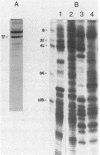
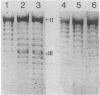
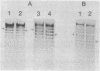
Abstract
Relaxation of Xenopus 5S plasmid DNA (pX1o8) in the presence of transcription factor (TF) IIIA reduces the linking number of the DNA. Parallel experiments with plasmid pMB9 or cloned hepatitis B viral DNA indicate a degree of non-specific unwinding by TF; however, 60% of the effect observed for pX1o8 is due to specific interaction of TF IIIA with the 5S rRNA gene internal promoter sequence. The extent of unwinding (0.2-0.4 helical turn per TF IIIA binding site) is not consistent with the complete denaturation of the 50-base-pair TF binding site; however, it is consistent with a change in helix rotation, denaturation of 2-4 nucleotides per binding site, or DNA wrapping about a protein core. We show that proteins other than TF IIIA (bovine serum albumin and RNase) have no effect on the linking number of DNA when present during relaxation and that the unwinding activity associated with TF is heat labile. These results suggest that TF IIIA may facilitate transcription by altering the helical configuration of 5S DNA.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnott S., Hukins D. W. Optimised parameters for A-DNA and B-DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jun 28;47(6):1504–1509. doi: 10.1016/0006-291X(72)90243-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkenmeier E. H., Brown D. D., Jordan E. A nuclear extract of Xenopus laevis oocytes that accurately transcribes 5S RNA genes. Cell. 1978 Nov;15(3):1077–1086. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90291-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogenhagen D. F., Sakonju S., Brown D. D. A control region in the center of the 5S RNA gene directs specific initiation of transcription: II. The 3' border of the region. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):27–35. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. D., Gurdon J. B. Cloned single repeating units of 5S DNA direct accurate transcription of 5S RNA when injected into Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2849–2853. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champoux J. J. Proteins that affect DNA conformation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:449–479. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.002313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelke D. R., Ng S. Y., Shastry B. S., Roeder R. G. Specific interaction of a purified transcription factor with an internal control region of 5S RNA genes. Cell. 1980 Mar;19(3):717–728. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(80)80048-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geider K., Hoffmann-Berling H. Proteins controlling the helical structure of DNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:233–260. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.001313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giacherio D., Hager L. P. A specific DNA unwinding activity associated with SV40 large T antigen. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 10;255(19):8963–8966. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller W. Determination of the number of superhelical turns in simian virus 40 DNA by gel electrophoresis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):4876–4880. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.4876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolb A., Buc H. Is DNA unwound by the cyclic AMP receptor protein? Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 22;10(2):473–485. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.2.473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korn L. J. Transcription of Xenopus 5S ribosomal RNA genes. Nature. 1982 Jan 14;295(5845):101–105. doi: 10.1038/295101a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay D. B., Steitz T. A. Structure of catabolite gene activator protein at 2.9 A resolution suggests binding to left-handed B-DNA. Nature. 1981 Apr 30;290(5809):744–749. doi: 10.1038/290744a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. M., Kligman M., Tjian R. Does simian virus 40 T antigen unwind DNA? J Biol Chem. 1981 Oct 10;256(19):10156–10160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker C. S., Roeder R. G. Selective and accurate transcription of the Xenopus laevis 5S RNA genes in isolated chromatin by purified RNA polymerase III. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jan;74(1):44–48. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.1.44. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peck L. J., Wang J. C. Sequence dependence of the helical repeat of DNA in solution. Nature. 1981 Jul 23;292(5821):375–378. doi: 10.1038/292375a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Brown D. D. A specific transcription factor that can bind either the 5S RNA gene or 5S RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4170–4174. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakonju S., Bogenhagen D. F., Brown D. D. A control region in the center of the 5S RNA gene directs specific initiation of transcription: I. The 5' border of the region. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):13–25. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90384-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R. The use of thin acrylamide gels for DNA sequencing. FEBS Lett. 1978 Mar 1;87(1):107–110. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80145-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. S., Thomas C. A., Jr The two-dimensional restriction analysis of Drosophila DNAs: males and females. Gene. 1981 May;13(4):395–408. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90019-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. C., Jacobsen J. H., Saucier J. M. Physiochemical studies on interactions between DNA and RNA polymerase. Unwinding of the DNA helix by Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977;4(5):1225–1241. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.5.1225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil P. A., Segall J., Harris B., Ng S. Y., Roeder R. G. Faithful transcription of eukaryotic genes by RNA polymerase III in systems reconstituted with purified DNA templates. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 10;254(13):6163–6173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wormington W. M., Bogenhagen D. F., Jordan E., Brown D. D. A quantitative assay for Xenopus 5S RNA gene transcription in vitro. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):809–817. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90106-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wormington W. M., Bogenhagen D. F., Jordan E., Brown D. D. A quantitative assay for Xenopus 5S RNA gene transcription in vitro. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):809–817. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90106-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]