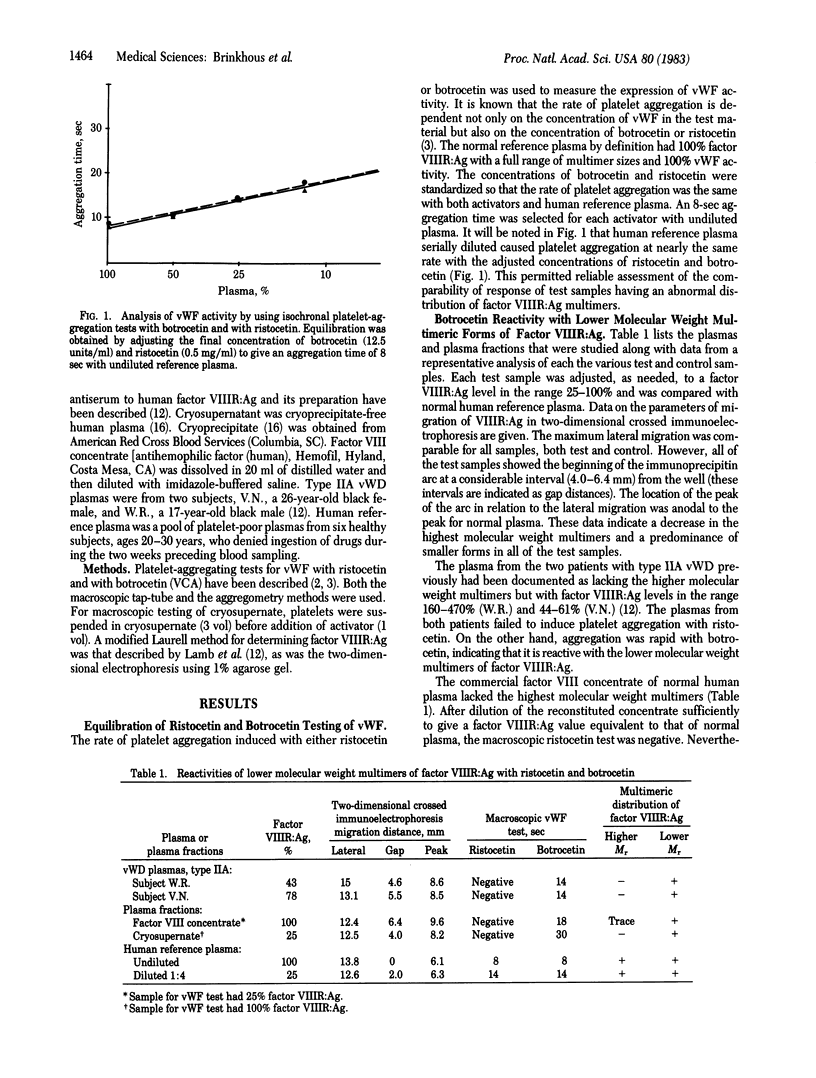
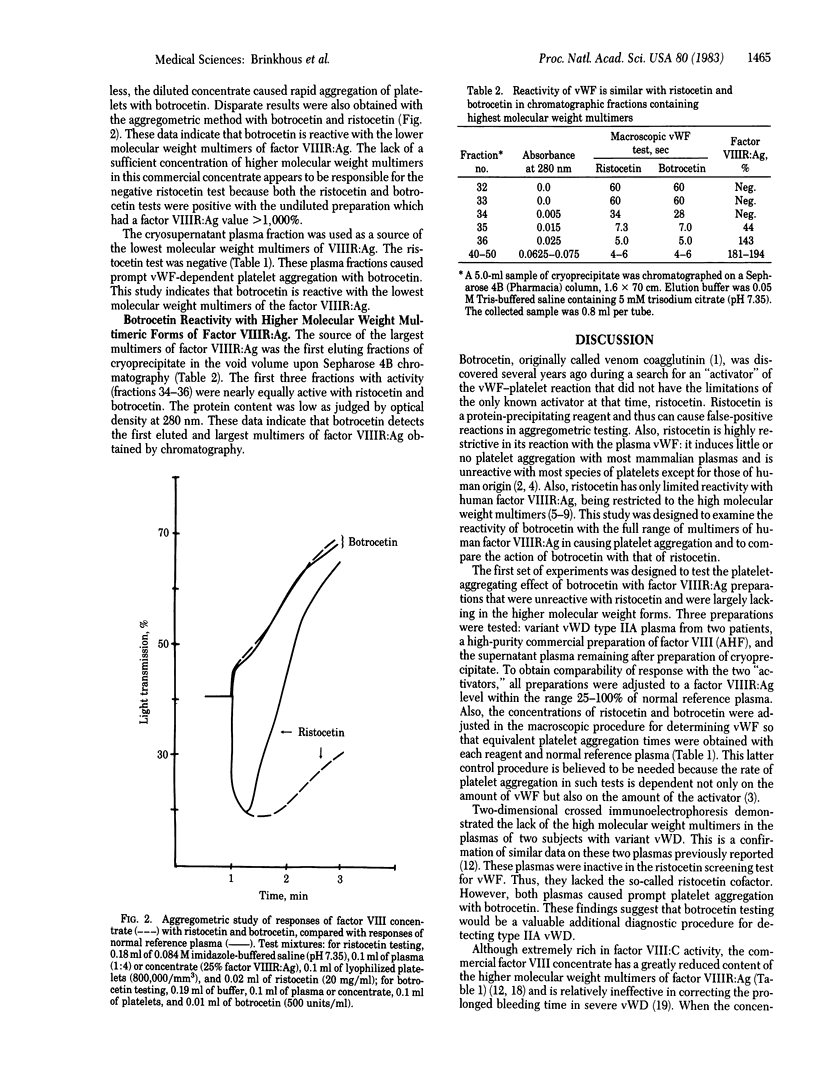
Abstract
Botrocetin, originally called venom coagglutinin, is a Bothrops factor that causes aggregation of blood platelets in the presence of the von Willebrand component of the factor VIII macromolecular complex. The complex consists of a series of multimers with a molecular weight of about 1-20 x 10(6). Ristocetin, another agent that causes platelet aggregation dependent on von Willebrand factor, reacts with only the higher molecular weight multimers. We report on the reactivity of botrocetin in relation to the multimeric structure of the factor VIII complex. Several plasmas or plasma fractions with abnormal distribution of the multimeric sizes were examined, including variant von Willebrand disease type IIA with lack of the higher molecular weight forms, commercial antihemophilic factor concentrates with a preponderance of lower molecular weight forms, cryoprecipitate-free plasma containing mainly the smaller multimers, and a chromatographic fraction of plasma containing only the highest molecular weight polymers. Factor VIII-related antigen content was adjusted to 25-100%. All of the preparations lacking the high molecular weight forms caused prompt platelet aggregation with botrocetin, but none of them caused aggregation in the ristocetin test made isochronal with the botrocetin test. The very high molecular weight polymers were equally effective with botrocetin and ristocetin. These findings indicate that the Bothrops factor is reactive with a broad spectrum of high to low molecular weight forms of the factor VIII complex, suggesting that bioassays of von Willebrand factor with botrocetin should correlate better with immunoassays for factor VIII-related antigen and could reflect better the full platelet-aggregating function of the complex than do ristocetin determinations.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allain J. P., Cooper H. A., Wagner R. H., Brinkhous K. M. Platelets fixed with paraformaldehyde: a new reagent for assay of von Willebrand factor and platelet aggregating factor. J Lab Clin Med. 1975 Feb;85(2):318–328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blatt P. M., Brinkhous K. M., Culp H. R., Krauss J. S., Roberts H. R. Antihemophilic factor concentrate therapy in von Willebrand disease. Dissociation of bleeding-time factor and ristocetin-cofactor activities. JAMA. 1976 Dec 13;236(24):2770–2772. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinkhous K. M., Barnes D. S., Potter J. Y., Read M. S. Von Willebrand syndrome induced by a Bothrops venom factor: bioassay for venom coagglutinin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):3230–3234. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.3230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinkhous K. M., Read M. S. Preservation of platelet receptors for platelet aggregating factor/von Willebrand factor by air drying, freezing, or lyophilization: new stable platelet preparations for von Willebrand factor assays. Thromb Res. 1978 Oct;13(4):591–597. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(78)90148-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinkhous K. M., Read M. S. Use of venom coagglutinin and lyophilized platelets in testing for platelet-aggregating von Willebrand factor. Blood. 1980 Mar;55(3):517–520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinkhous K. M., Thomas B. D., Ibrahim S. A., Read M. S. Plasma levels of platelet aggregating factor/vom Willebrand factor in various species. Thromb Res. 1977 Sep;11(3):345–355. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(77)90186-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doucet-de Bruïne M. H., Sixma J. J., Over J., Beeser-Visser N. H. Heterogeneity of human factor VIII. II. Characterization of forms of factor VIII binding to platelets in the presence of ristocetin. J Lab Clin Med. 1978 Jul;92(1):96–107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gralnick H. R., Williams S. B., Morisato D. K. Effect of multimeric structure of the factor VIII/von Willebrand factor protein on binding to platelets. Blood. 1981 Aug;58(2):387–397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard M. A., Salem H. H., Thomas K. B., Hau L., Perkin J., Coghlan M., Firkin B. G. Variant von Willebrand's disease type B--revisited. Blood. 1982 Dec;60(6):1420–1428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb M. A., Reisner H. M., Cooper H. A., Wagner R. H. The multimeric distribution of factor VIII-related antigen studied by an improved crossed-immunoelectrophoresis technique. J Lab Clin Med. 1981 Nov;98(5):751–763. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S. E., Marder V. J., Francis C. W., Barlow G. H. Structural studies of the functional heterogeneity of von Willebrand protein polymers. Blood. 1981 Feb;57(2):313–323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer D., Obert B., Pietu G., Lavergne J. M., Zimmerman T. S. Multimeric structure of factor VIII/von Willebrand factor in von Willebrand's disease. J Lab Clin Med. 1980 Apr;95(4):590–602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Over J., Bouma B. N., van Mourik J. A., Sixma J. J., Vlooswijk R., Bakker-Woudenberg I. Heterogeneity of human factor VIII. I. Characterization of factor VIII present in the supernatant of cryoprecipitate. J Lab Clin Med. 1978 Jan;91(1):32–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perret B. A., Furlan M., Kneubuehl F., Beck E. A. Fractionation of individual, biologically active factor VIII multimers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Jun 29;669(1):98–104. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(81)90228-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pietu G., Obert B., Larrieu M. J., Meyer D. Structure - function relationship of factor VIII/von Willebrand factor. Application to the study of variant von Willebrand's disease and cryosupernatant prepared from normal plasma. 1980 Aug 15-Sep 1Thromb Res. 19(4-5):671–685. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(80)90039-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Read M. S., Potter J. Y., Brinkhous K. M. Venom coagglutinin for detection of von Willebrand factor activity in animal plasmas. J Lab Clin Med. 1983 Jan;101(1):74–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Read M. S., Shermer R. W., Brinkhous K. M. Venom coagglutinin: an activator of platelet aggregation dependent on von Willebrand factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4514–4518. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruggeri Z. M., Pareti F. I., Mannucci P. M., Ciavarella N., Zimmerman T. S. Heightened interaction between platelets and factor VIII/von Willebrand factor in a new subtype of von Willebrand's disease. N Engl J Med. 1980 May 8;302(19):1047–1051. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198005083021902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruggeri Z. M., Zimmerman T. S. Variant von Willebrand's disease: characterization of two subtypes by analysis of multimeric composition of factor VIII/von Willebrand factor in plasma and platelets. J Clin Invest. 1980 Jun;65(6):1318–1325. doi: 10.1172/JCI109795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein M., Deykin D. Comparison of factor VIII-related von Willebrand factor proteins prepared from human cryoprecipitate and factor VIII concentrate. Blood. 1979 Jun;53(6):1095–1105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


