Abstract
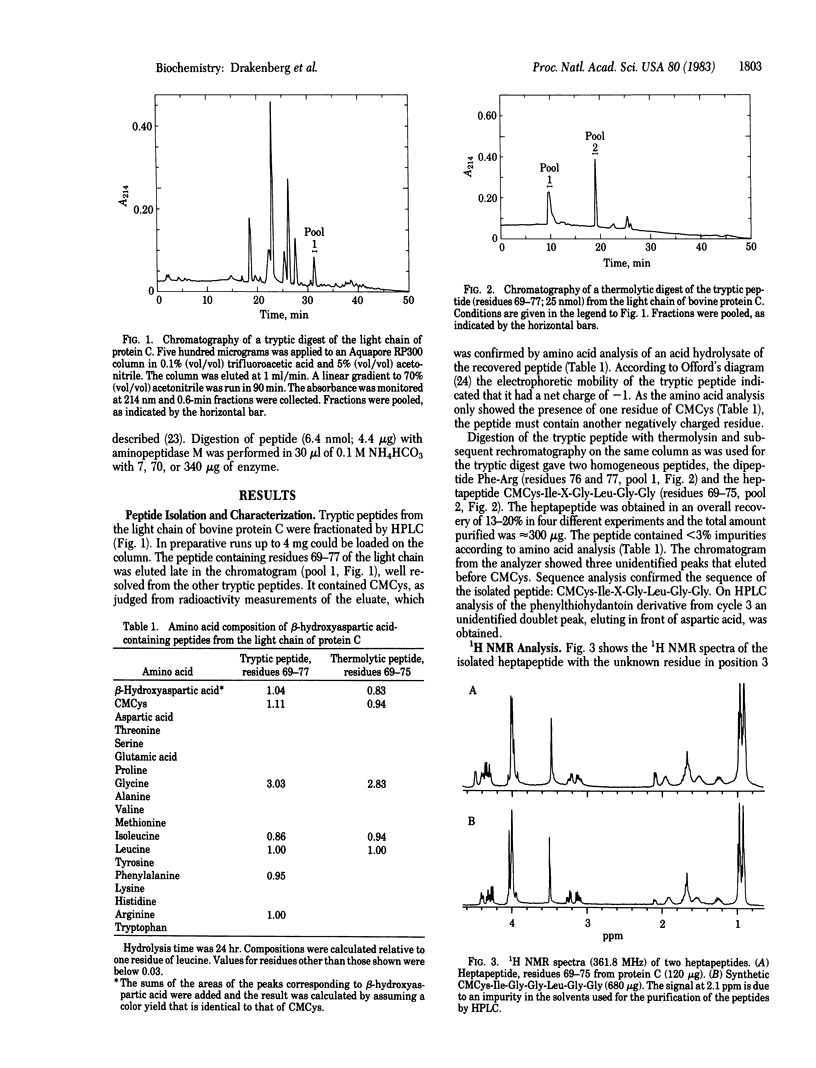
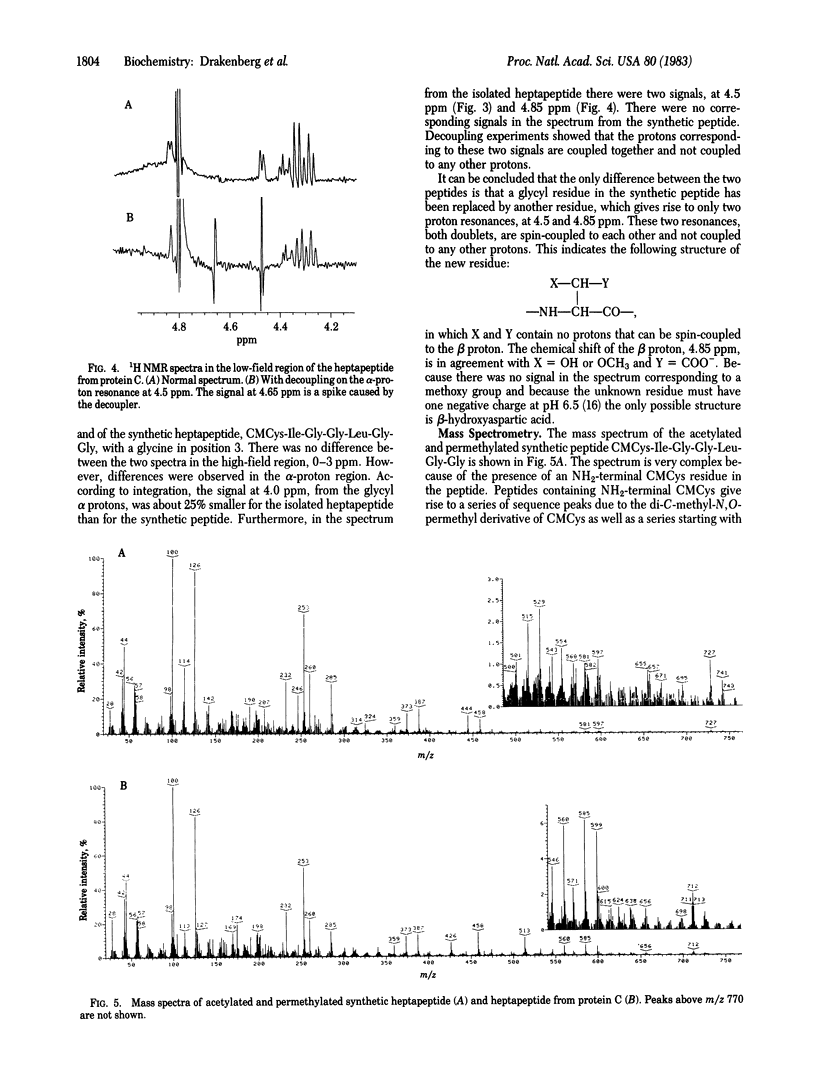
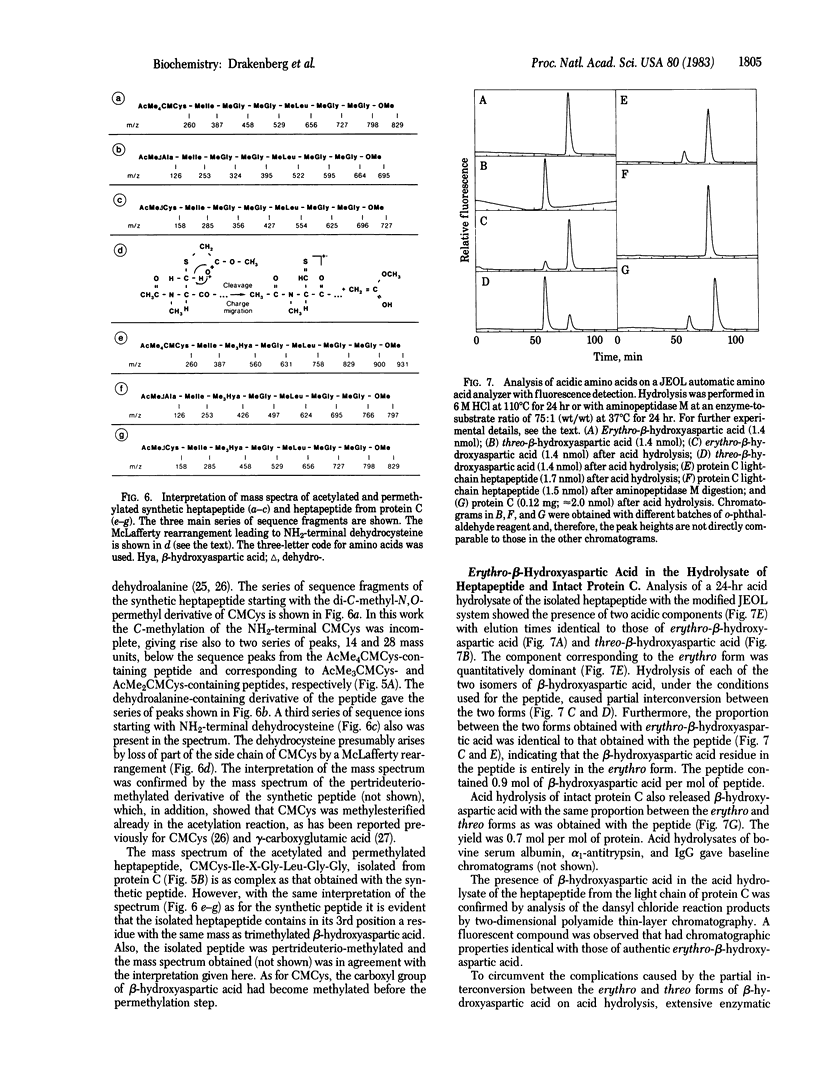
Previous work has shown that the light chain of protein C, an anticoagulant plasma protein, contains an unusual amino acid [Fernlund, P. & Stenflo, J. (1982) J. Biol. Chem. 257, 12170-12179]. To determine the structure of this amino acid a heptapeptide, CMCys-Ile-X-Gly-Leu-Gly-Gly (residues 69-75 in the light chain), was isolated from enzymatic digests of the light chain. According to automatic Edman sequence analysis, 1H NMR spectroscopy, and mass spectrometry the heptapeptide had beta-hydroxyaspartic acid in its third position, which corresponds to position 71 in the light chain of protein C. Analysis of acid and aminopeptidase M hydrolysates of the heptapeptide showed the beta-hydroxyaspartic acid to be the erythro form. Acid hydrolysis of protein C released approximately equal to 1 mol of beta-hydroxyaspartic acid per mol of protein. The function of this amino acid, which, to the best of our knowledge, has not been found previously in proteins, is unknown.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Choo K. H., Gould K. G., Rees D. J., Brownlee G. G. Molecular cloning of the gene for human anti-haemophilic factor IX. Nature. 1982 Sep 9;299(5879):178–180. doi: 10.1038/299178a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dell A., Morris H. R. Primary structure of a chloramphenicol acetyltransferase: mass spectrometric studies. Biomed Mass Spectrom. 1981 Mar;8(3):128–136. doi: 10.1002/bms.1200080310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon C. T., Owen W. G. Identification of an endothelial cell cofactor for thrombin-catalyzed activation of protein C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2249–2252. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon C. T., Stenflo J., Suttie J. W. A new vitamin K-dependent protein. A phospholipid-binding zymogen of a serine esterase. J Biol Chem. 1976 May 25;251(10):3052–3056. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernlund P., Stenflo J. Amino acid sequence of the light chain of bovine protein C. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 25;257(20):12170–12179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernlund P. gamma-Carboxyglutamic acid in human urine. Clin Chim Acta. 1976 Oct 1;72(1):147–155. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(76)90046-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin J. H., Evatt B., Zimmerman T. S., Kleiss A. J., Wideman C. Deficiency of protein C in congenital thrombotic disease. J Clin Invest. 1981 Nov;68(5):1370–1373. doi: 10.1172/JCI110385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikegami T. Studies on the metabolism of beta-hydroxy- aspartic acid. Acta Med Okayama. 1975 Aug;29(4):241–247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KORNBERG H. L., MORRIS J. G. THE UTILIZATION OF GLYCOLLATE BY MICROCOCCUS DENITRIFICANS: THE BETA-HYDROXYASPARTATE PATHWAY. Biochem J. 1965 Jun;95:577–586. doi: 10.1042/bj0950577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KORNGUTH M. L., SALLACH H. J. beta-Hydroxyaspartic acid: synthesis and separation of its diastereoisomers. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1960 Nov;91:39–42. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(60)90451-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katayama K., Ericsson L. H., Enfield D. L., Walsh K. A., Neurath H., Davie E. W., Titani K. Comparison of amino acid sequence of bovine coagulation Factor IX (Christmas Factor) with that of other vitamin K-dependent plasma proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4990–4994. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kisiel W., Canfield W. M., Ericsson L. H., Davie E. W. Anticoagulant properties of bovine plasma protein C following activation by thrombin. Biochemistry. 1977 Dec 27;16(26):5824–5831. doi: 10.1021/bi00645a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kisiel W., Ericsson L. H., Davie E. W. Proteolytic activation of protein C from bovine plasma. Biochemistry. 1976 Nov 2;15(22):4893–4900. doi: 10.1021/bi00667a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kisiel W. Human plasma protein C: isolation, characterization, and mechanism of activation by alpha-thrombin. J Clin Invest. 1979 Sep;64(3):761–769. doi: 10.1172/JCI109521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee H. M., Forde M. D., Lee M. C., Bucher D. J. Fluorometric microbore amino acid analyzer: the construction of an inexpensive, highly sensitive instrument using o-phthalaldehyde as a detection agent. Anal Biochem. 1979 Jul 15;96(2):298–307. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90585-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAMMEN E. F., THOMAS W. R., SEEGERS W. H. Activation of purified prothrombin to autoprothrombin I or autoprothrombin II (platelet cofactor II or autoprothrombin II-A). Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1960 Dec 15;5:218–249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris H. R., Dell A. Mass-spectrometric identification and sequence location of the ten residues of the new amino acid (gamma-Carboxyglutamic acid) in the N-terminal region of prothrombin. Biochem J. 1976 Mar 1;153(3):663–679. doi: 10.1042/bj1530663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris H. R., Dickinson R. J., Williams D. H. Studies towards the complete sequence determination of proteins by mass spectrometry: derivatisation of methionine, cysteine and arginine containing peptides. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Mar 5;51(1):247–255. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90535-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris H. R. Studies towards the complete sequence determination of proteins by mass spectrometry; a rapid procedure for the successful permethylation of histidine containing peptides. FEBS Lett. 1972 May 15;22(3):257–260. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80244-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offord R. E. Electrophoretic mobilities of peptides on paper and their use in the determination of amide groups. Nature. 1966 Aug 6;211(5049):591–593. doi: 10.1038/211591a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen W. G., Esmon C. T. Functional properties of an endothelial cell cofactor for thrombin-catalyzed activation of protein C. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 10;256(11):5532–5535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roepstorff P. Determination of the amino acid sequence of the C-terminal cyanogen bromide fragment of myoglobin from bottle nosed dolphin by mass spectrometric peptide mixture analysis. Biomed Mass Spectrom. 1978 May;5(5):362–366. doi: 10.1002/bms.1200050508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seegers W. H., Marlar R. A., Walz D. A. Anticoagulant effects of autoprothrombin II-A and prothrombin fragment 1. Thromb Res. 1978 Aug;13(2):233–243. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(78)90011-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seegers W. H., Novoa E., Henry R. L., Hassouna H. I. Relationship of "new" vitamin K-dependent Protein C and "old" autoprothrombin II-a. Thromb Res. 1976 May;8(5):543–552. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(76)90236-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenflo J. A new vitamin K-dependent protein. Purification from bovine plasma and preliminary characterization. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jan 25;251(2):355–363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vehar G. A., Davie E. W. Preparation and properties of bovine factor VIII (antihemophilic factor). Biochemistry. 1980 Feb 5;19(3):401–410. doi: 10.1021/bi00544a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker F. J., Sexton P. W., Esmon C. T. The inhibition of blood coagulation by activated Protein C through the selective inactivation of activated Factor V. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Dec 7;571(2):333–342. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(79)90103-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



