Abstract
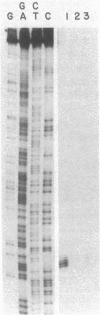
The first committed reaction in pyrimidine biosynthesis in Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium is catalyzed by the allosteric enzyme aspartate transcarbamoylase (aspartate carbamoyltransferase; carbamoylphosphate:L-aspartate carbamoyltransferase, EC 2.1.3.2), the product of the pyrB-pyrI operon. Regulation of the pyrimidine pathway is achieved in part by changes in the enzyme's catalytic activity as a function of the concentration of substrates and other metabolites as well as by variations in enzyme synthesis in response to changes in cellular levels of pyrimidine nucleotides. Although there is substantial evidence that UTP concentration has a marked influence on expression of the pyrB-pyrI operon, the mechanism of this control is not known. We have cloned the operon and determined the nucleotide sequence of the region preceding the first structural gene (pyrB). These studies show two regions sharing considerable homology with the consensus sequence of E. coli promoters, a segment that can code for a 44-amino-acid leader peptide, and a sequence very similar to that of the attenuator of the trp operon. RNA transcripts from several bacterial strains were studied by S1 nuclease mapping. Under conditions leading to extensive enzyme synthesis there was a large production of transcript whose 5' end correlated with the putative promoter closer to the structural genes. At low levels of operon expression there was little transcript in the extracts and both promoters appeared to serve as initiation sites. The results are interpreted in terms of transcriptional control of the pyrB-pyrI operon according to an attenuation model that differs in novel ways from the mechanisms proposed for the regulation of amino acid biosynthesis.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barry G., Squires C., Squires C. L. Attenuation and processing of RNA from the rplJL--rpoBC transcription unit of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3331–3335. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Spliced early mRNAs of simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1274–1278. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bethell M. R., Smith K. E., White J. S., Jones M. E. Carbamyl phosphate: an allosteric substrate for aspartate transcarbamylase of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Aug;60(4):1442–1449. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.4.1442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christie G. E., Farnham P. J., Platt T. Synthetic sites for transcription termination and a functional comparison with tryptophan operon termination sites in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4180–4184. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farnham P. J., Platt T. Rho-independent termination: dyad symmetry in DNA causes RNA polymerase to pause during transcription in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Feb 11;9(3):563–577. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.3.563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GERHART J. C., PARDEE A. B. The enzymology of control by feedback inhibition. J Biol Chem. 1962 Mar;237:891–896. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz H., Platt T. Identification of trp-p2, an internal promoter in the tryptophan operon of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1982 Apr 5;156(2):257–267. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90327-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenness D. D., Schachman H. K. Genetic characterization of the folding domains of the catalytic chains in aspartate transcarbamoylase. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 10;258(5):3266–3279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenness D. D., Schachman H. K. pryB mutations as suppressors of arginine auxotrophy in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jan;141(1):33–40. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.1.33-40.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen K. F., Neuhard J., Schack L. RNA polymerase involvement in the regulation of expression of Salmonella typhimurium pyr genes. Isolation and characterization of a fluorouracil-resistant mutant with high, constitutive expression of the pyrB and pyrE genes due to a mutation in rpoBC. EMBO J. 1982;1(1):69–74. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01126.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston H. M., Barnes W. M., Chumley F. G., Bossi L., Roth J. R. Model for regulation of the histidine operon of Salmonella. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):508–512. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Justesen J., Neuhard J. pyrR identical to pyrH in Salmonella typhimurium: control of expression of the pyr genes. J Bacteriol. 1975 Sep;123(3):851–854. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.3.851-854.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingston R. E., Chamberlin M. J. Pausing and attenuation of in vitro transcription in the rrnB operon of E. coli. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(3 Pt 2):523–531. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90394-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donovan G. A., Gerhart J. C. Isolation and partial characterization of regulatory mutants of the pyrimidine pathway in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1972 Mar;109(3):1085–1096. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.3.1085-1096.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pastra-Landis S. C., Foote J., Kantrowitz E. R. An improved colorimetric assay for aspartate and ornithine transcarbamylases. Anal Biochem. 1981 Dec;118(2):358–363. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90594-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauza C. D., Karels M. J., Navre M., Schachman H. K. Genes encoding Escherichia coli aspartate transcarbamoylase: the pyrB-pyrI operon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):4020–4024. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.4020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roof W. D., Foltermann K. F., Wild J. R. The organization and regulation of the pyrBI operon in E. coli includes a rho-independent attenuator sequence. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;187(3):391–400. doi: 10.1007/BF00332617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Court D. Regulatory sequences involved in the promotion and termination of RNA transcription. Annu Rev Genet. 1979;13:319–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.13.120179.001535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salser W., Gesteland R. F., Bolle A. In vitro synthesis of bacteriophage lysozyme. Nature. 1967 Aug 5;215(5101):588–591. doi: 10.1038/215588a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz M., Neuhard J. Control of expression of the pyr genes in Salmonella typhimurium: effects of variations in uridine and cytidine nucleotide pools. J Bacteriol. 1975 Mar;121(3):814–822. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.3.814-822.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. R., Calvo J. M. Nucleotide sequence of the E coli gene coding for dihydrofolate reductase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 May 24;8(10):2255–2274. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.10.2255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B., Reeder R. H. The nucleotide sequence of the initiation and termination sites for ribosomal RNA transcription in X. laevis. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):485–499. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stormo G. D., Schneider T. D., Gold L. M. Characterization of translational initiation sites in E. coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 11;10(9):2971–2996. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.9.2971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Syvanen J. M., Roth J. R. Structural genes for catalytic and regulatory subunits of aspartate transcarbamylase. J Mol Biol. 1973 May 25;76(3):363–378. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90510-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinoco I., Jr, Borer P. N., Dengler B., Levin M. D., Uhlenbeck O. C., Crothers D. M., Bralla J. Improved estimation of secondary structure in ribonucleic acids. Nat New Biol. 1973 Nov 14;246(150):40–41. doi: 10.1038/newbio246040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnbough C. L., Jr, Hicks K. L., Donahue J. P. Attenuation control of pyrBI operon expression in Escherichia coli K-12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(2):368–372. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler M. E., Yanofsky C. Pausing of RNA polymerase during in vitro transcription of the tryptophan operon leader region. Biochemistry. 1981 Jun 23;20(13):3738–3744. doi: 10.1021/bi00516a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanofsky C. Attenuation in the control of expression of bacterial operons. Nature. 1981 Feb 26;289(5800):751–758. doi: 10.1038/289751a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanofsky C., Horn V. Rifampin resistance mutations that alter the efficiency of transcription termination at the tryptophan operon attenuator. J Bacteriol. 1981 Mar;145(3):1334–1341. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.3.1334-1341.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]