Abstract
The primary heterodiploid bacteria regenerated after Bacillus subtilis fusion, although generally noncomplementing diploids, behave in pedigree analysis as multipotential systems. Individual diploid colonies yielding complete reciprocal recombinant (RR) progeny—often accompanied by one or both parents—constitute 10-30% of the total recombinant-forming units. The RR (reciprocal for 8-11 genes) usually occur in equivalent numbers both among and within individual colonies. Novel for bacteria, they demonstrate that entire parental genomes brought together within a diploid protoplast are retained as two independent replicons able to undergo classical recombination characteristic of eukaryotic gametogenesis. Parental or recombinant genomes are also subject to multiple rounds of recombination without obligate segregation and often not reciprocal. Diploid recombinant clones, sharing streptomycin resistance but reciprocal for auxotrophic markers, have displayed a partial ability to make a facultative shift in chromosome expression. They have also produced two types of prototrophs: a stable one (presumably haploid and recombinant) and an unstable one, (diploid and temporarily complementing at low frequency). It follows that chromosome extinction may affect both parental and recombinant chromosomes and does not interfere with recombination. Analysis of the number and chromosomal distribution of crossovers in all recombinants and those from single diploid clones shows increased frequency of exchange in the regions of the replication origin and terminus, possibly a result of the association of these sites with the cell wall or membrane.
Keywords: bacterial diploids, chromosome extinction, genome conservation and segregation, intraclonal genotype selection
Full text
PDF
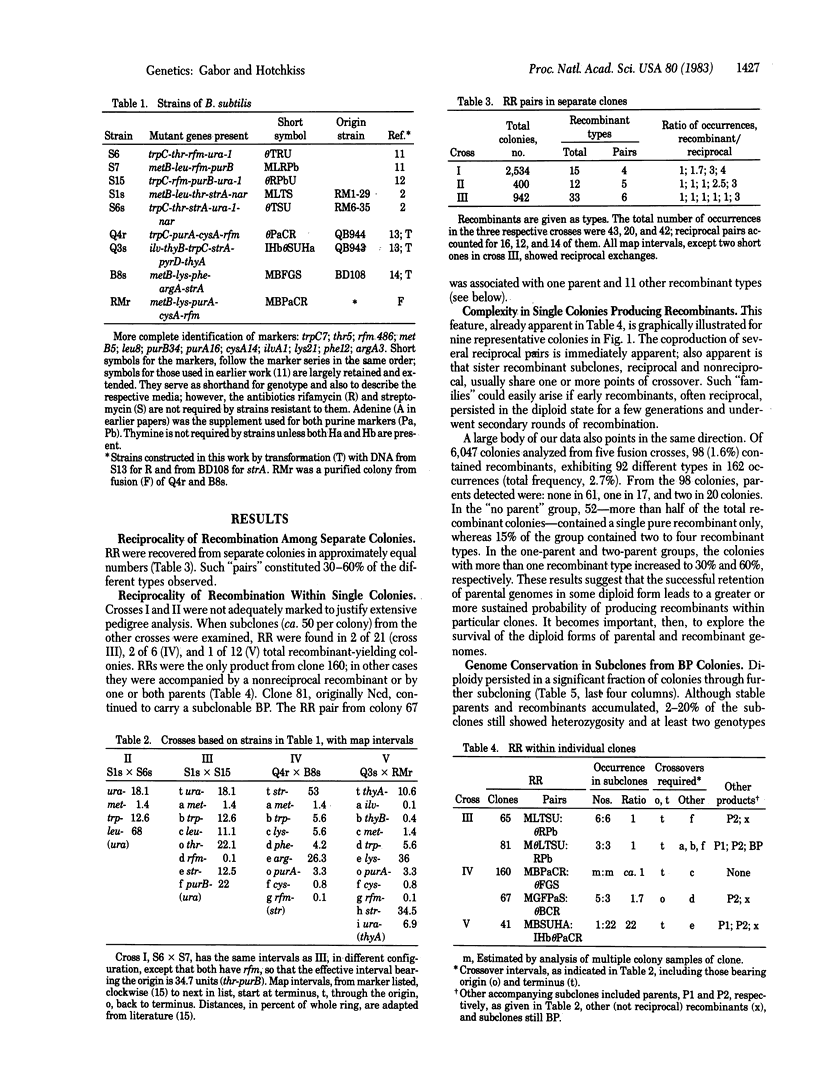
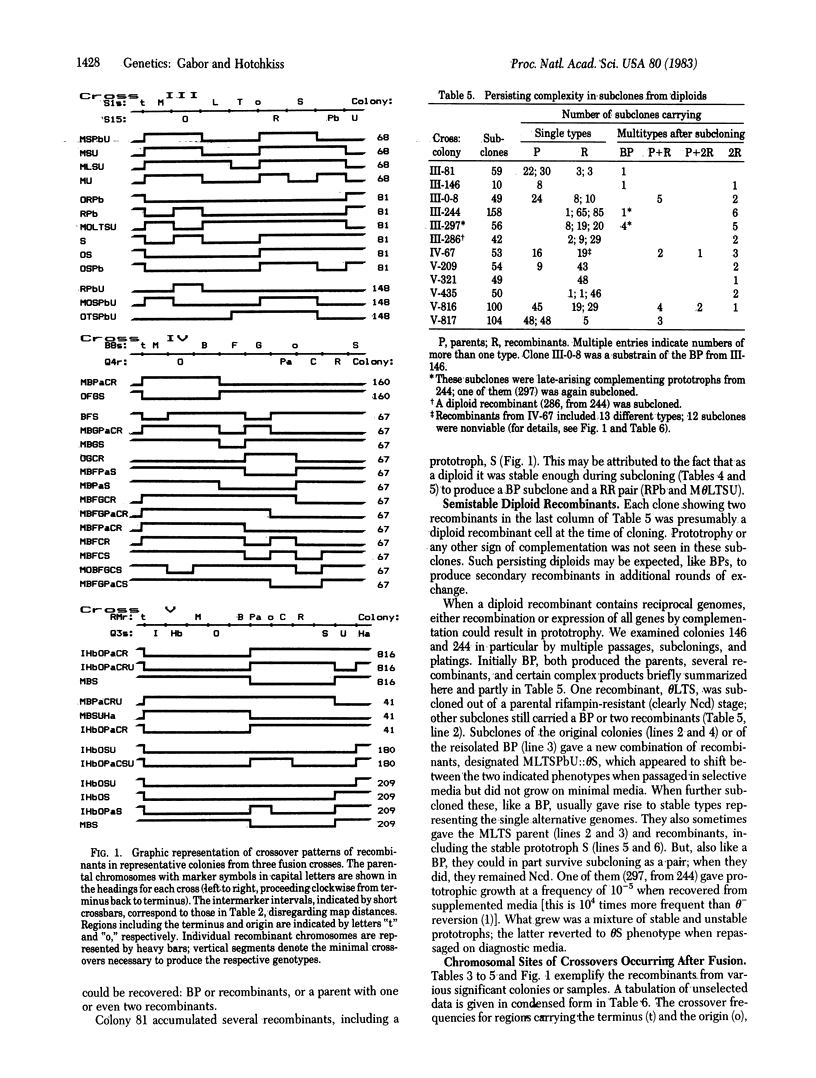


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boon T., Zinder N. D. A mechanism for genetic recombination generating one parent and one recombinant. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Oct;64(2):573–577. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.2.573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyle R. J., Streips U. N., Imada S., Fan V. S., Brown W. C. Genetic transformation with cell wall-associated deoxyribonucleic acid in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1980 Dec;144(3):957–966. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.3.957-966.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubnau D., Goldthwaite C., Smith I., Marmur J. Genetic mapping in Bacillus subtilis. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jul 14;27(1):163–185. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90358-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fodor K., Alföldi L. Fusion of protoplasts of Bacillus megaterium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jun;73(6):2147–2150. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.6.2147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fodor K., Alföldi L. Polyethylene-glycol induced fusion of bacterial protoplasts: direct selection of recombinants. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Jan 5;168(1):55–59. doi: 10.1007/BF00267933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frehel C., Lheritier A. M., Sanchez-Rivas C., Schaeffer P. Electron microscopic study of Bacillus subtilis protoplast fusion. J Bacteriol. 1979 Mar;137(3):1354–1361. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.3.1354-1361.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabor M. H., Hotchkiss R. D. Parameters governing bacterial regeneration and genetic recombination after fusion of Bacillus subtilis protoplasts. J Bacteriol. 1979 Mar;137(3):1346–1353. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.3.1346-1353.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillen N., Gabor M. H., Hotchkiss R. D., Hirschbein L. Isolation and characterization of the nucleoid of non-complementing diploids from protoplast fusion in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;185(1):69–74. doi: 10.1007/BF00333792. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henner D. J., Hoch J. A. The Bacillus subtilis chromosome. Microbiol Rev. 1980 Mar;44(1):57–82. doi: 10.1128/mr.44.1.57-82.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopwood D. A., Wright H. M. Bacterial protoplast fusion: recombination in fused protoplasts of Streptomyces coelicolor. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Jul 4;162(3):307–317. doi: 10.1007/BF00268856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopwood D. A., Wright H. M., Bibb M. J., Cohen S. N. Genetic recombination through protoplast fusion in Streptomyces. Nature. 1977 Jul 14;268(5616):171–174. doi: 10.1038/268171a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hotchkiss R. D., Gabor M. H. Biparental products of bacterial protoplast fusion showing unequal parental chromosome expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3553–3557. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hotchkiss R. D. Models of genetic recombination. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1974;28(0):445–468. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.28.100174.002305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lepesant-Kejzlarová J., Lepesant J. A., Walle J., Billault A., Dedonder R. Revision of the linkage map of Bacillus subtilis 168: indications for circularity of the chromosome. J Bacteriol. 1975 Mar;121(3):823–834. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.3.823-834.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lévi-Meyrueis C., Sanchez-Rivas C., Schaeffer P. Formation de bactéries diploïdes stables par fusion de protoplastes de Bacillus subtilis et effet de mutations rec- sur les produits de fusion formés. C R Seances Acad Sci D. 1980 Jul 7;291(1):67–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Rivas C. Direct selection of complementing diploids from PEG-induced fusion of Bacillus subtilis protoplasts. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;185(2):329–333. doi: 10.1007/BF00330807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Rivas C., Garro A. J. Bacterial fusion assayed by a prophage complementation test. J Bacteriol. 1979 Mar;137(3):1340–1345. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.3.1340-1345.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer P., Cami B., Hotchkiss R. D. Fusion of bacterial protoplasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jun;73(6):2151–2155. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.6.2151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sueoka N., Quinn W. G. Membrane attachment of the chromosome replication origin in Bacillus subtilis. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1968;33:695–705. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1968.033.01.078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi K., Yoshikawa H. Association of the replication terminus of the Bacillus subtilis chromosome to the cell membrane. J Bacteriol. 1975 Nov;124(2):1030–1033. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.2.1030-1033.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


