Abstract
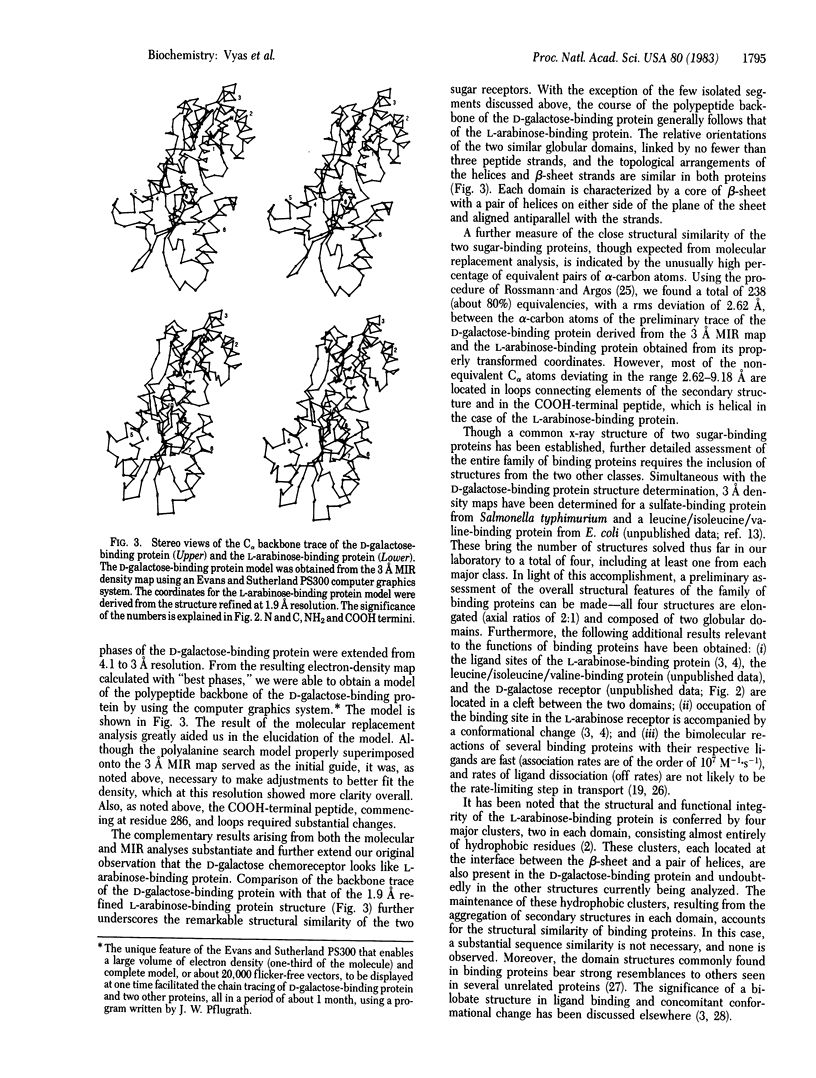
X-ray diffraction studies of a D-galactose-binding protein essential for transport and chemotaxis in Escherichia coli have yielded a model of the polypeptide chain backbone. An initial polyalanine backbone trace was obtained at 3.2 A resolution by the molecular replacement technique, using a polyalanine search model derived from the refined structure of the L-arabinose-binding protein. Concurrently, a 3 A resolution electron-density map of the D-galactose receptor was determined from multiple isomorphous replacement (MIR) phases. The properly transformed initial polyalanine model superimposed on the MIR electron-density map proved to be an excellent guide in obtaining a final trace. The few changes made in the polyalanine model to improve the fit to the density were confined primarily to the COOH-terminal peptide and some loops connecting the elements of the secondary structure. Despite the lack of significant sequence homology, the overall course of the polypeptide backbone of the D-galactose-binding protein is remarkably similar to that of the L-arabinose-binding protein, the first structure in a series to be solved from this family of binding proteins. Both structures are elongated (axial ratios of 2:1) and composed of two globular domains. For both proteins, the arrangements of the elements of the secondary structure in both domains are identical; both lobes contain a core of beta-pleated sheet with a pair of helices on either side of the plane of the sheet. The four major hydrophobic clusters that stabilize the structure of the L-arabinose-binding protein are also present in the D-galactose-binding protein.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Argos P., Mahoney W. C., Hermodson M. A., Hanei M. Structural prediction of sugar-binding proteins functional in chemotaxis and transport. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 10;256(9):4357–4361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buehner M., Lifchitz A., Bally R., Mornon J. P. Use of molecular replacement in the structure determination of the P21212 and the P21 (pseudo P21212) crystal forms of oxidized uteroglobin. J Mol Biol. 1982 Aug 5;159(2):353–358. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90499-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilliland G. L., Quiocho F. A. Structure of the L-arabinose-binding protein from Escherichia coli at 2.4 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1981 Mar 5;146(3):341–362. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90392-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazelbauer G. L., Adler J. Role of the galactose binding protein in chemotaxis of Escherichia coli toward galactose. Nat New Biol. 1971 Mar 24;230(12):101–104. doi: 10.1038/newbio230101a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins C. F., Haag P. D., Nikaido K., Ardeshir F., Garcia G., Ames G. F. Complete nucleotide sequence and identification of membrane components of the histidine transport operon of S. typhimurium. Nature. 1982 Aug 19;298(5876):723–727. doi: 10.1038/298723a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogg R. W., Hermodson M. A. Amino acid sequence of the L-arabinose-binding protein from Escherichia coli B/r. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jul 25;252(14):5135–5141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isihara H., Hogg R. W. Amino acid sequence of the sulfate-binding protein from Salmonella typhimurium LT2. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4614–4618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koshland D. E., Jr Biochemistry of sensing and adaptation in a simple bacterial system. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:765–782. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.004001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahoney W. C., Hogg R. W., Hermodson M. A. The amino acid sequence of the D-galactose-binding protein from Escherichia coli B/r. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 10;256(9):4350–4356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. M., 3rd, Olson J. S., Quiocho F. A. The mechanism of sugar binding to the periplasmic receptor for galactose chemotaxis and transport in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 25;255(6):2465–2471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murthy M. R., Garavito R. M., Johnson J. E., Rossmann M. G. Structure of lobster apo-D-glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase at 3.0 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1980 Apr 25;138(4):859–872. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90069-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navia M. A., Segal D. M., Padlan E. A., Davies D. R., Rao N., Rudikoff S., Potter M. Crystal structure of galactan-binding mouse immunoglobulin J539 Fab at 4.5-A resolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):4071–4074. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.4071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newcomer M. E., Gilliland G. L., Quiocho F. A. L-Arabinose-binding protein-sugar complex at 2.4 A resolution. Stereochemistry and evidence for a structural change. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 25;256(24):13213–13217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newcomer M. E., Lewis B. A., Quiocho F. A. The radius of gyration of L-arabinose-binding protein decreases upon binding of ligand. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 25;256(24):13218–13222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newcomer M. E., Miller D. M., 3rd, Quiocho F. A. Location of the sugar-binding site of L-arabinose-binding protein. Sugar derivative syntheses, sugar binding specificity, and difference Fourier analyses. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 25;254(16):7529–7533. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ovchinnikov Y. A., Aldanova N. A., Grinkevich V. A., Arzamazova N. M., Moroz I. N. The primary structure of a Leu, Ile and Val (LIV)-binding protein from Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1977 Jun 15;78(2):313–316. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80331-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons R. G., Hogg R. W. A comparison of the L-arabinose- and D-galactose-binding proteins of Escherichia coli B-r. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jun 10;249(11):3608–3614. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips G. N., Jr, Mahajan V. K., Siu A. K., Quiocho F. A. Structure of L-arabinose-binding protein from Escherichia coli at 5 A resolution and preliminary results at 3.5 A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2186–2190. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quiocho F. A., Gilliland G. L., Miller D. M., Newcomer M. E. Crystallographic and chemical studies of the L-arabinose-binding protein from E. coli. J Supramol Struct. 1977;6(4):503–518. doi: 10.1002/jss.400060405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quiocho F. A., Meador W. E., Pflugrath J. W. Preliminary crystallographic data of receptors for transport and chemotaxis in Escherichia coli: D-galactose and maltose-binding proteins. J Mol Biol. 1979 Sep 5;133(1):181–184. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90256-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quiocho F. A., Pflugrath J. W. The structure of D-galactose-binding protein at 4.1 A resolution looks like L-arabinose-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 25;255(14):6559–6551. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remington S., Wiegand G., Huber R. Crystallographic refinement and atomic models of two different forms of citrate synthase at 2.7 and 1.7 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jun 15;158(1):111–152. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90452-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossmann M. G., Argos P. A comparison of the heme binding pocket in globins and cytochrome b5. J Biol Chem. 1975 Sep 25;250(18):7525–7532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




