypothalamic neurons. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Dec 15;103(3):951–958. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)90902-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber E., Roth K. A., Barchas J. D. Immunohistochemical distribution of alpha-neo-endorphin/dynorphin neuronal systems in rat brain: evidence for colocalization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(9):3062–3066. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.9.3062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]







