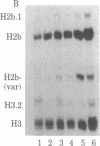
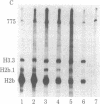
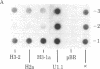
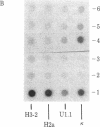
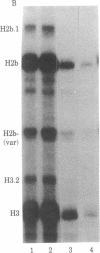
Abstract
The levels of histone mRNA are rapidly reduced after treatment of cultured cells with hydroxyurea or cytosine arabinonucleoside. The histone mRNA for the replicative histone variants is destroyed rapidly, with a half-life of 10-15 min. The levels of mRNA coding for the replacement histone variant H3.3 were unchanged after treatment with DNA synthesis inhibitors. In addition to the rapid destruction of histone mRNA, there was a reduction to 1/5th in the rate of transcription of the histone genes. Lymphoma cells (S49) arrested in G1 by cyclic AMP produce and contain significant levels of histone mRNA. Hydroxyurea reduces the rate of transcription and the levels of histone mRNA in the G1-arrested cells.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blin N., Sperrazza J. M., Wilson F. E., Bieber D. G., Mickel F. S., Stafford D. W. Organization of the ribosomal RNA gene cluster in Lytechinus variegatus. Restriction analysis and cloning of restriction fragments. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 25;254(8):2716–2721. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borun T. W., Scharff M. D., Robbins E. Rapidly labeled, polyribosome-associated RNA having the properties of histone messenger. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Nov;58(5):1977–1983. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.5.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breindl M., Gallwitz D. Identification of histone messenger RNA from HeLa cells. Appearance of histone mRNA in the cytoplasm and its translation in a rabbit-reticulocyte cell-free system. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Jan 15;32(2):381–391. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02620.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler W. B., Mueller G. C. Control of histone synthesis in HeLa cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Feb 4;294(1):481–496. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(73)90104-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin S. G., Zweidler A. Non-allelic variants of histones 2a, 2b and 3 in mammals. Nature. 1977 Mar 17;266(5599):273–275. doi: 10.1038/266273a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallwitz D. Kinetics of inactivation of histone mRNA in the cytoplasm after inhibition of DNA replication in synchronised HeLa cells. Nature. 1975 Sep 18;257(5523):247–248. doi: 10.1038/257247a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallwitz D., Mueller G. C. Histone synthesis in vitro by cytoplasmic microsomes from HeLa cells. Science. 1969 Mar 21;163(3873):1351–1353. doi: 10.1126/science.163.3873.1351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallwitz D., Mueller G. C. Histone synthesis in vitro on HeLa cell microsomes. The nature of the coupling to deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Nov 10;244(21):5947–5952. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groppi V. E., Jr, Coffino P. G1 and S phase mammalian cells synthesize histones at equivalent rates. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):195–204. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90127-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurley L. R., Walters R. A., Tobey R. A. The metabolism of histone fractions. IV. Synthesis of histones during the G1-phase of the mammalian life cycle. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Feb;148(2):633–641. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90182-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heintz N., Zernik M., Roeder R. G. The structure of the human histone genes: clustered but not tandemly repeated. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):661–668. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90092-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hereford L. M., Osley M. A., Ludwig T. R., 2nd, McLaughlin C. S. Cell-cycle regulation of yeast histone mRNA. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):367–375. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90326-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob E. Histone-gene reiteration in the genome of mouse. Eur J Biochem. 1976 May 17;65(1):275–284. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10415.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinkade J. M., Jr, Cole R. D. The resolution of four lysine-rich histones derived from calf thymus. J Biol Chem. 1966 Dec 25;241(24):5790–5797. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemaire I., Coffino P. Cyclic AMP-induced cytolysis in S49 cells: selection of an unresponsive "deathless" mutant. Cell. 1977 May;11(1):149–155. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90325-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley J. L., Sharp P. A., Gefter M. L. RNA synthesis in isolated nuclei: identification and comparison of adenovirus 2 encoded transcripts synthesized in vitro and vivo. J Mol Biol. 1979 Nov 25;135(1):171–197. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90346-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marzluff W. F., Jr, Murphy E. C., Jr, Huang R. C. Transcription of ribonucleic acid in isolated mouse myeloma nuclei. Biochemistry. 1973 Aug 28;12(18):3440–3446. doi: 10.1021/bi00742a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marzluff W. F., Jr, Pan C. J., Cooper D. L. RNA synthesis in myeloma cells synchronized by isoleucine starvation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Nov;5(11):4177–4193. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.11.4177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marzluff W. F., Jr Transcription of RNA in isolated nuclei. Methods Cell Biol. 1978;19:317–332. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60032-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight G. S., Palmiter R. D. Transcriptional regulation of the ovalbumin and conalbumin genes by steroid hormones in chick oviduct. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 25;254(18):9050–9058. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rickles R., Marashi F., Sierra F., Clark S., Wells J., Stein J., Stein G. Analysis of histone gene expression during the cell cycle in HeLa cells by using cloned human histone genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(3):749–753. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.3.749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schibler U., Marcu K. B., Perry R. P. The synthesis and processing of the messenger RNAs specifying heavy and light chain immunoglobulins in MPC-11 cells. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1495–1509. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90072-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sittman D. B., Chiu I. M., Pan C. J., Cohn R. H., Kedes L. H., Marzluff W. F. Isolation of two clusters of mouse histone genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4078–4082. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl H., Gallwitz D. Fate of histone messenger RNA in synchronized HeLa cells in the absence of initiation of protein synthesis. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Jan;72(2):385–392. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11263.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver R. F., Weissmann C. Mapping of RNA by a modification of the Berk-Sharp procedure: the 5' termini of 15 S beta-globin mRNA precursor and mature 10 s beta-globin mRNA have identical map coordinates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 10;7(5):1175–1193. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.5.1175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu R. S., Bonner W. M. Separation of basal histone synthesis from S-phase histone synthesis in dividing cells. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):321–330. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90415-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]