Abstract
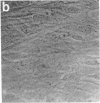
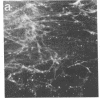
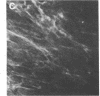
Thrombospondin, a major glycoprotein released from alpha granules of thrombin-stimulated platelets, is a disulfide-bonded trimer of 160-kilodalton subunits. Cultured human foreskin and fetal lung fibroblasts secreted thrombospondin (determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) into the culture medium in a time-dependent manner (15.7 and 5.8 micrograms per 10(6) cells per 24 hr, respectively); secretion was blocked by cycloheximide. [3H]Thrombospondin was isolated from [3H]leucine-labeled fibroblast postculture medium and from cell layers with rabbit polyclonal or mouse monoclonal anti-thrombospondin coupled to staphylococcal protein A-Sepharose. The immunologically isolated [3H]thrombospondin migrated in NaDodSO4/polyacrylamide gels with purified marker platelet thrombospondin both with and without reduction. Immunofluorescence microscopy using rabbit polyclonal and mouse monoclonal anti-thrombospondin antibodies localized thrombospondin to the fibrillar extracellular matrix surrounding the cells. Thus, cultured human fibroblasts secrete thrombospondin and incorporate it into the extracellular matrix.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alitalo K., Vaheri A., Krieg T., Timpl R. Biosynthesis of two subunits of type IV procollagen and of other basement membrane proteins by a human tumor cell line. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Aug;109(1):247–255. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04790.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baenziger N. L., Brodie G. N., Majerus P. W. A thrombin-sensitive protein of human platelet membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jan;68(1):240–243. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.1.240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baenziger N. L., Brodie G. N., Majerus P. W. Isolation and properties of a thrombin-sensitive protein of human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1972 May 10;247(9):2723–2731. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornstein P., Ash J. F. Cell surface-associated structural proteins in connective tissue cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jun;74(6):2480–2484. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.6.2480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter W. G., Hakomori S. A new cell surface, detergent-insoluble glycoprotein matrix of human and hamster fibroblasts. The role of disulfide bonds in stabilization of the matrix. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 10;256(13):6953–6960. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter W. G. The cooperative role of the transformation-sensitive glycoproteins, GP140 and fibronectin, in cell attachment and spreading. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):3249–3257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartner T. K., Gerrard J. M., White J. G., Williams D. C. Fibrinogen is the receptor for the endogenous lectin of human platelets. Nature. 1981 Feb 19;289(5799):688–690. doi: 10.1038/289688a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartner T. K., Gerrard J. M., White J. G., Williams D. C. The endogenous lectin of human platelets is an alpha-granule component. Blood. 1981 Jul;58(1):153–157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartner T. K., Phillips D. R., Williams D. C. Expression of thrombin-enhanced platelet lectin activity is controlled by secretion. FEBS Lett. 1980 May 5;113(2):196–199. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80590-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartner T. K., Williams D. C., Minion F. C., Phillips D. R. Thrombin-induced platelet aggregation is mediated by a platelet plasma membrane-bound lectin. Science. 1978 Jun 16;200(4347):1281–1283. doi: 10.1126/science.663608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartner T. K., Williams D. C., Phillips D. R. Platelet plasma membrane lectin activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Nov 21;79(2):592–599. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90198-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George J. N., Lyons R. M., Morgan R. K. Membrane changes associated with platelet activation. Exposure of actin on the platelet surface after thrombin-induced secretion. J Clin Invest. 1980 Jul;66(1):1–9. doi: 10.1172/JCI109821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George J. N. Studies on platelet plasma membranes. IV. Quantitative analysis of platelet membrane glycoproteins by (125I)-diazotized diiodosulfanilic acid labeling and SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Lab Clin Med. 1978 Sep;92(3):430–446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagen I. Effects of thrombin on washed, human platelets: changes in the subcellular fractions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jun 12;392(2):242–254. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(75)90006-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagen I., Olsen T., Solum N. O. Studies on subcellular fractions of human platelets by the lactoperoxidase-iodination technique. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Nov 11;455(1):214–225. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90165-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayman E. G., Oldberg A., Martin G. R., Ruoslahti E. Codistribution of heparan sulfate proteoglycan, laminin, and fibronectin in the extracellular matrix of normal rat kidney cells and their coordinate absence in transformed cells. J Cell Biol. 1982 Jul;94(1):28–35. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.1.28. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayman E. G., Ruoslahti E. Distribution of fetal bovine serum fibronectin and endogenous rat cell fibronectin in extracellular matrix. J Cell Biol. 1979 Oct;83(1):255–259. doi: 10.1083/jcb.83.1.255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedman K., Johansson S., Vartio T., Kjellén L., Vaheri A., Hök M. Structure of the pericellular matrix: association of heparan and chondroitin sulfates with fibronectin-procollagen fibers. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):663–671. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90221-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe E. A., Leung L. L., Nachman R. L., Levin R. I., Mosher D. F. Thrombospondin is the endogenous lectin of human platelets. Nature. 1982 Jan 21;295(5846):246–248. doi: 10.1038/295246a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe E. A., Mosher D. F. Synthesis of fibronectin by cultured human endothelial cells. J Exp Med. 1978 Jun 1;147(6):1779–1791. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.6.1779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe E. A., Nachman R. L., Becker C. G., Minick C. R. Culture of human endothelial cells derived from umbilical veins. Identification by morphologic and immunologic criteria. J Clin Invest. 1973 Nov;52(11):2745–2756. doi: 10.1172/JCI107470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jilek F., Hörmann H. Fibronectin (cold-insoluble globulin), VI. Influence of heparin and hyaluronic acid on the binding of native collagen. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1979 Apr;360(4):597–603. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1979.360.1.597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson S., Hök M. Heparin enhances the rate of binding of fibronectin to collagen. Biochem J. 1980 May 1;187(2):521–524. doi: 10.1042/bj1870521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):495–497. doi: 10.1038/256495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawler J. W., Chao F. C., Fang P. H. Observation of a high molecular weight platelet protein released by thrombin. Thromb Haemost. 1977 Apr 30;37(2):355–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawler J. W., Slayter H. S., Coligan J. E. Isolation and characterization of a high molecular weight glycoprotein from human blood platelets. J Biol Chem. 1978 Dec 10;253(23):8609–8616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung L. L., Nachman R. L. Complex formation of platelet thrombospondin with fibrinogen. J Clin Invest. 1982 Sep;70(3):542–549. doi: 10.1172/JCI110646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margossian S. S., Lawler J. W., Slayter H. S. Physical characterization of platelet thrombospondin. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 25;256(14):7495–7500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPherson J., Sage H., Bornstein P. Isolation and characterization of a glycoprotein secreted by aortic endothelial cells in culture. Apparent identity with platelet thrombospondin. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 10;256(21):11330–11336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosher D. F., Doyle M. J., Jaffe E. A. Synthesis and secretion of thrombospondin by cultured human endothelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1982 May;93(2):343–348. doi: 10.1083/jcb.93.2.343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosher D. F. Fibronectin. Prog Hemost Thromb. 1980;5:111–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins M. E., Ji T. H., Hynes R. O. Cross-linking of fibronectin to sulfated proteoglycans at the cell surface. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):941–952. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90109-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips D. R., Jennings L. K., Prasanna H. R. Ca2+-mediated association of glycoprotein G (thrombinsensitive protein, thrombospondin) with human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):11629–11632. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E., Engvall E. Complexing of fibronectin glycosaminoglycans and collagen. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Aug 13;631(2):350–358. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(80)90308-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E., Vaheri A., Kuusela P., Linder E. Fibroblast surface antigen: a new serum protein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Oct 18;322(2):352–358. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(73)90310-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakashita S., Engvall E., Ruoslahti E. Basement membrane glycoprotein laminin binds to heparin. FEBS Lett. 1980 Jul 28;116(2):243–246. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80654-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terranova V. P., Rohrbach D. H., Martin G. R. Role of laminin in the attachment of PAM 212 (epithelial) cells to basement membrane collagen. Cell. 1980 Dec;22(3):719–726. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90548-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaheri A., Kurkinen M., Lehto V. P., Linder E., Timpl R. Codistribution of pericellular matrix proteins in cultured fibroblasts and loss in transformation: fibronectin and procollagen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4944–4948. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada K. M., Yamada S. S., Pastan I. The major cell surface glycoprotein of chick embryo fibroblasts is an agglutinin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):3158–3162. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.3158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young B. R., Doyle M. J., Collins W. E., Lambrecht L. K., Jordan C. A., Albrecht R. M., Mosher D. F., Cooper S. L. Effect of thrombospondin and other platelet alpha-granule proteins on artificial surface-induced thrombosis. Trans Am Soc Artif Intern Organs. 1982;28:498–503. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]