Abstract
Many peptides and proteins that act at lipid--water interfaces assume a unique amphiphilic secondary structure which is induced by the anisotropy of the interface. By using synthetic peptides in which these inducible amphiphilic structures have been optimized, one can show that the amphiphilic alpha helix is a functional determinant of representative apolipoproteins, peptide toxins, and peptide hormones. By increasing the amphiphilicity of the structurally important regions of the molecule, one can enhance the biological activity of the peptide even beyond that of the naturally occurring polypeptide. It is proposed that rigid amphiphilic secondary structures such as alpha helix, beta sheet, or pi helix will be found in most medium-sized peptides acting at membranes and lipid--water interfaces.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Batzri S., Korn E. D. Single bilayer liposomes prepared without sonication. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Apr 16;298(4):1015–1019. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90408-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Empirical predictions of protein conformation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:251–276. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.001343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeGrado W. F., Musso G. F., Lieber M., Kaiser E. T., Kézdy F. J. Kinetics and mechanism of hemolysis induced by melittin and by a synthetic melittin analogue. Biophys J. 1982 Jan;37(1):329–338. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(82)84681-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelstein C., Kézdy F. J., Scanu A. M., Shen B. W. Apolipoproteins and the structural organization of plasma lipoproteins: human plasma high density lipoprotein-3. J Lipid Res. 1979 Feb;20(2):143–153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitch W. M. Phylogenies constrained by the crossover process as illustrated by human hemoglobins and a thirteen-cycle, eleven-amino-acid repeat in human apolipoprotein A-I. Genetics. 1977 Jul;86(3):623–644. doi: 10.1093/genetics/86.3.623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukushima D., Yokoyama S., Kroon D. J., Kézdy F. J., Kaiser E. T. Chain length-function correlation of amphiphilic peptides. Synthesis and surface properties of a tetratetracontapeptide segment of apolipoprotein A-I. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 25;255(22):10651–10657. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukushima D., Yokoyama S., Kézdy F. J., Kaiser E. T. Binding of amphiphilic peptides to phospholipid/cholesterol unilamellar vesicles: a model for protein--cholesterol interaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2732–2736. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2732. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habermann E. Bee and wasp venoms. Science. 1972 Jul 28;177(4046):314–322. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4046.314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitt M., Chothia C. Structural patterns in globular proteins. Nature. 1976 Jun 17;261(5561):552–558. doi: 10.1038/261552a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiffer M., Edmundson A. B. Use of helical wheels to represent the structures of proteins and to identify segments with helical potential. Biophys J. 1967 Mar;7(2):121–135. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(67)86579-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröder E., Lübke K., Lehmann M., Beetz I. Haemolytic activity and action on the surface tension of aqueous solutions of synthetic melittins and their derivatives. Experientia. 1971 Jul;27(7):764–765. doi: 10.1007/BF02136851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segrest J. P., Jackson R. L., Morrisett J. D., Gotto A. M., Jr A molecular theory of lipid-protein interactions in the plasma lipoproteins. FEBS Lett. 1974 Jan 15;38(3):247–258. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80064-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
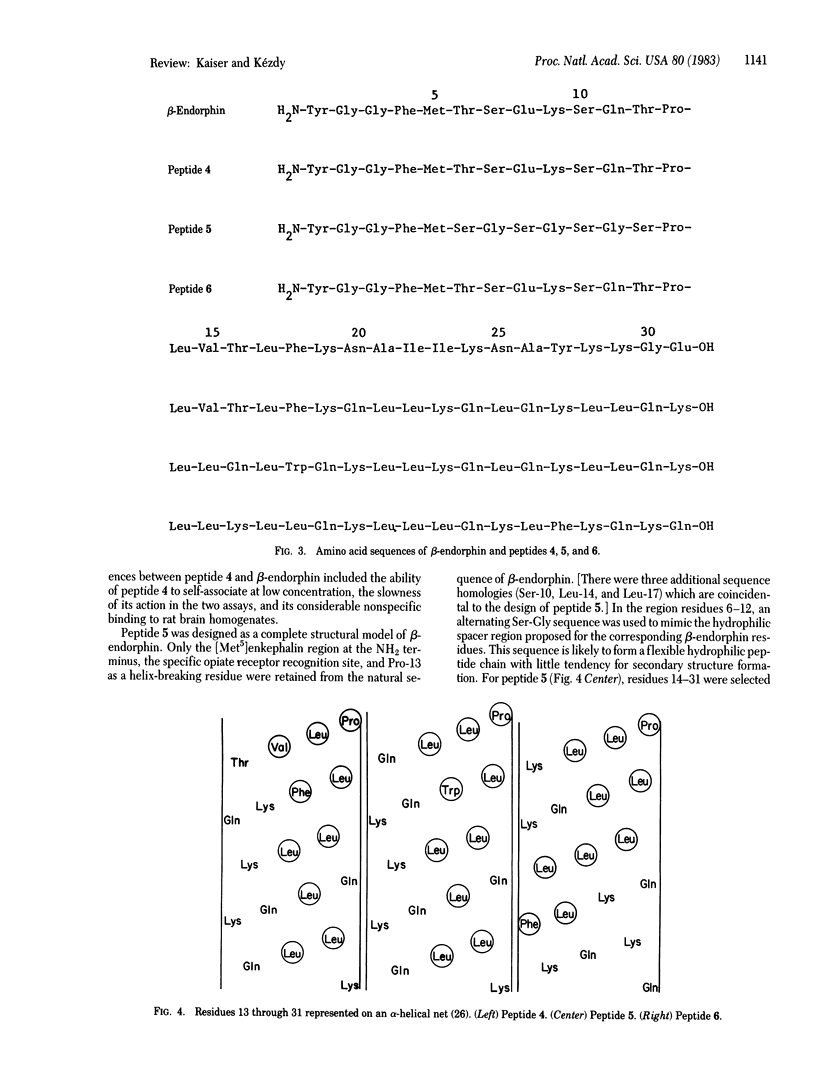
- Taylor J. W., Miller R. J., Kaiser E. T. Structural characterization of beta-endorphin through the design, synthesis, and study of model peptides. Mol Pharmacol. 1982 Nov;22(3):657–666. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terwilliger T. C., Weissman L., Eisenberg D. The structure of melittin in the form I crystals and its implication for melittin's lytic and surface activities. Biophys J. 1982 Jan;37(1):353–361. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(82)84683-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokoyama S., Fukushima D., Kupferberg J. P., Kézdy F. J., Kaiser E. T. The mechanism of activation of lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase by apolipoprotein A-I and an amphiphilic peptide. J Biol Chem. 1980 Aug 10;255(15):7333–7339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



