Abstract
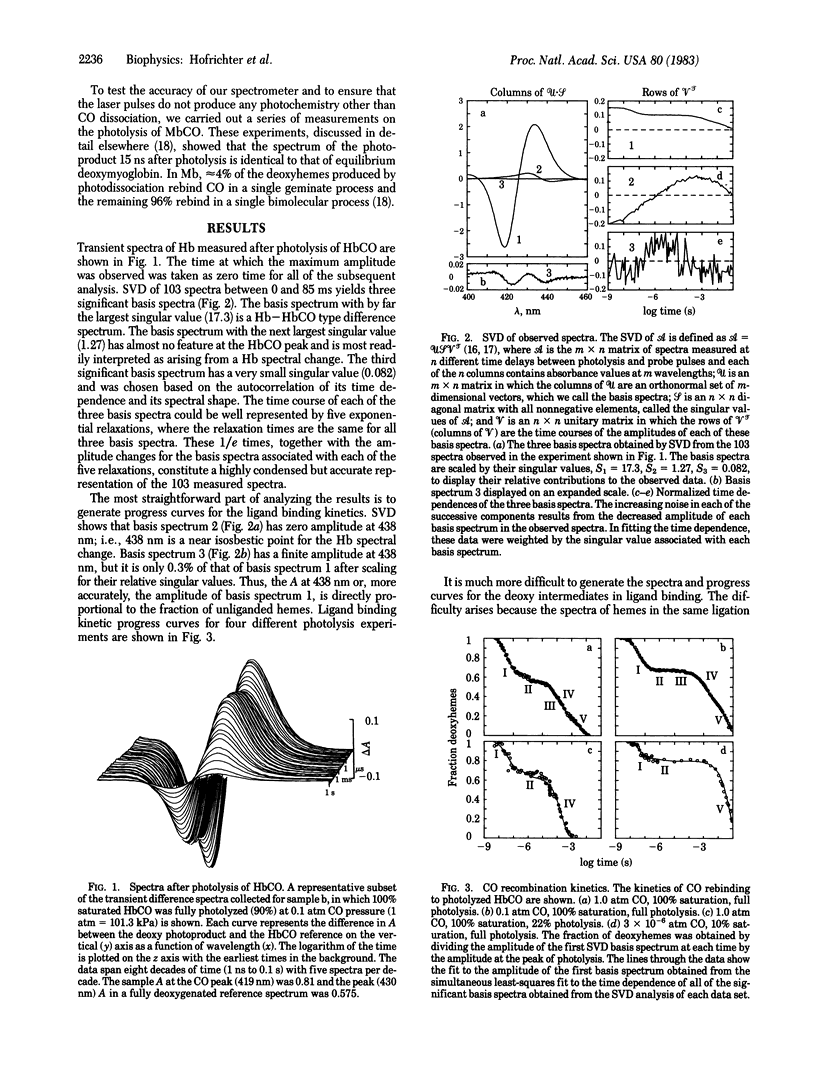
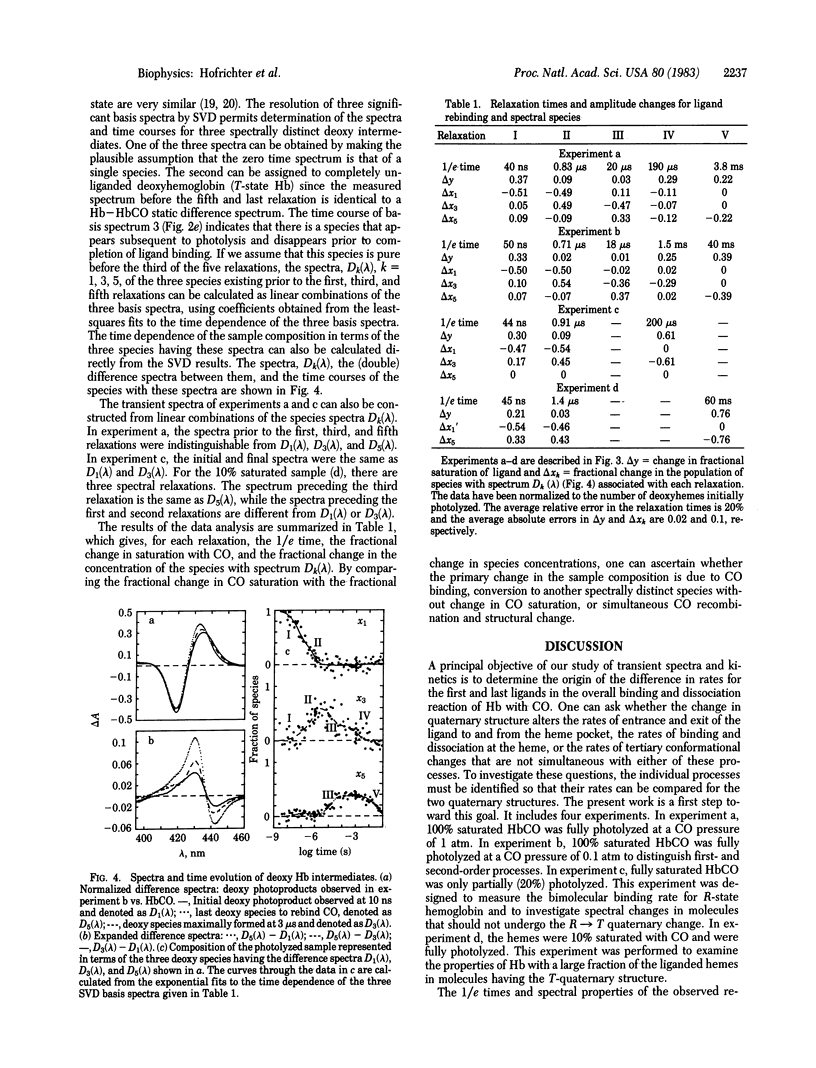
A nanosecond absorption spectrometer has been used to measure the optical spectra of hemoglobin between 3 ns and 100 ms after photolysis of the CO complex. The data from a single experiment comprise a surface, defined by the time-ordered set of 50-100 spectra. Singular value decomposition is used to represent the observed spectra in terms of a minimal set of basis spectra and the time course of their amplitudes. Both CO rebinding and conformational changes are found to be multiphasic. Prior to the quaternary structural change, two relaxations are observed that are assigned to geminate recombination followed by a tertiary structural change. These relaxations are interpreted in terms of a kinetic model that points out their potential role in kinetic cooperativity. The rapid escape of CO from the heme pocket compared with the rate of rebinding observed for both R and T quaternary states shows that the quaternary structure controls the overall dissociation rate by changing the rate at which the Fe--CO bond is broken. A comparable description of the control of the overall association rates must await a more complete experimental description of the kinetics of the quaternary T state.
Full text
PDF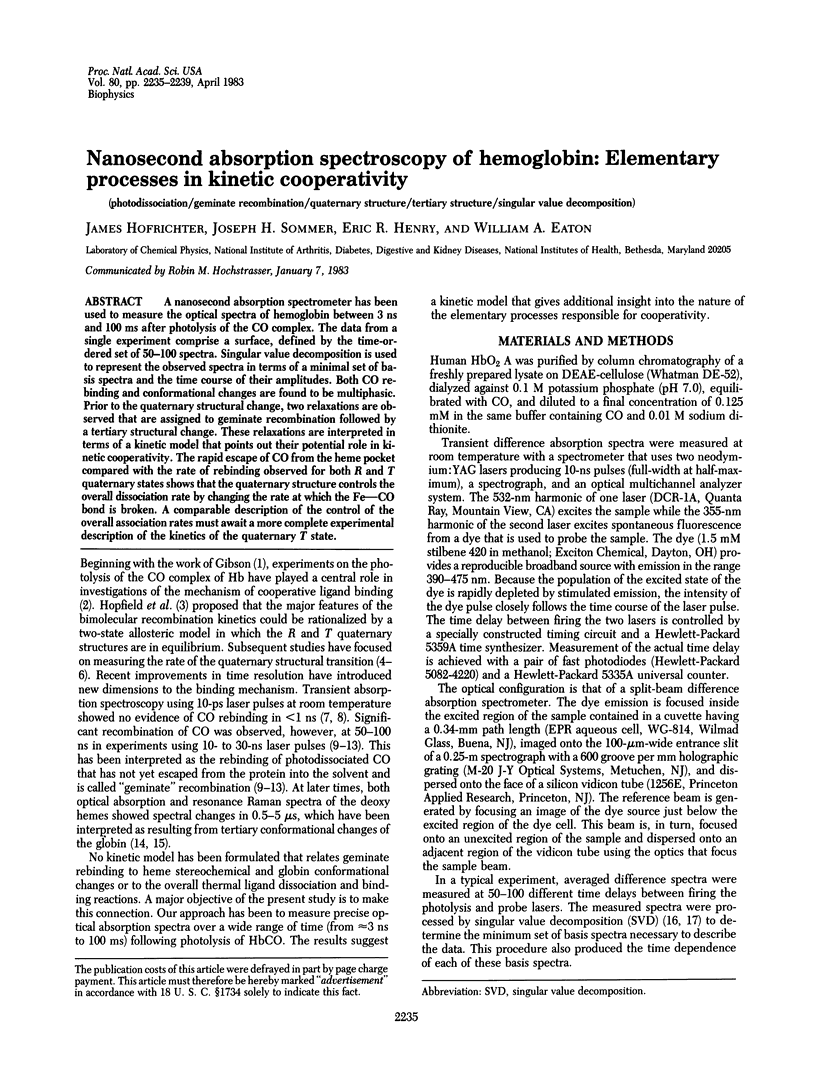


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Catterall R., Duddell D. A., Morris R. J., Richards J. T. Recombination kinetics following nanosecond laser photolysis of carbonmonoxyhaemogloblin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Jul 26;705(2):257–263. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(82)90186-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chernoff D. A., Hochstrasser R. M., Steele A. W. Geminate recombination of O2 and hemoglobin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5606–5610. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho K. C., Hopfield J. J. Spin equilibrium and quaternary structure change in hemoglobin A. Experiments on a quantitative probe of the stereochemical mechanism of hemoglobin cooperativity. Biochemistry. 1979 Dec 25;18(26):5826–5833. doi: 10.1021/bi00593a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeYoung A., Pennelly R. R., Tan-Wilson A. L., Noble R. W. Kinetic studies on the binding affinity of human hemoglobin for the 4th carbon monoxide molecule, L4. J Biol Chem. 1976 Nov 10;251(21):6692–6698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrone F. A., Hopfield J. J. Rate of quaternary structure change in hemoglobin measured by modulated excitation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4497–4501. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman J. M., Lyons K. B. Transient Raman study of CO-haemoprotein photolysis: origin of the quantum yield. Nature. 1980 Apr 10;284(5756):570–572. doi: 10.1038/284570a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIBSON Q. H. The photochemical formation of a quickly reacting form of haemoglobin. Biochem J. 1959 Feb;71(2):293–303. doi: 10.1042/bj0710293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene B. I., Hochstrasser R. M., Weisman R. B., Eaton W. A. Spectroscopic studies of oxy- and carbonmonoxyhemoglobin after pulsed optical excitation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5255–5259. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopfield J. J., Shulman R. G., Ogawa S. An allosteric model of hemoglobin. I. Kinetics. J Mol Biol. 1971 Oct 28;61(2):425–443. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90391-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindqvist L., El Mohsni S., Tfibel F., Alpert B. Transient haem-globin interactions in photodeligated carboxyhaemoglobin and subunits. Nature. 1980 Dec 25;288(5792):729–730. doi: 10.1038/288729a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moffat K., Deatherage J. F., Seybert D. W. A structural model for the kinetic behavior of hemoglobin. Science. 1979 Nov 30;206(4422):1035–1042. doi: 10.1126/science.493990. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson J. S. Stopped-flow, rapid mixing measurements of ligand binding to hemoglobin and red cells. Methods Enzymol. 1981;76:631–651. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(81)76148-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perutz M. F., Ladner J. E., Simon S. R., Ho C. Influence of globin structure on the state of the heme. I. Human deoxyhemoglobin. Biochemistry. 1974 May 7;13(10):2163–2173. doi: 10.1021/bi00707a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perutz M. F. Stereochemistry of cooperative effects in haemoglobin. Nature. 1970 Nov 21;228(5273):726–739. doi: 10.1038/228726a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawicki C. A., Gibson Q. H. Dependence of the quantum efficiency for photolysis of carboxyhemoglobin on the degree of ligation. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 25;254(10):4058–4062. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawicki C. A., Gibson Q. H. Quaternary conformational changes in human hemoglobin studied by laser photolysis of carboxyhemoglobin. J Biol Chem. 1976 Mar 25;251(6):1533–1542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma V. S., Schmidt M. R., Ranney H. M. Dissociation of CO from carboxyhemoglobin. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jul 25;251(14):4267–4272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugita Y. Differences in spectra of alpha and beta chains of hemoglobin between isolated state and in tetramer. J Biol Chem. 1975 Feb 25;250(4):1251–1256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sunshine H. R., Hofrichter J., Ferrone F. A., Eaton W. A. Oxygen binding by sickle cell hemoglobin polymers. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jun 25;158(2):251–273. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90432-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szabo A. Kinetics of hemoglobin and transition state theory. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2108–2111. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


