Abstract
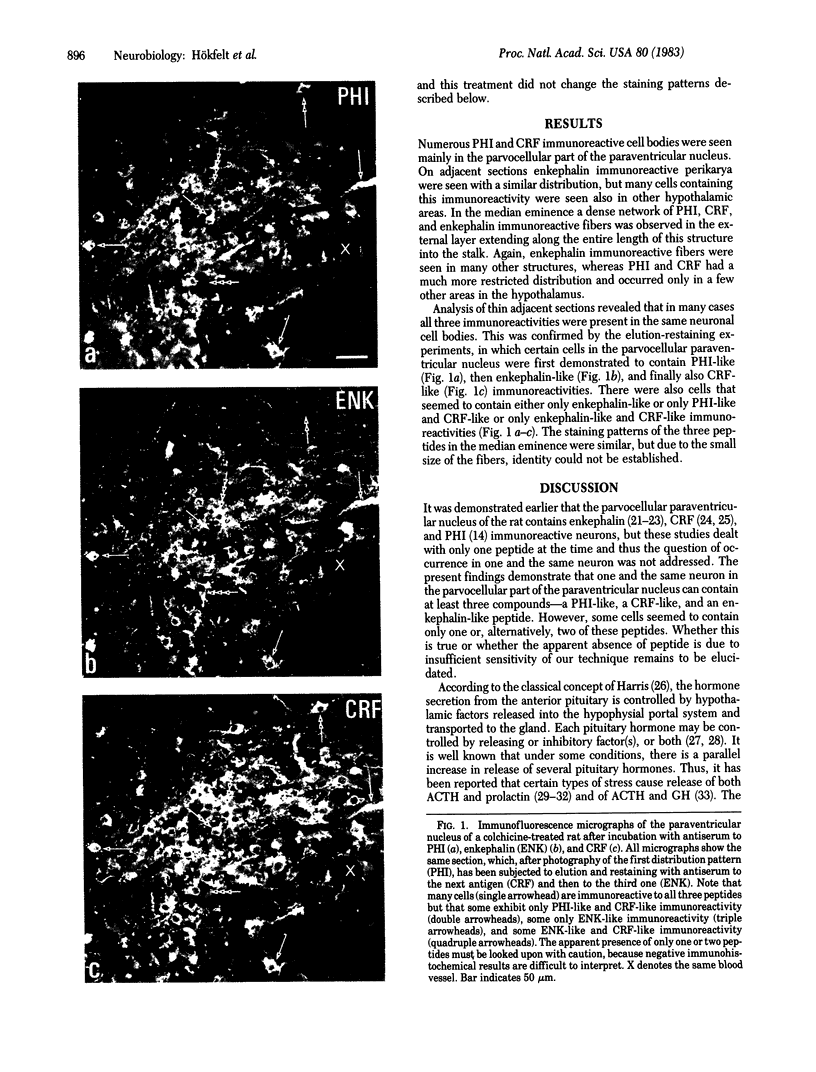
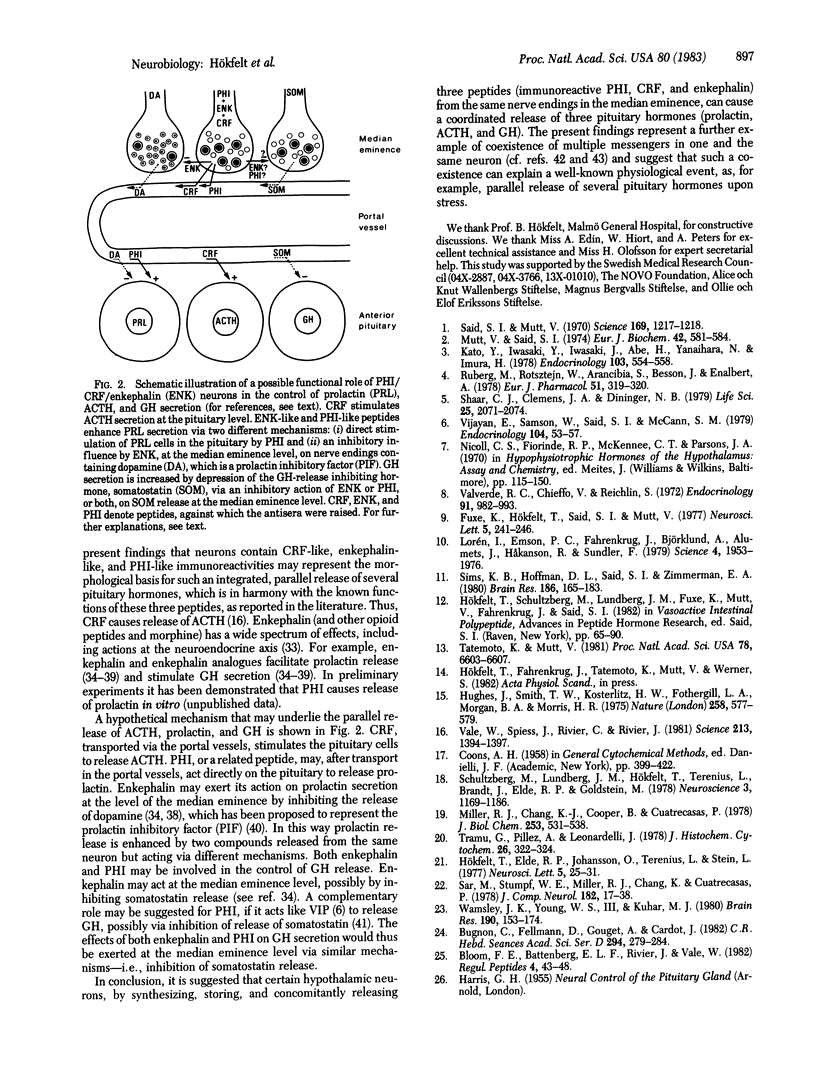
By using the indirect immunofluorescence technique, one and the same neuron in the parvocellular part of the paraventricular nucleus has been shown to stain with antisera against three different peptides: PHI (PHI-27), corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF), and enkephalin. This could explain the well-known parallel increase in plasma prolactin, corticotropin, and growth hormone levels--for example, under certain types of stress--as being due to a concomitant release of PHI-like, CRF-like, and enkephalin-like peptides from the same nerve endings in the median eminence. A hypothetical mechanism for the co-ordinated release of these three anterior pituitary hormones is discussed.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bloom F. E., Battenberg E. L., Rivier J., Vale W. Corticotropin releasing factor (CRF): immunoreactive neurones and fibers in rat hypothalamus. Regul Pept. 1982 Jun;4(1):43–48. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(82)90107-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown G. M., Martin J. B. Corticosterone, prolactin, and growth hormone responses to handling and new environment in the rat. Psychosom Med. 1974 May-Jun;36(3):241–247. doi: 10.1097/00006842-197405000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown G. M., Schalch D. S., Reichlin S. Hypothalamic mediation of growth hormone and adrenal stress response in the squirrel monkey. Endocrinology. 1971 Sep;89(3):694–703. doi: 10.1210/endo-89-3-694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruni J. F., Van Vugt D., Marshall S., Meites J. Effects of naloxone, morphine and methionine enkephalin on serum prolactin, luteinizing hormone, follicle stimulating hormone, thyroid stimulating hormone and growth hormone. Life Sci. 1977 Aug 1;21(3):461–466. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(77)90528-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bugnon C., Fellmann D., Gouget A., Cardot J. Mise en évidence immunocytochimique du système neuroglandulaire à-CRF dans l'hypothalamus du rat. C R Seances Acad Sci III. 1982 Feb 8;294(6):279–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COONS A. H. Fluorescent antibody methods. Gen Cytochem Methods. 1958;1:399–422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cocchi D., Santagostino A., Gil-Ad I., Ferri S., Müller E. E. Leu-enkephalin-stimulated growth hormone and prolactin release in the rat: comparison with the effect of morphine. Life Sci. 1977 Jun 15;20(12):2041–2045. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(77)90184-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cusan L., Dupont A., Kledzik G. S., Labrie F., Coy D. H., Schally A. V. Potent prolactin and growth hormone releasing activity of more analogues of Met-enkephalin. Nature. 1977 Aug 11;268(5620):544–547. doi: 10.1038/268544a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epelbaum J., Tapia-Arancibia L., Besson J., Rotsztejn W. H., Kordon C. Vasoactive intestinal peptide inhibits release of somatostatin from hypothalamus in vitro. Eur J Pharmacol. 1979 Oct 15;58(4):493–495. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(79)90323-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferland L., Fuxe K., Eneroth P., Gustafsson J. A., Skett P. Effects of methionine-enkephalin on prolactin release and catecholamine levels and turnover in the median eminence. Eur J Pharmacol. 1977 May 1;43(1):89–90. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(77)90164-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harms P. G., Langlier P., McCann S. M. Modification of stress-induced prolactin release by dexamethasone or adrenalectomy. Endocrinology. 1975 Feb;96(2):475–478. doi: 10.1210/endo-96-2-475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes J., Smith T. W., Kosterlitz H. W., Fothergill L. A., Morgan B. A., Morris H. R. Identification of two related pentapeptides from the brain with potent opiate agonist activity. Nature. 1975 Dec 18;258(5536):577–580. doi: 10.1038/258577a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hökfelt T., Johansson O., Ljungdahl A., Lundberg J. M., Schultzberg M. Peptidergic neurones. Nature. 1980 Apr 10;284(5756):515–521. doi: 10.1038/284515a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato Y., Iwasaki Y., Iwasaki J., Abe H., Yanaihara N., Imura H. Prolactin release by vasoactive intestinal polypeptide in rats. Endocrinology. 1978 Aug;103(2):554–558. doi: 10.1210/endo-103-2-554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorén I., Emson P. C., Fahrenkrug J., Björklund A., Alumets J., Håkanson R., Sundler F. Distribution of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide in the rat and mouse brain. Neuroscience. 1979;4(12):1953–1976. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(79)90068-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLeod R. M., Lehmeyer J. E. Studies on the mechanism of the dopamine-mediated inhibition of prolactin secretion. Endocrinology. 1974 Apr;94(4):1077–1085. doi: 10.1210/endo-94-4-1077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meites J., Bruni J. F., Van Vugt D. A., Smith A. F. Relation of endogenous opioid peptides and morphine to neuroendocrine functions. Life Sci. 1979 Apr 9;24(15):1325–1336. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(79)90001-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. J., Chang K. J., Cooper B., Cuatrecasas P. Radioimmunoassay and characterization of enkephalins in rat tissues. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jan 25;253(2):531–538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mutt V., Said S. I. Structure of the porcine vasoactive intestinal octacosapeptide. The amino-acid sequence. Use of kallikrein in its determination. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Mar 1;42(2):581–589. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03373.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruberg M., Rotsztejn W. H., Arancibia S., Besson J., Enjalbert A. Stimulation of prolactin release by vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP). Eur J Pharmacol. 1978 Oct 1;51(3):319–320. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(78)90421-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Said S. I., Mutt V. Polypeptide with broad biological activity: isolation from small intestine. Science. 1970 Sep 18;169(3951):1217–1218. doi: 10.1126/science.169.3951.1217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schally A. V., Arimura A., Kastin A. J. Hypothalamic regulatory hormones. Science. 1973 Jan 26;179(4071):341–350. doi: 10.1126/science.179.4071.341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultzberg M., Lundberg J. M., Hökfelt T., Terenius L., Brandt J., Elde R. P., Goldstein M. Enkephalin-like immunoreactivity in gland cells and nerve terminals of the adrenal medulla. Neuroscience. 1978;3(12):1169–1186. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(78)90137-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaar C. J., Clemens J. A., Dininger N. B. Effect of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide on prolactin release in vitro. Life Sci. 1979 Dec 10;25(24-25):2071–2074. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(79)90199-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaar C. J., Frederickson R. C., Dininger N. B., Jackson L. Enkephalin analogues and naloxone modulate the release of growth hormone and prolactin--evidence for regulation by an endogenous opioid peptide in brain. Life Sci. 1977 Sep 15;21(6):853–860. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(77)90415-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sims K. B., Hoffman D. L., Said S. I., Zimmerman E. A. Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP) in mouse and rat brain: an immunocytochemical study. Brain Res. 1980 Mar 17;186(1):165–183. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)90263-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatemoto K., Mutt V. Isolation and characterization of the intestinal peptide porcine PHI (PHI-27), a new member of the glucagon--secretin family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6603–6607. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tramu G., Pillez A., Leonardelli J. An efficient method of antibody elution for the successive or simultaneous localization of two antigens by immunocytochemistry. J Histochem Cytochem. 1978 Apr;26(4):322–324. doi: 10.1177/26.4.207771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vale W., Spiess J., Rivier C., Rivier J. Characterization of a 41-residue ovine hypothalamic peptide that stimulates secretion of corticotropin and beta-endorphin. Science. 1981 Sep 18;213(4514):1394–1397. doi: 10.1126/science.6267699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valverde R. C., Chieffo V., Reichlin S. Prolactin releasing factor in porcine and rat hypothalamic tissue. Endocrinology. 1972 Oct;91(4):982–993. doi: 10.1210/endo-91-4-982. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vijayan E., Samson W. K., Said S. I., McCann S. M. Vasoactive intestinal peptide: evidence for a hypothalamic site of action to release growth hormone, luteinizing hormone, and prolactin in conscious ovariectomized rats. Endocrinology. 1979 Jan;104(1):53–57. doi: 10.1210/endo-104-1-53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wamsley J. K., Young W. S., 3rd, Kuhar M. J. Immunohistochemical localization of enkephalin in rat forebrain. Brain Res. 1980 May 19;190(1):153–174. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)91166-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]