Abstract
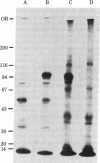
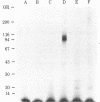
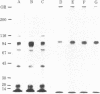
Insulin stimulates the phosphorylation of its own receptor. In the work reported here, the kinase activity responsible for the insulin-stimulated phosphorylation of the insulin receptor was localized. In a first approach, partially purified insulin receptors derived from normal rat hepatocytes were immunoprecipitated with antibodies specific for the insulin receptor; thereafter, the immunoprecipitates were incubated with [γ-32P]-ATP in the absence or presence of insulin (1 μM). NaDodSO4/polyacrylamide gel electrophoretic analysis of the immunoprecipitates under reducing conditions revealed autophosphorylation of the β subunit (Mr 95,000) of the insulin receptor; the α subunit (Mr 130,000) was not phosphorylated. Further, insulin specifically increased 3- to 4-fold the labeling of its own receptor β subunit, indicating that anti-receptor antibodies precipitate a functional and insulin-stimulable protein kinase that appears to be independent of cyclic AMP and calcium. To localize more precisely the insulin receptor-related kinase activity, we searched for an ATP-binding site on solubilized insulin receptors. By using covalent labeling with oxidized [α-32P]ATP, a labeled polypeptide with precisely the same electrophoretic mobility as that of the β subunit of the insulin receptor (Mr 95,000) was specifically immunoprecipitated with anti-receptor antibodies. Further, its appearance was prevented when the immunoprecipitation was preceded by incubation with unlabeled insulin. In conclusion, we have shown that an insulin-stimulated phosphorylation site and an ATP-binding site coexist on the β subunit of the insulin receptor. The simultaneous presence of these two sites on the same receptor subunit indicates that the insulin receptor acts as its own protein kinase.
Keywords: autoantibodies against insulin receptors, covalent affinity labeling, ATP
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carpenter G., King L., Jr, Cohen S. Epidermal growth factor stimulates phosphorylation in membrane preparations in vitro. Nature. 1978 Nov 23;276(5686):409–410. doi: 10.1038/276409a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clertant P., Cuzin F. Covalent affinity labeling by periodate-oxidized [alpha-32P]ATP of the large-T proteins of polyoma and SV40 viruses. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 10;257(11):6300–6305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S., Carpenter G., King L., Jr Epidermal growth factor-receptor-protein kinase interactions. Co-purification of receptor and epidermal growth factor-enhanced phosphorylation activity. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4834–4842. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S., Ushiro H., Stoscheck C., Chinkers M. A native 170,000 epidermal growth factor receptor-kinase complex from shed plasma membrane vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 10;257(3):1523–1531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czech M. P. Molecular basis of insulin action. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:359–384. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.002043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denton R. M., Brownsey R. W., Belsham G. J. A partial view of the mechanism of insulin action. Diabetologia. 1981 Oct;21(4):347–362. doi: 10.1007/BF00252681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ek B., Westermark B., Wasteson A., Heldin C. H. Stimulation of tyrosine-specific phosphorylation by platelet-derived growth factor. Nature. 1982 Feb 4;295(5848):419–420. doi: 10.1038/295419a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon A. S., Davis C. G., Milfay D., Diamond I. Phosphorylation of acetylcholine receptor by endogenous membrane protein kinase in receptor-enriched membranes of Torpedo californica. Nature. 1977 Jun 9;267(5611):539–540. doi: 10.1038/267539a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison L. C., Flier J. S., Roth J., Karlsson F. A., Kahn C. R. Immunoprecipitation of the insulin receptor: a sensitive assay for receptor antibodies and a specific technique for receptor purification. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1979 Jan;48(1):59–65. doi: 10.1210/jcem-48-1-59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedo J. A., Harrison L. C., Roth J. Binding of insulin receptors to lectins: evidence for common carbohydrate determinants on several membrane receptors. Biochemistry. 1981 Jun 9;20(12):3385–3393. doi: 10.1021/bi00515a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedo J. A., Kasuga M., Van Obberghen E., Roth J., Kahn C. R. Direct demonstration of glycosylation of insulin receptor subunits by biosynthetic and external labeling: evidence for heterogeneity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4791–4795. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs S., Hazum E., Shechter Y., Cuatrecasas P. Insulin receptor: covalent labeling and identification of subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4918–4921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R., Flier J. S., Bar R. S., Archer J. A., Gorden P., Martin M. M., Roth J. The syndromes of insulin resistance and acanthosis nigricans. Insulin-receptor disorders in man. N Engl J Med. 1976 Apr 1;294(14):739–745. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197604012941401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R. Membrane receptors for hormones and neurotransmitters. J Cell Biol. 1976 Aug;70(2 Pt 1):261–286. doi: 10.1083/jcb.70.2.261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasuga M., Kahn C. R., Hedo J. A., Van Obberghen E., Yamada K. M. Insulin-induced receptor loss in cultured human lymphocytes is due to accelerated receptor degradation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6917–6921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasuga M., Karlsson F. A., Kahn C. R. Insulin stimulates the phosphorylation of the 95,000-dalton subunit of its own receptor. Science. 1982 Jan 8;215(4529):185–187. doi: 10.1126/science.7031900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasuga M., Zick Y., Blithe D. L., Crettaz M., Kahn C. R. Insulin stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation of the insulin receptor in a cell-free system. Nature. 1982 Aug 12;298(5875):667–669. doi: 10.1038/298667a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasuga M., van Obberghen E., Yamada K. M., Harrison L. C. Autoantibodies against the insulin receptor recognize the insulin binding subunits of an oligomeric receptor. Diabetes. 1981 Apr;30(4):354–357. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.4.354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krebs E. G., Beavo J. A. Phosphorylation-dephosphorylation of enzymes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:923–959. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.004423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Cam A., Freychet P. Neutral amino acid transport. Characterization of the A and L systems in isolated rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jan 10;252(1):148–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilch P. F., Czech M. P. Interaction of cross-linking agents with the insulin effector system of isolated fat cells. Covalent linkage of 125I-insulin to a plasma membrane receptor protein of 140,000 daltons. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 10;254(9):3375–3381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proia R. L., Wray S. K., Hart D. A., Eidels L. Characterization and affinity labeling of the cationic phosphate-binding (nucleotide-binding) peptide located in the receptor-binding region of the B-fragment of diphtheria toxin. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):12025–12033. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds F. H., Jr, Todaro G. J., Fryling C., Stephenson J. R. Human transforming growth factors induce tyrosine phosphorylation of EGF receptors. Nature. 1981 Jul 16;292(5820):259–262. doi: 10.1038/292259a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teichberg V. I., Sobel A., Changeux J. P. In vitro phosphorylation of the acetylcholine receptor. Nature. 1977 Jun 9;267(5611):540–542. doi: 10.1038/267540a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Obberghen E., Kahn C. R. Autoantibodies to insulin receptors. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1981 Jun;22(3):277–293. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(81)90037-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Obberghen E., Kowalski A. Phosphorylation of the hepatic insulin receptor: stimulating effect of insulin on intact cells and in a cell-free system. FEBS Lett. 1982 Jul 5;143(2):179–182. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80094-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Obberghen E., Ksauga M., Le Cam A., Hedo J. A., Itin A., Harrison L. C. Biosynthetic labeling of insulin receptor: studies of subunits in cultured human IM-9 lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1052–1056. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisher M. H., Baron M. D., Jones R. H., Sönksen P. H. Photoreactive insulin analogues used to characterise the insulin receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Jan 29;92(2):492–498. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90360-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yip C. C., Yeung C. W., Moule M. L. Photoaffinity labeling of insulin receptor of rat adiopocyte plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 1978 Mar 25;253(6):1743–1745. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]