Abstract
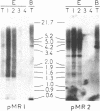
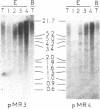
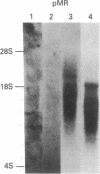
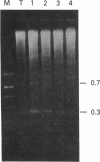
We investigated the genomic distribution of mouse and human repeated sequences by assessing their relative amounts in the four major components into which these genomes can be resolved by density gradient centrifugation techniques. These components are families of fragments that account for most or all of main-band DNAs, range in dG + dC content from 37% to 49%, and are derived by preparative breakage from long DNA segments (greater than 300 kb) of fairly homogeneous composition, the isochores. The results indicate that the short repeats of the B1 family of mouse and of the Alu I family of man are most frequent in the heavy components, whereas the long repeats of the BamHI family of mouse and of the Kpn I family of man are mainly present in the two light components. These results show that the genomic distribution of repeated sequences is nonuniform and conserved in two mammalian species. In addition, we observed that the base composition of two classes of repeats (60% dG + dC for short repeats; 39% dG + dC for long repeats) is correlated with the composition of the major components in which they are embedded. Finally, we obtained evidence that not only the short repeats but also the long repeats are transcribed, these transcripts having been found in mouse poly(A)+ mRNA.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brégégère F., Abastado J. P., Kvist S., Rask L., Lalanne J. L., Garoff H., Cami B., Wiman K., Larhammar D., Peterson P. A. Structure of C-terminal half of two H-2 antigens from cloned mRNA. Nature. 1981 Jul 2;292(5818):78–81. doi: 10.1038/292078a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cami B., Brégégère F., Abastado J. P., Kourilsky P. Multiple sequences related to classical histocompatibility antigens in the mouse genome. Nature. 1981 Jun 25;291(5817):673–675. doi: 10.1038/291673a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cortadas J., Macaya G., Bernardi G. An analysis of the bovine genome by density gradient centrifugation: fractionation in Cs2SO4/3,6-bis(acetatomercurimethyl)dioxane density gradient. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Jun 1;76(1):13–19. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11565.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cortadas J., Olofsson B., Meunier-Rotival M., Macaya G., Bernardi G. THE DNA components of the chicken genome. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Aug 15;99(1):179–186. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13244.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuny G., Soriano P., Macaya G., Bernardi G. The major components of the mouse and human genomes. 1. Preparation, basic properties and compositional heterogeneity. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Apr;115(2):227–233. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05227.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darling S. M., Crampton J. M., Williamson R. Organization of a family of highly repetitive sequences within the human genome. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jan 5;154(1):51–63. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90416-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodemont H. J., Soriano P., Quax W. J., Ramaekers F., Lenstra J. A., Groenen M. A., Bernardi G., Bloemendal H. The genes coding for the cytoskeletal proteins actin and vimentin in warm-blooded vertebrates. EMBO J. 1982;1(2):167–171. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01142.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eigner J., Doty P. The native, denatured and renatured states of deoxyribonucleic acid. J Mol Biol. 1965 Jul;12(3):549–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80312-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filipski J., Thiery J. P., Bernardi G. An analysis of the bovine genome by Cs2SO4-Ag density gradient centrifugation. J Mol Biol. 1973 Oct 15;80(1):177–197. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90240-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgiev G. P., Ilyin Y. V., Chmeliauskaite V. G., Ryskov A. P., Kramerov D. A., Skryabin K. G., Krayev A. S., Lukanidin E. M., Grigoryan M. S. Mobile dispersed genetic elements and other middle repetitive DNA sequences in the genomes of Drosophila and mouse: transcription and biological significance. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1981;45(Pt 2):641–654. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1981.045.01.082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimaldi G., Queen C., Singer M. F. Interspersed repeated sequences in the African green monkey genome that are homologous to the human Alu family. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 11;9(21):5553–5568. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.21.5553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Hogness D. S. Colony hybridization: a method for the isolation of cloned DNAs that contain a specific gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3961–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramerov D. A., Grigoryan A. A., Ryskov A. P., Georgiev G. P. Long double-stranded sequences (dsRNA-B) of nuclear pre-mRNA consist of a few highly abundant classes of sequences: evidence from DNA cloning experiments. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Feb;6(2):697–713. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.2.697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krayev A. S., Kramerov D. A., Skryabin K. G., Ryskov A. P., Bayev A. A., Georgiev G. P. The nucleotide sequence of the ubiquitous repetitive DNA sequence B1 complementary to the most abundant class of mouse fold-back RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Mar 25;8(6):1201–1215. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.6.1201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macaya G., Thiery J. P., Bernardi G. An approach to the organization of eukaryotic genomes at a macromolecular level. J Mol Biol. 1976 Nov;108(1):237–254. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(76)80105-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manuelidis L. Chromosomal localization of complex and simple repeated human DNAs. Chromosoma. 1978 Mar 22;66(1):23–32. doi: 10.1007/BF00285813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster G. K., Carmichael G. G. Analysis of single- and double-stranded nucleic acids on polyacrylamide and agarose gels by using glyoxal and acridine orange. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4835–4838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meunier-Rotival M., Soriano P., Cuny G., Strauss F., Bernardi G. Sequence organization and genomic distribution of the major family of interspersed repeats of mouse DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):355–359. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olofsson B., Bernardi G. Organization of nucleotide sequences in the chicken genome. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Feb 1;130(2):241–245. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07142.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan J., Elder J. T., Duncan C. H., Weissman S. M. Structural analysis of interspersed repetitive polymerase III transcription units in human DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Mar 11;9(5):1151–1170. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prunell A., Bernardi G. Fractionation of native and denatured deoxyribonucleic acid on agarose columns. J Biol Chem. 1973 May 25;248(10):3433–3440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsey J. C., Steele W. J. A procedure for the quantitative recovery of homogeneous populations of undegraded free and bound polysomes from rat liver. Biochemistry. 1976 Apr 20;15(8):1704–1712. doi: 10.1021/bi00653a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin C. M., Deininger P. L., Houck C. M., Schmid C. W. A dimer satellite sequence in bonnet monkey DNA consists of distinct monomer subunits. J Mol Biol. 1980 Jan 15;136(2):151–167. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90310-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid C. W., Jelinek W. R. The Alu family of dispersed repetitive sequences. Science. 1982 Jun 4;216(4550):1065–1070. doi: 10.1126/science.6281889. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer M. F. Highly repeated sequences in mammalian genomes. Int Rev Cytol. 1982;76:67–112. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61789-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer M. F. SINEs and LINEs: highly repeated short and long interspersed sequences in mammalian genomes. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):433–434. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90194-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soriano P., Macaya G., Bernardi G. The major components of the mouse and human genomes. 2. Reassociation kinetics. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Apr;115(2):235–239. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05228.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soriano P., Szabo P., Bernardi G. The scattered distribution of actin genes in the mouse and human genomes. EMBO J. 1982;1(5):579–583. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01211.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Long range periodicities in mouse satellite DNA. J Mol Biol. 1975 May 5;94(1):51–69. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90404-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmetz M., Frelinger J. G., Fisher D., Hunkapiller T., Pereira D., Weissman S. M., Uehara H., Nathenson S., Hood L. Three cDNA clones encoding mouse transplantation antigens: homology to immunoglobulin genes. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):125–134. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90508-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stumph W. E., Kristo P., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. A chicken middle-repetitive DNA sequence which shares homology with mammalian ubiquitous repeats. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Oct 24;9(20):5383–5397. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.20.5383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tashima M., Calabretta B., Torelli G., Scofield M., Maizel A., Saunders G. F. Presence of a highly repetitive and widely dispersed DNA sequence in the human genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1508–1512. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiery J. P., Macaya G., Bernardi G. An analysis of eukaryotic genomes by density gradient centrifugation. J Mol Biol. 1976 Nov;108(1):219–235. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(76)80104-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J. C., Manuelidis L. Sequence definition and organization of a human repeated DNA. J Mol Biol. 1980 Sep 25;142(3):363–386. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90277-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]