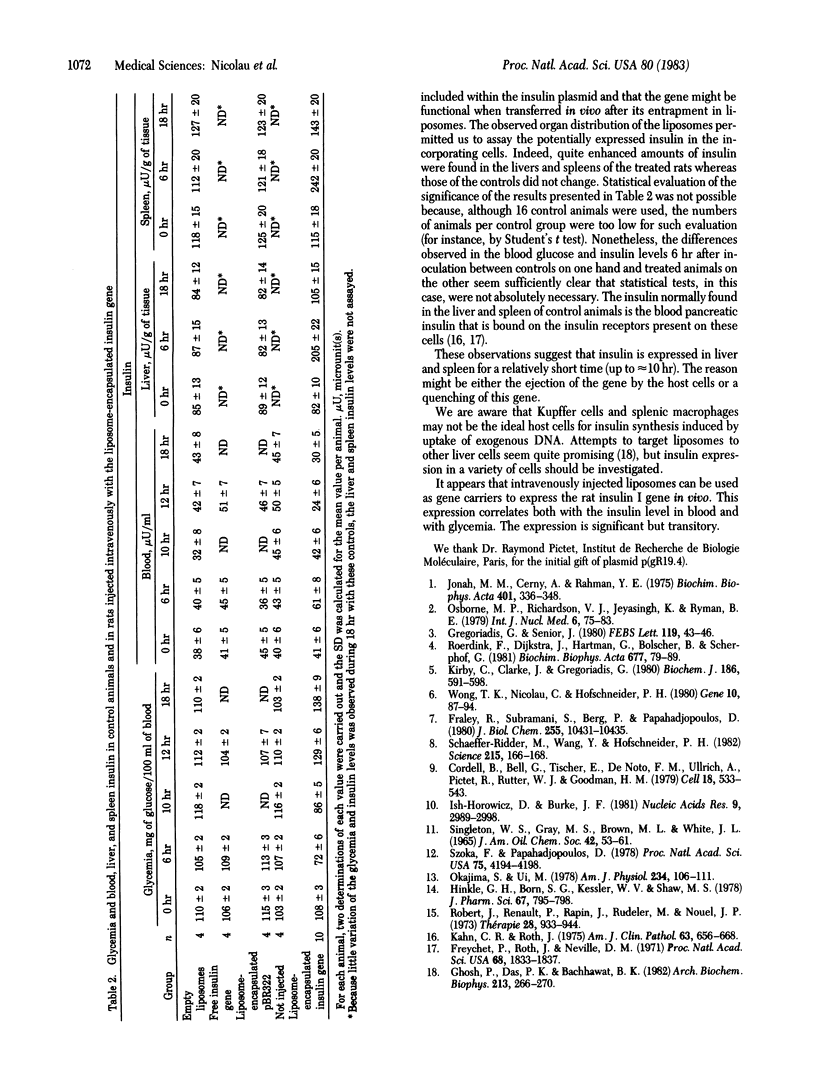
Abstract
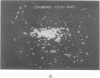
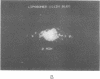
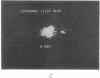
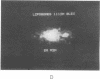
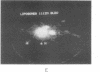
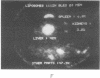
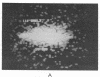
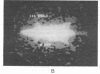
A recombinant plasmid encoding rat preproinsulin I was encapsulated in large liposomes and intravenously injected in rats. Glycemia and blood, splenic, and hepatic insulin were assayed at various times beginning 6 hr after inoculation. The results were compared with controls that had received (i) empty liposomes, (ii) liposomes carrying the Escherichia coli pBR322 plasmid, (iii) the free rat insulin I gene, and (iv) no injection at all. Whereas all controls showed unchanged glucose and insulin levels, the treated animals had, 6 hr after inoculation, a blood glucose level of 72 +/- 5 mg of glucose/100 ml of blood as compared with 107 +/- 2 mg/ml for controls. Radioimmunoassay of blood insulin gave 61 +/- 8 microunits/ml as compared with 43 +/- 5 microunits/ml for controls and the spleen and liver values were 242 +/- 22 and 204 +/- 20 microunits/g of tissue, respectively, as compared with 112 +/- 20 and 87 +/- 15 microunits/g in controls. External gamma-camera imaging of the organ uptake of 111In-labeled liposomes permitted study of the kinetics and extent of uptake of the liposomes by spleen and liver, results that support the findings concerning insulin synthesis in the two organs.
Full text
PDF
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cordell B., Bell G., Tischer E., DeNoto F. M., Ullrich A., Pictet R., Rutter W. J., Goodman H. M. Isolation and characterization of a cloned rat insulin gene. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):533–543. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90070-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraley R., Subramani S., Berg P., Papahadjopoulos D. Introduction of liposome-encapsulated SV40 DNA into cells. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 10;255(21):10431–10435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freychet P., Roth J., Neville D. M., Jr Insulin receptors in the liver: specific binding of ( 125 I)insulin to the plasma membrane and its relation to insulin bioactivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Aug;68(8):1833–1837. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.8.1833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregoriadis G., Senior J. The phospholipid component of small unilamellar liposomes controls the rate of clearance of entrapped solutes from the circulation. FEBS Lett. 1980 Sep 22;119(1):43–46. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80994-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinkle G. H., Born G. S., Kessler W., Shaw S. M. Preferential localization of radiolabeled liposomes in liver. J Pharm Sci. 1978 Jun;67(6):795–798. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600670617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ish-Horowicz D., Burke J. F. Rapid and efficient cosmid cloning. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):2989–2998. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.2989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonah M. M., Cerny E. A., Rahman Y. E. Tissue distribution of EDTA encapsulated within liposomes of varying surface properties. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Sep 2;401(3):336–348. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90234-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R., Roth J. Cell membrane receptors for polypeptide hormones. Application to the study of disease states in mice, and men. Am J Clin Pathol. 1975 May;63(5):656–667. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/63.5.656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirby C., Clarke J., Gregoriadis G. Effect of the cholesterol content of small unilamellar liposomes on their stability in vivo and in vitro. Biochem J. 1980 Feb 15;186(2):591–598. doi: 10.1042/bj1860591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborne M. P., Richardson V. J., Jeyasingh K., Ryman B. E. Radionuclide-labelled liposomes--a new lymph node imaging agent. Int J Nucl Med Biol. 1979;6(2):75–83. doi: 10.1016/0047-0740(79)90001-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robert J., Renault H., Rapin J., Rudler M., Nouel J. P. Métabolisme de la bléomycine marquée au cobalt 57 chez la souris. 1. Distribution et cinétique. Therapie. 1973 Sep-Oct;28(5):933–940. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roerdink F., Dijkstra J., Hartman G., Bolscher B., Scherphof G. The involvement of parenchymal, Kupffer and endothelial liver cells in the hepatic uptake of intravenously injected liposomes. Effects of lanthanum and gadolinium salts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Sep 18;677(1):79–89. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(81)90148-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SINGLETON W. S., GRAY M. S., BROWN M. L., WHITE J. L. CHROMATOGRAPHICALLY HOMOGENEOUS LECITHIN FROM EGG PHOSPHOLIPIDS. J Am Oil Chem Soc. 1965 Jan;42:53–56. doi: 10.1007/BF02558256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefer-Ridder M., Wang Y., Hofschneider P. H. Liposomes as gene carriers: efficient transformation of mouse L cells by thymidine kinase gene. Science. 1982 Jan 8;215(4529):166–168. doi: 10.1126/science.7053567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szoka F., Jr, Papahadjopoulos D. Procedure for preparation of liposomes with large internal aqueous space and high capture by reverse-phase evaporation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4194–4198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong T. K., Nicolau C., Hofschneider P. H. Appearance of beta-lactamase activity in animal cells upon liposome-mediated gene transfer. Gene. 1980 Jul;10(2):87–94. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90126-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]