Abstract
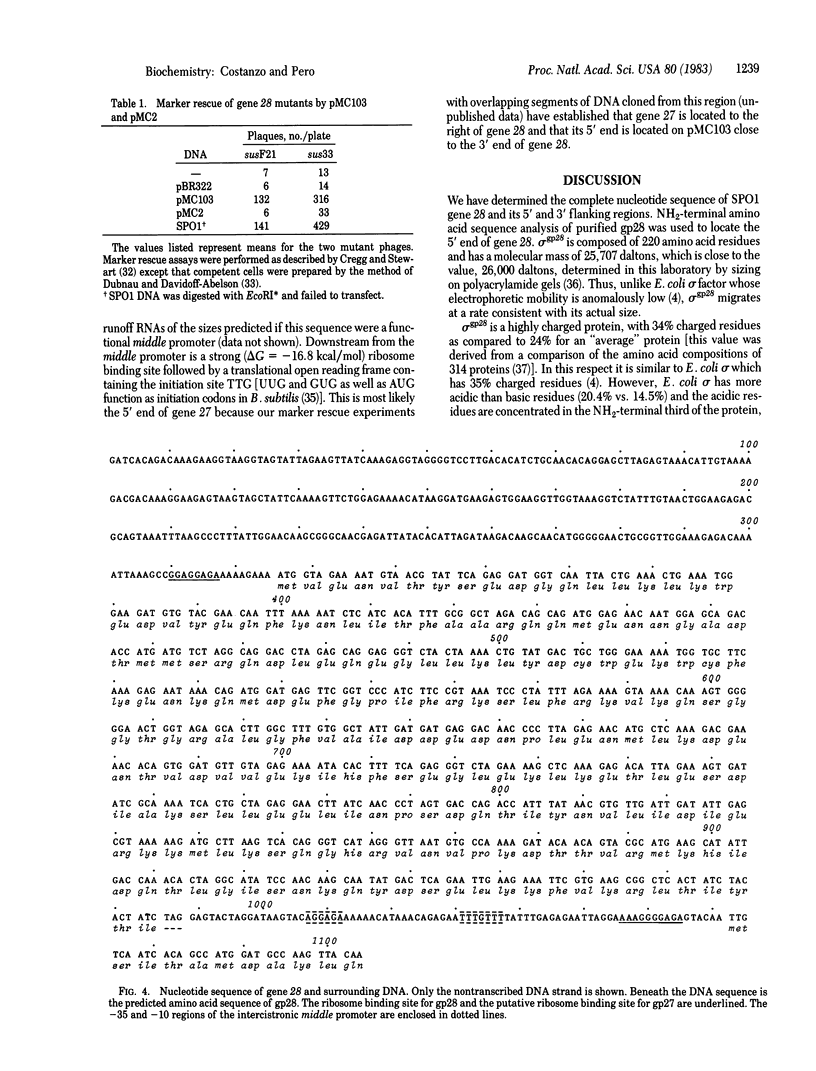
Gene 28 of Bacillus subtilis bacteriophage SPO1 codes for a regulatory protein, a sigma factor known as sigma gp28, that binds to the bacterial core RNA polymerase to direct the recognition of phage middle gene promoters. middle promoters exhibit distinctive and conserved nucleotide sequences in two regions centered about 10 and 35 base pairs upstream from the start point of mRNA synthesis. Here we report the cloning of gene 28 and its complete nucleotide sequence. We infer that sigma gp28 is a 25,707-dalton protein of 220 amino acids. Neither the nucleotide sequence of gene 28 nor the inferred amino acid sequence of sigma gp28 exhibits extensive homology to the gene or protein sequence of Escherichia coli sigma factor.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Achberger E. C., Whiteley H. R. The interaction of Escherichia coli core RNA polymerase with specificity-determining subunits derived from unmodified and SP82-modified Bacillus subtilis RNA polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):11957–11964. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkner K. L., Folk W. R. Polynucleotide kinase exchange reaction: quantitave assay for restriction endonuclease-generated 5'-phosphoroyl termini in DNA. J Biol Chem. 1977 May 25;252(10):3176–3184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton Z., Burgess R. R., Lin J., Moore D., Holder S., Gross C. A. The nucleotide sequence of the cloned rpoD gene for the RNA polymerase sigma subunit from E coli K12. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jun 25;9(12):2889–2903. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.12.2889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chelm B. K., Romeo J. M., Brennan S. M., Geiduschek E. P. A transcriptional map of the bacteriophage SPO1 genome. III. A region of early and middle promoters (the gene 28 region). Virology. 1981 Jul 30;112(2):572–588. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90303-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Prediction of the secondary structure of proteins from their amino acid sequence. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1978;47:45–148. doi: 10.1002/9780470122921.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cregg J. M., Stewart C. R. Terminal redundancy of "high frequency of recombination" markers of Bacillus subtilis phage SPO1. Virology. 1978 May 15;86(2):530–541. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90091-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubnau D., Davidoff-Abelson R. Fate of transforming DNA following uptake by competent Bacillus subtilis. I. Formation and properties of the donor-recipient complex. J Mol Biol. 1971 Mar 14;56(2):209–221. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90460-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duffy J. J., Geiduschek E. P. Purification of a positive regulatory subunit from phage SP01-modified RNA polymerase. Nature. 1977 Nov 3;270(5632):28–32. doi: 10.1038/270028a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox T. D., Losick R., Pero J. Regulatory gene 28 of bacteriophage SPO1 codes for a phage-induced subunit of RNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1976 Mar 5;101(3):427–433. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90157-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman M. Z., Wiggs J. L., Chamberlin M. J. Nucleotide sequences of two Bacillus subtilis promoters used by Bacillus subtilis sigma-28 RNA polymerase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 25;9(22):5991–6000. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.22.5991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene J. R., Chelm B. K., Geiduschek E. P. SP01 gene 27 is required for viral late transcription. J Virol. 1982 Feb;41(2):715–720. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.2.715-720.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klenow H., Henningsen I. Selective elimination of the exonuclease activity of the deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase from Escherichia coli B by limited proteolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jan;65(1):168–175. doi: 10.1073/pnas.65.1.168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee G., Hannett N. M., Korman A., Pero J. Transcription of cloned DNA from Bacillus subtilis phage SP01. Requirement for hydroxymethyluracil-containing DNA by phage-modified RNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1980 May 25;139(3):407–422. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90138-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee G., Pero J. Conserved nucleotide sequences in temporally controlled bacteriophage promoters. J Mol Biol. 1981 Oct 25;152(2):247–265. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90242-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee G., Talkington C., Pero J. Nucleotide sequence of a promoter recognized by Bacillus subtilis RNA polymerase. Mol Gen Genet. 1980;180(1):57–65. doi: 10.1007/BF00267352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Losick R., Pero J. Cascades of Sigma factors. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):582–584. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90164-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin J. R., Murray C. L., Rabinowitz J. C. Unique features in the ribosome binding site sequence of the gram-positive Staphylococcus aureus beta-lactamase gene. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 10;256(21):11283–11291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran C. P., Jr, Lang N., LeGrice S. F., Lee G., Stephens M., Sonenshein A. L., Pero J., Losick R. Nucleotide sequences that signal the initiation of transcription and translation in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;186(3):339–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00729452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran C. P., Jr, Lang N., Losick R. Nucleotide sequence of a Bacillus subtilis promoter recognized by Bacillus subtilis RNA polymerase containing sigma 37. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 25;9(22):5979–5990. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.22.5979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okubo S., Yanagida T., Fujita D. J., Olsson-Wilhelm B. M. The genetics of bacteriophage SPO1. Biken J. 1972 Jun;15(2):81–97. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pero J., Hannett N. M., Talkington C. Restriction cleavage map of SP01 DNA: general location of early, middle, and late genes. J Virol. 1979 Jul;31(1):156–171. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.1.156-171.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pero J., Nelson J., Fox T. D. Highly asymmetric transcription by RNA polymerase containing phage-SP01-induced polypeptides and a new host protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1589–1593. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pustell J., Kafatos F. C. A high speed, high capacity homology matrix: zooming through SV40 and polyoma. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Aug 11;10(15):4765–4782. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.15.4765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed R. R. Transposon-mediated site-specific recombination: a defined in vitro system. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):713–719. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90178-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Court D. Regulatory sequences involved in the promotion and termination of RNA transcription. Annu Rev Genet. 1979;13:319–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.13.120179.001535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweiger M., Herrlich P. DNA-directed enzyme synthesis in vitro. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1974;65:59–132. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-65875-4_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segall J., Losick R. Cloned Bacillus subtilis DNA containing a gene that is activated early during sporulation. Cell. 1977 Aug;11(4):751–761. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90289-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shorenstein R. G., Losick R. Comparative size and properties of the sigma subunits of ribonucleic acid polymerase from Bacillus subtilis and Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1973 Sep 10;248(17):6170–6173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebenlist U., Simpson R. B., Gilbert W. E. coli RNA polymerase interacts homologously with two different promoters. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):269–281. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90613-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talkington C., Pero J. Distinctive nucleotide sequences of promoters recognized by RNA polymerase containing a phage-coded "sigma-like" protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5465–5469. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talkington C., Pero J. Promoter recognition by phage SP01-modified RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1185–1189. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talkington C., Pero J. Restriction fragment analysis of the temporal program of bacteriophage SPO1 transcription and its control by phage-modified RNA polymerases. Virology. 1977 Dec;83(2):365–379. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90181-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinoco I., Jr, Borer P. N., Dengler B., Levin M. D., Uhlenbeck O. C., Crothers D. M., Bralla J. Improved estimation of secondary structure in ribonucleic acids. Nat New Biol. 1973 Nov 14;246(150):40–41. doi: 10.1038/newbio246040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelstein B., Gillespie D. Preparative and analytical purification of DNA from agarose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):615–619. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




