Abstract
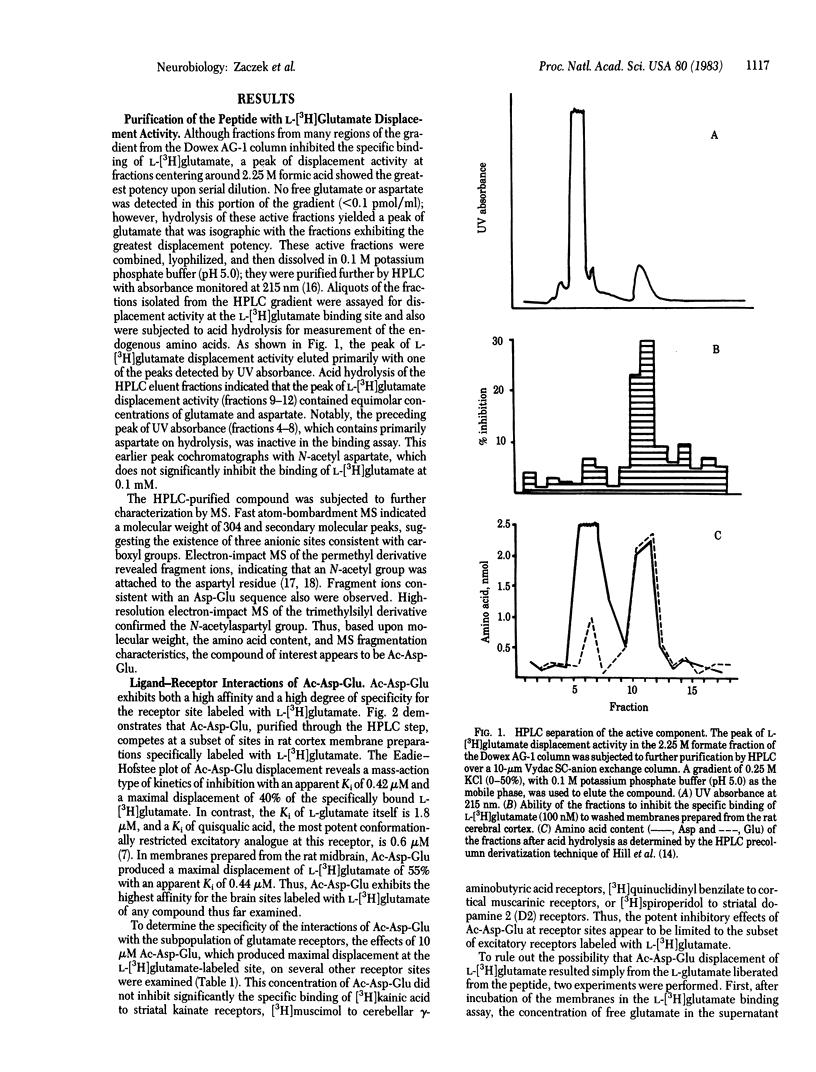
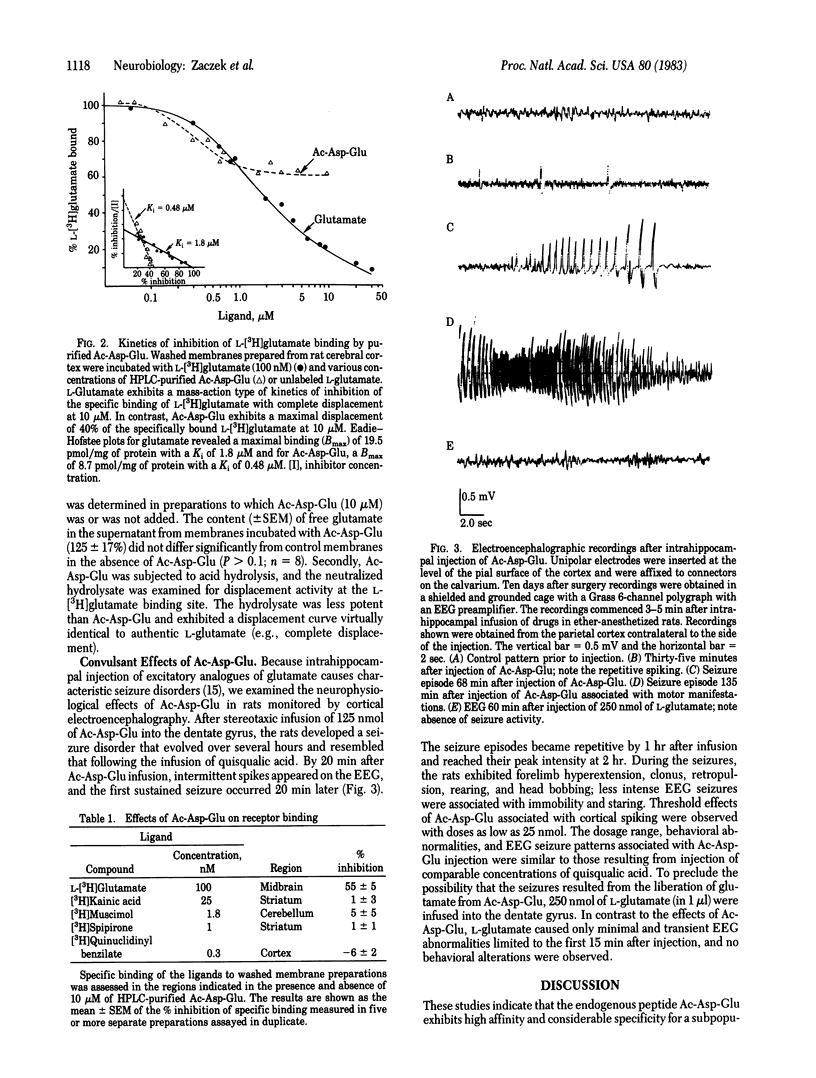
A brain peptide with high affinity (420 nM) and marked specificity for brain receptor sites labeled with L-[3H]glutamate has been identified. Amino acid analysis and mass spectroscopy indicate that the peptide is N-acetylaspartylglutamate. The peptide exhibits potent convulsant properties when injected into the rat hippocampus, similar to those produced by the glutamate receptor agonist, quisqualic acid. These findings raise the question whether endogenous brain peptides enriched in acidic amino acids may serve as excitatory neurotransmitters.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avoli M., Barra P. F., Brancati A., Cecchi L., Deodati M. Effetti degli acidi N-acetilaspartico ed N-acetilaspartilglutammico applicati iontoforeticamente in alcune strutture del nevrasse di ratto. Boll Soc Ital Biol Sper. 1976 Sep 30;52(18):1525–1530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balcar V. J., Johnston G. A. The structural specificity of the high affinity uptake of L-glutamate and L-aspartate by rat brain slices. J Neurochem. 1972 Nov;19(11):2657–2666. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1972.tb01325.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baudry M., Lynch G. Characterization of two [3H]glutamate binding sites in rat hippocampal membranes. J Neurochem. 1981 Mar;36(3):811–820. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1981.tb01666.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaumont K., Chilton W. S., Yamamura H. I., Enna S. J. Muscimol binding in rat brain: association with synaptic GABA receptors. Brain Res. 1978 Jun 9;148(1):153–162. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CURATOLO A., D ARCANGELO P., LINO A., BRANCATI A. DISTRIBUTION OF N-ACETYL-ASPARTIC AND N-ACETYL-ASPARTYL-GLUTAMIC ACIDS IN NERVOUS TISSUE. J Neurochem. 1965 Apr;12:339–342. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1965.tb06771.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis D. R., Johnston G. A. Amino acid transmitters in the mammalian central nervous system. Ergeb Physiol. 1974;69(0):97–188. doi: 10.1007/3-540-06498-2_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster A. C., Roberts P. J. High affinity l-[3h]glutamate binding to postsynaptic receptor sites on rat cerebellar membranes. J Neurochem. 1978 Dec;31(6):1467–1477. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1978.tb06574.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill D. W., Walters F. H., Wilson T. D., Stuart J. D. High performance liquid chromatographic determination of amino acids in the picomole range. Anal Chem. 1979 Jul;51(8):1338–1341. doi: 10.1021/ac50044a055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hori N., Auker C. R., Braitman D. J., Carpenter D. O. Lateral olfactory tract transmitter: glutamate, aspartate, or neither? Cell Mol Neurobiol. 1981 Mar;1(1):115–120. doi: 10.1007/BF00736043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanazawa I., Sutoo D. Decrease of a peptide in the cat spinal cord after upper cervical transection. Neurosci Lett. 1981 Oct 23;26(2):113–117. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(81)90335-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laduron P. M., Janssen P. F., Leysen J. E. Spiperone: a ligand of choice for neuroleptic receptors. 3. Subcellular distribution of neuroleptic drugs and their receptors in various rat brain areas. Biochem Pharmacol. 1978 Feb 1;27(3):323–328. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(78)90235-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- London E. D., Coyle J. T. Specific binding of [3H]kainic acid to receptor sites in rat brain. Mol Pharmacol. 1979 May;15(3):492–505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyake M., Kakimoto Y., Sorimachi M. A gas chromatographic method for the determination of N-acetyl-L-aspartic acid, N-acetyl-alpha-aspartylglutamic acid and beta-citryl-L-glutamic acid and their distributions in the brain and other organs of various species of animals. J Neurochem. 1981 Mar;36(3):804–810. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1981.tb01665.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichelt K. L., Fonnum F. Subcellular localization of N-acetyl-aspartyl-glutamate, N-acetyl-glutamate and glutathione in brain. J Neurochem. 1969 Sep;16(9):1409–1416. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1969.tb05993.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiells R. A., Falk G., Naghshineh S. Action of glutamate and aspartate analogues on rod horizontal and bipolar cells. Nature. 1981 Dec 10;294(5841):592–594. doi: 10.1038/294592a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slevin J. T., Coyle J. T. Ontogeny of receptor binding sites for [3H]glutamic acid and [3H]kainic acid in the rat cerebellum. J Neurochem. 1981 Aug;37(2):531–533. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1981.tb00491.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slevin J., Collins J., Lindsley K., Coyle J. T. Specific binding of [3H]L-glutamate to cerebellar membranes: evidence for recognition site heterogeneity. Brain Res. 1982 Oct 14;249(2):353–360. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90069-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins J. C., Evans R. H. Excitatory amino acid transmitters. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1981;21:165–204. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.21.040181.001121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamura H. I., Snyder S. H. Muscarinic cholinergic binding in rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 May;71(5):1725–1729. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.5.1725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaczek R., Coyle J. T. Excitatory amino acid analogues: neurotoxicity and seizures. Neuropharmacology. 1982 Jan;21(1):15–26. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(82)90205-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


