Abstract
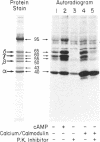
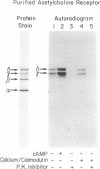
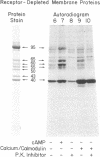
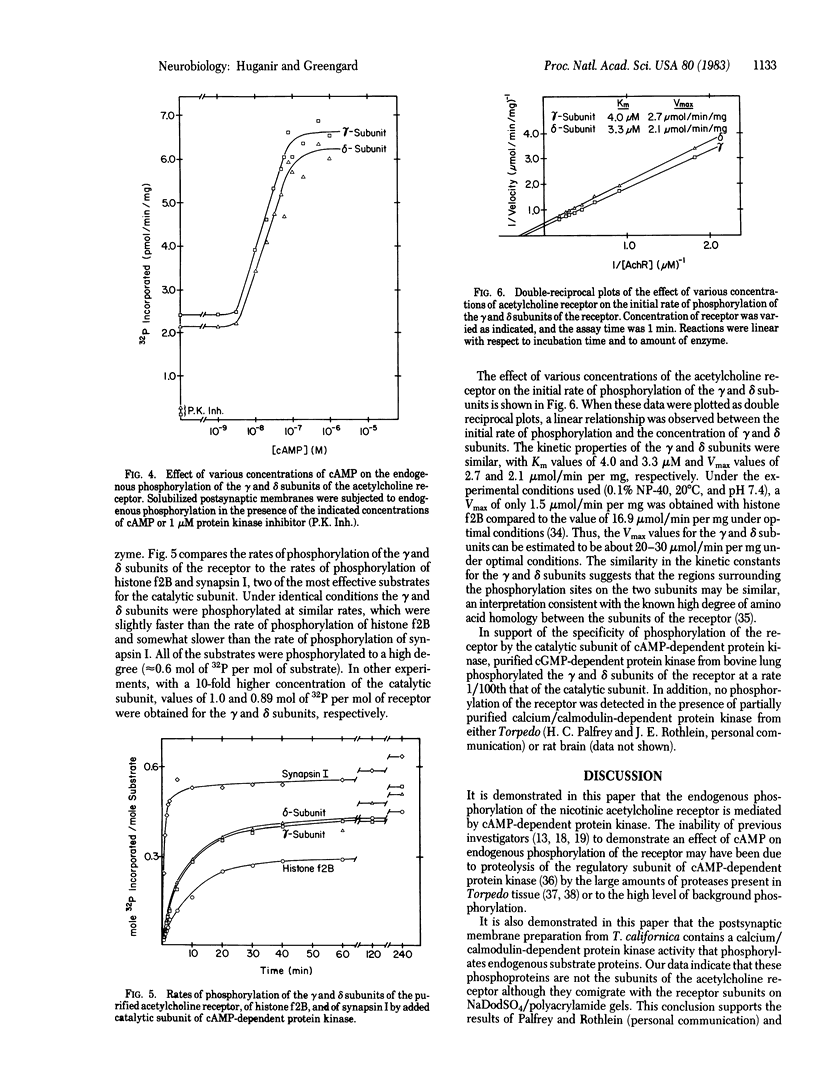
Postsynaptic membranes, rich in the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor, were isolated from the electric organ of Torpedo californica and shown to contain a cAMP-dependent protein kinase and a calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase. The cAMP-dependent protein kinase phosphorylated the γ and δ subunits of the acetylcholine receptor. The phosphorylated subunits were identified after purification of the acetylcholine receptor by affinity chromatography on a choline carboxymethyl affinity gel. In contrast, the calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase phosphorylated proteins that were separated from the acetylcholine receptor by affinity chromatography. Protein kinase inhibitor, a specific inhibitor of the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase, abolished the basal endogenous phosphorylation of the γ and δ subunits of the receptor. cAMP activation of the endogenous phosphorylation of the γ and δ subunits was dose dependent with a half-maximal response at 25 nM. Studies were also carried out with acetylcholine receptor purified from T. californica and catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase purified from bovine heart. The purified acetylcholine receptor was rapidly and specifically phosphorylated on the γ and δ subunits by the purified catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase to a stoichiometry of 1.0 and 0.89 mol of 32P per mol of receptor, respectively. The initial rates of phosphorylation of the γ and δ subunits of the receptor were comparable to those of histone f2B and synapsin I (protein I), two of the most effective substrates for the catalytic subunit. Under the conditions used, the γ and δ subunits had Km values of 4.0 and 3.3 μM and Vmax values of 2.7 and 2.1 μmol/min per mg, respectively. The results are consistent with the idea that the acetylcholine receptor is phosphorylated in vivo by a cAMP-dependent protein kinase.
Keywords: membrane channel, calmodulin, calcium
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brockes J. P., Berg D. K., Hall Z. W. The biochemical properties and regulation of acetylcholine receptors in normal and denervated muscle. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1976;40:253–262. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1976.040.01.026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Changeux J. P. The acetylcholine receptor: an "allosteric" membrane protein. Harvey Lect. 1979 1980;75:85–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis C. G., Gordon A. S., Diamond I. Specificity and localization of the acetylcholine receptor kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(11):3666–3670. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.11.3666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duguid J. R., Raftery M. A. Fractionation and partial characterization of membrane particles from Torpedo californica electroplax. Biochemistry. 1973 Sep 11;12(19):3593–3597. doi: 10.1021/bi00743a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eldefrawi M. E., Eldefrawi A. T. Purification and molecular properties of the acetylcholine receptor from Torpedo electroplax. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Nov;159(1):362–373. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(73)90462-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein M., Racker E. Reconstitution of carbamylcholine-dependent sodium ion flux and desensitization of the acetylcholine receptor from Torpedo californica. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 10;253(19):6660–6662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froehner S. C., Rafto S. Comparison of the subunits of Torpedo californica acetylcholine receptor by peptide mapping. Biochemistry. 1979 Jan 23;18(2):301–307. doi: 10.1021/bi00569a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass D. B., Krebs E. G. Comparison of the substrate specificity of adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate- and guanosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinases. Kinetic studies using synthetic peptides corresponding to phosphorylation sites in histone H2B. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 10;254(19):9728–9738. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon A. S., Davis C. G., Diamond I. Phosphorylation of membrane proteins at a cholinergic synapse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jan;74(1):263–267. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.1.263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon A. S., Davis C. G., Milfay D., Diamond I. Phosphorylation of acetylcholine receptor by endogenous membrane protein kinase in receptor-enriched membranes of Torpedo californica. Nature. 1977 Jun 9;267(5611):539–540. doi: 10.1038/267539a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon A. S., Milfay D., Davis C. G., Diamond I. Protein phosphatase activity in acetylcholine receptor-enriched membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Apr 13;87(3):876–883. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)92039-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grand R. J., Perry S. V., Weeks R. A. Troponin C-like proteins (calmodulins) from mammalian smooth muscle and other tissues. Biochem J. 1979 Feb 1;177(2):521–529. doi: 10.1042/bj1770521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greengard P. Phosphorylated proteins as physiological effectors. Science. 1978 Jan 13;199(4325):146–152. doi: 10.1126/science.22932. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greengard P. Possible role for cyclic nucleotides and phosphorylated membrane proteins in postsynaptic actions of neurotransmitters. Nature. 1976 Mar 11;260(5547):101–108. doi: 10.1038/260101a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartig P. R., Raftery M. A. Preparation of right-side-out, acetylcholine receptor enriched intact vesicles from Torpedo californica electroplaque membranes. Biochemistry. 1979 Apr 3;18(7):1146–1150. doi: 10.1021/bi00574a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang L. C., Huang C. Rabbit skeletal muscle protein kinase. Conversion from cAMP dependent to independent form by chemical perturbations. Biochemistry. 1975 Jan 14;14(1):18–24. doi: 10.1021/bi00672a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huganir R. L., Racker E. Endogenous and exogenous proteolysis of the acetylcholine receptor from Torpedo californica. J Supramol Struct. 1980;14(1):13–19. doi: 10.1002/jss.400140103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huganir R. L., Racker E. Properties of proteoliposomes reconstituted with acetylcholine receptor from Torpedo californica. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 25;257(16):9372–9378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaczmarek L. K., Jennings K. R., Strumwasser F., Nairn A. C., Walter U., Wilson F. D., Greengard P. Microinjection of catalytic subunit of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase enhances calcium action potentials of bag cell neurons in cell culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7487–7491. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlin A., Cowburn D. The affinity-labeling of partially purified acetylcholine receptor from electric tissue of Electrophorus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3636–3640. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. The statistical nature of the acetycholine potential and its molecular components. J Physiol. 1972 Aug;224(3):665–699. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPherson J. M., Whitehouse S., Walsh D. A. Possibility of shape conformers of the protein inhibitor of the cyclic adenosine monophosphate dependent protein kinase. Biochemistry. 1979 Oct 30;18(22):4835–4845. doi: 10.1021/bi00589a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E., Sakmann B. Single-channel currents recorded from membrane of denervated frog muscle fibres. Nature. 1976 Apr 29;260(5554):799–802. doi: 10.1038/260799a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):346–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raftery M. A., Hunkapiller M. W., Strader C. D., Hood L. E. Acetylcholine receptor: complex of homologous subunits. Science. 1980 Jun 27;208(4451):1454–1456. doi: 10.1126/science.7384786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rephaeli A., Parsons S. M. Calmodulin stimulation of 45Ca2+ transport and protein phosphorylation in cholinergic synaptic vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):5783–5787. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.5783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds J. A., Karlin A. Molecular weight in detergent solution of acetylcholine receptor from Torpedo californica. Biochemistry. 1978 May 30;17(11):2035–2038. doi: 10.1021/bi00604a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saitoh T., Changeux J. P. Change in state of phosphorylation of acetylcholine receptor during maturation of the electromotor synapse in Torpedo marmorata electric organ. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4430–4434. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saitoh T., Changeux J. P. Phosphorylation in vitro of membrane fragments from Torpedo marmorata electric organ. Effect on membrane solubilization by detergents. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Mar;105(1):51–62. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04473.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smilowitz H., Hadjian R. A., Dwyer J., Feinstein M. B. Regulation of acetylcholine receptor phosphorylation by calcium and calmodulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4708–4712. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teichberg V. I., Changeux J. P. Evidence for protein phosphorylation and dephosphorylation in membrane fragments isolated from the electric organ of Electrophorus electricus. FEBS Lett. 1977 Feb 15;74(1):71–76. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80755-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda T., Greengard P. Adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-regulated phosphoprotein system of neuronal membranes. I. Solubilization, purification, and some properties of an endogenous phosphoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jul 25;252(14):5155–5163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandlen R. L., Wu W. C., Eisenach J. C., Raftery M. A. Studies of the composition of purified Torpedo californica acetylcholine receptor and of its subunits. Biochemistry. 1979 May 15;18(10):1845–1854. doi: 10.1021/bi00577a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter U., Miller P., Wilson F., Menkes D., Greengard P. Immunological distinction between guanosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent and adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1980 Apr 25;255(8):3757–3762. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wennogle L. P., Changeux J. P. Transmembrane orientation of proteins present in acetylcholine receptor-rich membranes from Torpedo marmorata studied by selective proteolysis. Eur J Biochem. 1980 May;106(2):381–393. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04584.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]