Abstract
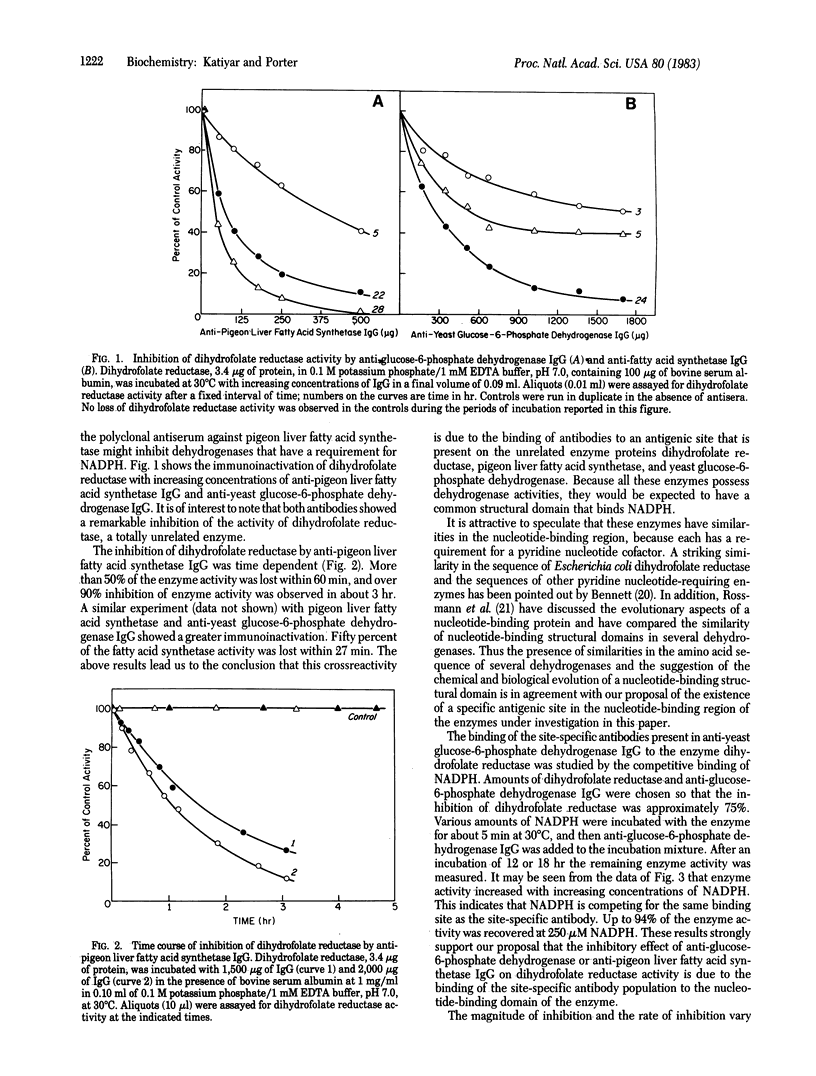
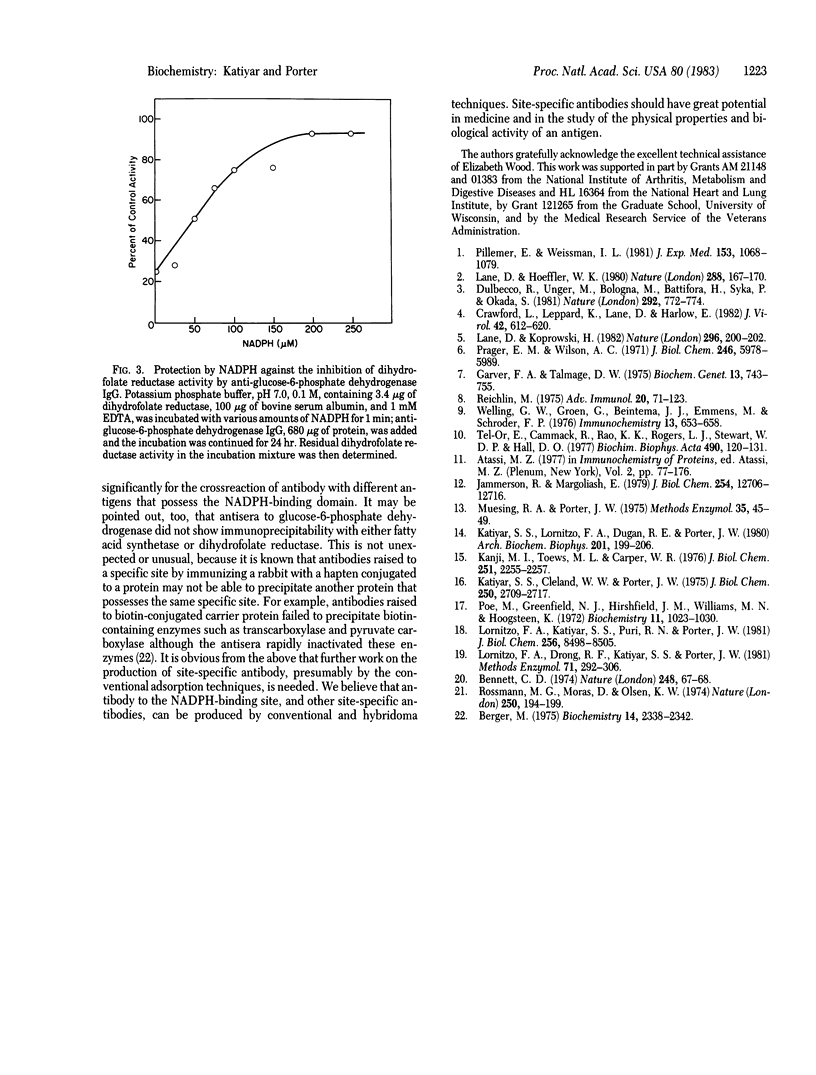
The results reported in this paper show the presence of a population of antibodies in rabbit polyclonal antiserum that recognize an antigenic site at the NADPH-binding region of enzymes possessing dehydrogenase activities. Antisera from rabbits immunized with glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase or fatty acid synthetase were found to inactivate the enzyme dihydrofolate reductase. The inhibitory effect of this site-specific antibody is a time- and concentration-dependent reaction. This immunoinactivation is prevented by preincubation of the enzyme with NADPH.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennett C. D. Similarity in the sequence of Escherichia coli dihydrofolate reductase with other pyridine nucleotide-requiring enzymes. Nature. 1974 Mar 1;248(5443):67–68. doi: 10.1038/248067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger M. Production of antibodies that bind biotin and inhibit biotin containing enzymes. Biochemistry. 1975 Jun 3;14(11):2338–2342. doi: 10.1021/bi00682a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford L., Leppard K., Lane D., Harlow E. Cellular proteins reactive with monoclonal antibodies directed against simian virus 40 T-antigen. J Virol. 1982 May;42(2):612–620. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.2.612-620.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dulbecco R., Unger M., Bologna M., Battifora H., Syka P., Okada S. Cross-reactivity between Thy-1 and a component of intermediate filaments demonstrated using a monoclonal antibody. Nature. 1981 Aug 20;292(5825):772–774. doi: 10.1038/292772a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garver F. A., Talmage D. W. Comparative immunochemical studies of primate hemoglobins. Biochem Genet. 1975 Dec;13(11-12):743–757. doi: 10.1007/BF00484406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jemmerson R., Margoliash E. Topographic antigenic determinants on cytochrome c. Immunoadsorbent separation of the rabbit antibody populations directed against horse cytochrome. J Biol Chem. 1979 Dec 25;254(24):12706–12716. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanji M. I., Toews M. L., Carper W. R. Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase. Purification and partial characterization. J Biol Chem. 1976 Apr 25;251(8):2255–2257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katiyar S. S., Cleland W. W., Porter J. W. Fatty acid synthetase. A steady state kinetic analysis of the reaction catalyzed by the enzyme from pigeon liver. J Biol Chem. 1975 Apr 10;250(7):2709–2717. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katiyar S. S., Lornitzo F. A., Dugan R. E., Porter J. W. Affinity purification of anti-pigeon liver fatty acid synthetase immunoglobulin and comparative immunoreactivity of the catalytic reactions. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1980 Apr 15;201(1):199–206. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(80)90503-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane D. P., Hoeffler W. K. SV40 large T shares an antigenic determinant with a cellular protein of molecular weight 68,000. Nature. 1980 Nov 13;288(5787):167–170. doi: 10.1038/288167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane D., Koprowski H. Molecular recognition and the future of monoclonal antibodies. Nature. 1982 Mar 18;296(5854):200–202. doi: 10.1038/296200a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lornitzo F. A., Drong R. F., Katiyar S. S., Porter J. W. Estimation of active and inactive forms of fatty acid synthase and acetyl-CoA carboxylase by immunotitration. Methods Enzymol. 1981;71(Pt 100):292–306. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(81)71038-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lornitzo F. A., Katiyar S. S., Puri R. N., Porter J. W. Demonstration of the occurrence of inactive fatty acid synthetase in rat liver by immunotitration and its in vitro partial activation. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 25;256(16):8498–8505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muesing R. A., Porter J. W. Fatty acid synthase from pigeon liver. Methods Enzymol. 1975;35:45–59. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(75)35137-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pillemer E., Weissman I. L. A monoclonal antibody that detects a V kappa-TEPC15 idiotypic determinant cross-reactive with a Thy-1 determinant. J Exp Med. 1981 May 1;153(5):1068–1079. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.5.1068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poe M., Greenfield N. J., Hirshfield J. M., Williams M. N., Hoogsteen K. Dihydrofolate reductase. Purification and characterization of the enzyme from an amethopterin-resistant mutant of Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1972 Mar 14;11(6):1023–1030. doi: 10.1021/bi00756a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prager E. M., Wilson A. C. The dependence of immunological cross-reactivity upon sequence resemblance among lysozymes. I. Micro-complement fixation studies. J Biol Chem. 1971 Oct 10;246(19):5978–5989. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichlin M. Amino acid substitution and the antigenicity of globular proteins. Adv Immunol. 1975;20:71–123. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60207-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossmann M. G., Moras D., Olsen K. W. Chemical and biological evolution of nucleotide-binding protein. Nature. 1974 Jul 19;250(463):194–199. doi: 10.1038/250194a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tel-Or E., Cammack R., Rao K. K., Rogers L. J., Stewart W. D., Hall D. O. Comparative immunochemistry of bacterial, algal and plant ferredoxins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Jan 25;490(1):120–131. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(77)90112-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welling G. W., Groen G., Beintema J. J., Emmens M., Schröder F. P. Immunologic comparison of pancreatic ribonucleases. Immunochemistry. 1976 Aug;13(8):653–658. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(76)90205-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


