Abstract
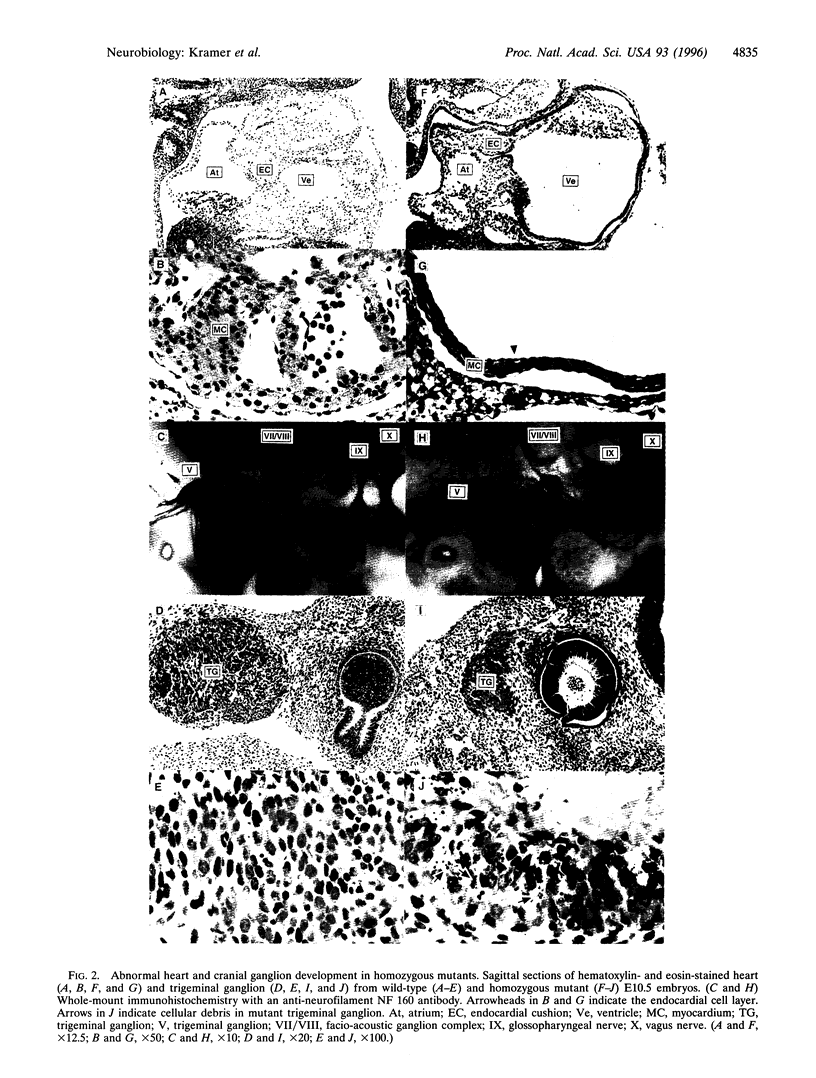
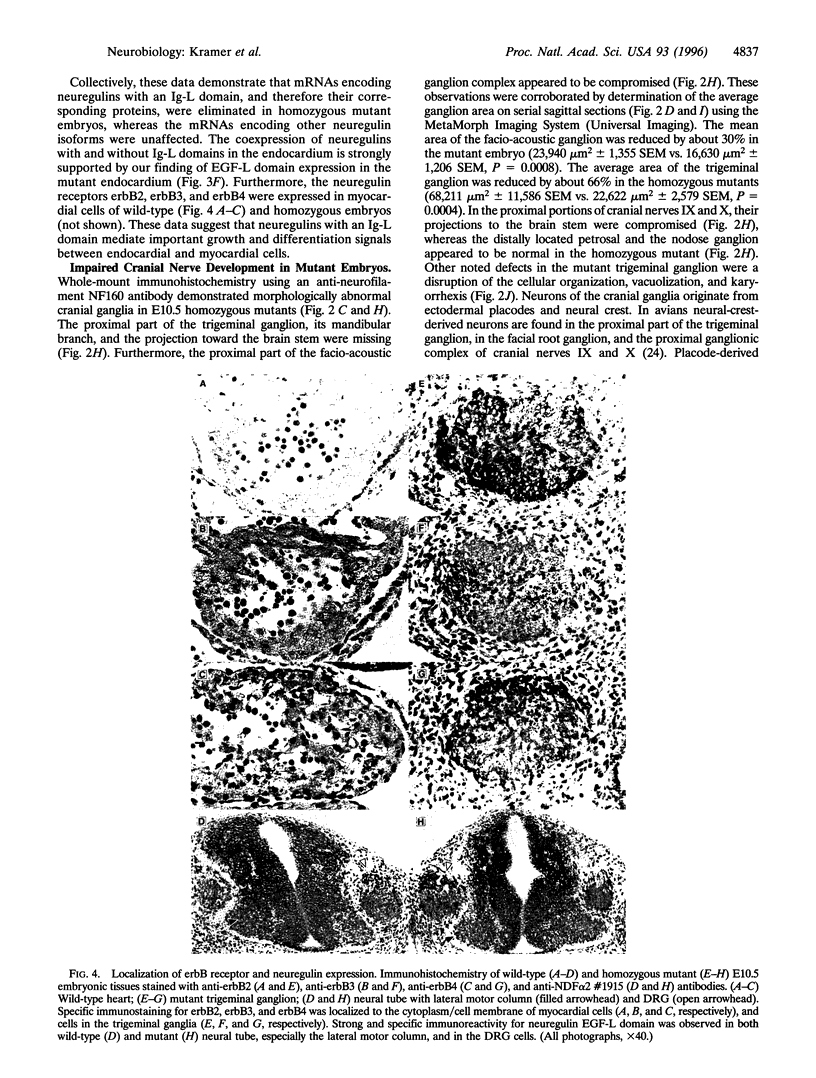
Neuregulins are ligands for the erbB family of receptor tyrosine kinases and mediate growth and differentiation of neural crest, muscle, breast cancer, and Schwann cells. Neuregulins contain an epidermal growth factor-like domain located C-terminally to either an Ig-like domain or a cysteine-rich domain specific to the sensory and motor neuron-derived isoform. Here it is shown that elimination of the Ig-like domain-containing neuregulins by homologous recombination results in embryonic lethality associated with a deficiency of ventricular myocardial trabeculation and impairment of cranial ganglion development. The erbB receptors are expressed in myocardial cells and presumably mediate the neuregulin signal originating from endocardial cells. The trigeminal ganglion is reduced in size and lacks projections toward the brain stem and mandible. We conclude that IgL-domain-containing neuregulins play a major role in cardiac and neuronal development.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ben-Baruch N., Yarden Y. Neu differentiation factors: a family of alternatively spliced neuronal and mesenchymal factors. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1994 Jul;206(3):221–227. doi: 10.3181/00379727-206-43746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brutsaert D. L., Andries L. J. The endocardial endothelium. Am J Physiol. 1992 Oct;263(4 Pt 2):H985–1002. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1992.263.4.H985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carraway K. L., 3rd, Cantley L. C. A neu acquaintance for erbB3 and erbB4: a role for receptor heterodimerization in growth signaling. Cell. 1994 Jul 15;78(1):5–8. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90564-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carraway K. L., 3rd, Sliwkowski M. X., Akita R., Platko J. V., Guy P. M., Nuijens A., Diamonti A. J., Vandlen R. L., Cantley L. C., Cerione R. A. The erbB3 gene product is a receptor for heregulin. J Biol Chem. 1994 May 13;269(19):14303–14306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Z., Friedrich G. A., Soriano P. Transcriptional enhancer factor 1 disruption by a retroviral gene trap leads to heart defects and embryonic lethality in mice. Genes Dev. 1994 Oct 1;8(19):2293–2301. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.19.2293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corfas G., Fischbach G. D. The number of Na+ channels in cultured chick muscle is increased by ARIA, an acetylcholine receptor-inducing activity. J Neurosci. 1993 May;13(5):2118–2125. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-05-02118.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corfas G., Rosen K. M., Aratake H., Krauss R., Fischbach G. D. Differential expression of ARIA isoforms in the rat brain. Neuron. 1995 Jan;14(1):103–115. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(95)90244-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Amico-Martel A., Noden D. M. Contributions of placodal and neural crest cells to avian cranial peripheral ganglia. Am J Anat. 1983 Apr;166(4):445–468. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001660406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dong Z., Brennan A., Liu N., Yarden Y., Lefkowitz G., Mirsky R., Jessen K. R. Neu differentiation factor is a neuron-glia signal and regulates survival, proliferation, and maturation of rat Schwann cell precursors. Neuron. 1995 Sep;15(3):585–596. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(95)90147-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumont D. J., Gradwohl G., Fong G. H., Puri M. C., Gertsenstein M., Auerbach A., Breitman M. L. Dominant-negative and targeted null mutations in the endothelial receptor tyrosine kinase, tek, reveal a critical role in vasculogenesis of the embryo. Genes Dev. 1994 Aug 15;8(16):1897–1909. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.16.1897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falls D. L., Rosen K. M., Corfas G., Lane W. S., Fischbach G. D. ARIA, a protein that stimulates acetylcholine receptor synthesis, is a member of the neu ligand family. Cell. 1993 Mar 12;72(5):801–815. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90407-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho W. H., Armanini M. P., Nuijens A., Phillips H. S., Osheroff P. L. Sensory and motor neuron-derived factor. A novel heregulin variant highly expressed in sensory and motor neurons. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jun 16;270(24):14523–14532. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.24.14523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes W. E., Sliwkowski M. X., Akita R. W., Henzel W. J., Lee J., Park J. W., Yansura D., Abadi N., Raab H., Lewis G. D. Identification of heregulin, a specific activator of p185erbB2. Science. 1992 May 22;256(5060):1205–1210. doi: 10.1126/science.256.5060.1205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jo S. A., Zhu X., Marchionni M. A., Burden S. J. Neuregulins are concentrated at nerve-muscle synapses and activate ACh-receptor gene expression. Nature. 1995 Jan 12;373(6510):158–161. doi: 10.1038/373158a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kastner P., Grondona J. M., Mark M., Gansmuller A., LeMeur M., Decimo D., Vonesch J. L., Dollé P., Chambon P. Genetic analysis of RXR alpha developmental function: convergence of RXR and RAR signaling pathways in heart and eye morphogenesis. Cell. 1994 Sep 23;78(6):987–1003. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90274-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb J. A., Fischbach G. D. ARIA can be released from extracellular matrix through cleavage of a heparin-binding domain. J Cell Biol. 1995 Jul;130(1):127–135. doi: 10.1083/jcb.130.1.127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyons I., Parsons L. M., Hartley L., Li R., Andrews J. E., Robb L., Harvey R. P. Myogenic and morphogenetic defects in the heart tubes of murine embryos lacking the homeo box gene Nkx2-5. Genes Dev. 1995 Jul 1;9(13):1654–1666. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.13.1654. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansour S. L., Thomas K. R., Capecchi M. R. Disruption of the proto-oncogene int-2 in mouse embryo-derived stem cells: a general strategy for targeting mutations to non-selectable genes. Nature. 1988 Nov 24;336(6197):348–352. doi: 10.1038/336348a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchionni M. A., Goodearl A. D., Chen M. S., Bermingham-McDonogh O., Kirk C., Hendricks M., Danehy F., Misumi D., Sudhalter J., Kobayashi K. Glial growth factors are alternatively spliced erbB2 ligands expressed in the nervous system. Nature. 1993 Mar 25;362(6418):312–318. doi: 10.1038/362312a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer D., Birchmeier C. Distinct isoforms of neuregulin are expressed in mesenchymal and neuronal cells during mouse development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Feb 1;91(3):1064–1068. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.3.1064. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer D., Birchmeier C. Multiple essential functions of neuregulin in development. Nature. 1995 Nov 23;378(6555):386–390. doi: 10.1038/378386a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mima T., Ueno H., Fischman D. A., Williams L. T., Mikawa T. Fibroblast growth factor receptor is required for in vivo cardiac myocyte proliferation at early embryonic stages of heart development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Jan 17;92(2):467–471. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.2.467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perantoni A. O., Rice J. M., Reed C. D., Watatani M., Wenk M. L. Activated neu oncogene sequences in primary tumors of the peripheral nervous system induced in rats by transplacental exposure to ethylnitrosourea. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(17):6317–6321. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.17.6317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plowman G. D., Green J. M., Culouscou J. M., Carlton G. W., Rothwell V. M., Buckley S. Heregulin induces tyrosine phosphorylation of HER4/p180erbB4. Nature. 1993 Dec 2;366(6454):473–475. doi: 10.1038/366473a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandrock A. W., Jr, Goodearl A. D., Yin Q. W., Chang D., Fischbach G. D. ARIA is concentrated in nerve terminals at neuromuscular junctions and at other synapses. J Neurosci. 1995 Sep;15(9):6124–6136. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.15-09-06124.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah N. M., Marchionni M. A., Isaacs I., Stroobant P., Anderson D. J. Glial growth factor restricts mammalian neural crest stem cells to a glial fate. Cell. 1994 May 6;77(3):349–360. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90150-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonet W. S., Bucay N., Lauer S. J., Taylor J. M. A far-downstream hepatocyte-specific control region directs expression of the linked human apolipoprotein E and C-I genes in transgenic mice. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 15;268(11):8221–8229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soriano P., Montgomery C., Geske R., Bradley A. Targeted disruption of the c-src proto-oncogene leads to osteopetrosis in mice. Cell. 1991 Feb 22;64(4):693–702. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90499-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sucov H. M., Dyson E., Gumeringer C. L., Price J., Chien K. R., Evans R. M. RXR alpha mutant mice establish a genetic basis for vitamin A signaling in heart morphogenesis. Genes Dev. 1994 May 1;8(9):1007–1018. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.9.1007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swiatek P. J., Gridley T. Perinatal lethality and defects in hindbrain development in mice homozygous for a targeted mutation of the zinc finger gene Krox20. Genes Dev. 1993 Nov;7(11):2071–2084. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.11.2071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wen D., Peles E., Cupples R., Suggs S. V., Bacus S. S., Luo Y., Trail G., Hu S., Silbiger S. M., Levy R. B. Neu differentiation factor: a transmembrane glycoprotein containing an EGF domain and an immunoglobulin homology unit. Cell. 1992 May 1;69(3):559–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90456-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wen D., Suggs S. V., Karunagaran D., Liu N., Cupples R. L., Luo Y., Janssen A. M., Ben-Baruch N., Trollinger D. B., Jacobsen V. L. Structural and functional aspects of the multiplicity of Neu differentiation factors. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Mar;14(3):1909–1919. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.3.1909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]