Abstract
The scientific community and general public have been exposed to a series of achievements attributed to a new area of knowledge: Nanotechnology. Both abroad and in Brazil, funding agencies have launched programs aimed at encouraging this type of research. Indeed, for many who come into contact with this subject it will be clear the key role that chemical knowledge will play in the evolution of this subject. And even more, will see that it is a science in which the basic structure is formed by distilling different areas of inter-and multidisciplinary knowledge along the lines of new paradigms. In this article, we attempt to clarify the foundations of nanotechnology, and demonstrate their contribution to new advances in dermatology as well as medicine in general. Nanotechnology is clearly the future.
Keywords: Drug delivery systems, Drug interchangeability, Nanoparticles, Nanostructures
WHAT IS NANOTECHNOLOGY?
Nanoscience is the study of particles on an atomic or molecular scale, whose size is measured in nanometres. A nanometre is a billionth of a metre.1 Thus, nanotechnology can be described as a collection of methods and techniques for processing materials at an atomic and molecular scale to create products with special physicochemical properties in relation to conventional products. In turn, nanobiotechnology, both at the molecular and cellular level, deals with the development of components on the biomolecular nanoscale and of instruments for investigating cellular biology.2
HISTORY AND EVOLUTION
In the 1950's, physicist Richard Feynman, considered "the father of nanotechnology", launched the idea on the power of manipulating molecules and atoms, resulting in components so small they are invisible to the naked eye.3-5 However, the term "nanotechnology" was only defined in 1974, by Professor Norio Taniguchi at Tokyo University, as a process of separating, consolidating, and deforming materials atom by atom or molecule by molecule. Between 1980 and 1990, many advances were made in materials, for example, IBM (International Business Machines) developed the scanning tunnelling microscope (STM) in 1981 and the book "Models of Molecular Gears" in 1986 by Eric Dexler. "Engines of Creation" in 1986 by Eric Drexler?1 From 2000, nanotechnology has gained more and more space in different scientific areas, with the development of different studies and increased attention from laboratories.
Therefore, nanotechnology is not just related to nanoscale, but also to developing manufacture, design, precision, and specificity.6 Skin is the first point of contact for a series of nanomaterials - from topical applications, articles of clothing, domestic utensils, to sports items and industrial manufactured products. Nanomedicine applications in dermatology also embrace new directions for medical diagnosis, follow up, and treatment.7 Gold nanoparticles, quantic points, and magnetic nanoparticles are present in high resolution non-invasive nanoimages in dermoscopy, microscopy, nanopunch, and spectroscopy, offering advanced diagnosis and treatment methods. Nanotherapies are gaining space in immunotherapy, gene therapy, and medication therapy. In this, due to the reduced size or encapsulation of medication, the therapeutic potential of water-insoluble and unstable drugs tends to improve, which also facilitates delivering small molecules through the skin, blood, nails, and pilosebaceous unit (Table 1). 8
TABLE 1.
Promising areas in nanodermatology research2
| Area of Development | Potential Areas of Application |
|---|---|
| Consumer Products | Sunscreen, antimicrobials, dressings, slow liberation volatile compounds (such as perfumes and insect repellents). |
| Diagnostic Equipment | Real time visualisation of tumours and sentinel lymphnodules, real time diagnosis of infections and malignant diseases, minimally invasive biopsies. |
| Therapeutic Agents | Antimicrobials, skin fillers, cutaneous paralyzing agents, corticosteroids located in the epidermis, gene silencers, cutaneous vaccines, induced skin treatments (for example, optical, magnetic, thermal, and radiofrequency). |
NANOTECHNOLOGY FROM A DERMATOLOGIST'S PERSPECTIVE
Expectations of nanotechnology are positive and have spread through all academic sectors of medicine, the scientific community, and industry in a general way.
Friedman et al. in September 2011 performed a study in the USA aimed at evaluating the basic understanding and perception of nanotechnology in dermatology teaching programs.9 They evaluated interns, investigators, and professors in this area via an on-line questionnaire randomly sent to members of a dermatological community (from 100 participants, the response rate was 23%). Participants responded to questions using a five point scale of strongly disagree, disagree, uncertain, agree, and strongly agree. Approximately equal numbers of interns and residents responded (52% and 47.75%, respectively). Most of those questioned did not attend any educational activity on nanotechnology (69.57%) and agreed about the need for more education related to this theme, as well as it being incorporated into the dermatology residence curriculum (60.87% in favour and 13.04% disagree). They also agreed that a large proportion of nanoresearch could contribute to better understanding of cutaneous diseases (78.26%), to advances in skin disease diagnosis (73.91%), and treatments (78.26%). A large majority of the participants recognised the importance of intensifying scientific research (82.60%) and funding in nanotechnology (78.26%).
Not surprisingly, participants demonstrated uncertainty in relation to questions on the safety of nanotechnology in both the pharmaceutical (60.87%) and cosmetic (69.57%) spheres. Furthermore, an overwhelming majority responded positively in relation to needing more studies to evaluate the safety of nanomaterials (86.96%).
NANOPARTICLES
Nanoparticles are small substances which behave and react as a total unit, with dimensions between 1 nm and 100 nm. They can be divided into organic and inorganic substances or classified according to their shape, size, surface, and physicochemical properties. As the particles interact with biological surfaces, it becomes more interesting to distinguish between the malleable and rigid ones.10
Malleable nanoparticles are made from organic materials (lipids, proteins, polymers) and can have their shape changed by stress or contact with surfaces.10 Malleable particles include:
• Liposomes - hydrophilic and lipophilic substances, which demonstrate high penetration into hair follicles when associated to medication;11
• ISCOMs - are matrixes composed of phospholipids, cholesterol, saponifiers, antigens used in vaccines;12
• Virosomes - are viral hybrid liposomes and proteins applied in vaccines (HBV and HPV);13,14
• Polymerised particles (PLA; PLGA; CL) - are mainly studied due to their cytotoxicity and nonbiodegradable accumulation, a factor limiting their use in humans;15
• Fullerenes - are supermolecular structures, considered nanoparticles - they are investigated due to their capacity to absorb UV radiation and eliminate free radicals;16,17
• Dendrimers - are used to transport medication;18
• PAMAM - have been used to increase substance skin penetration;19
• Solid Lipid Nanoparticles (SLN) and Nanostructured Lipid Carriers (NLC) - loose the liposome micelle structure, are stable in both lipophilic and hydrophilic environments, and are very safe for carrying and liberating substances in the skin.20,21,22
Rigid nanoparticles are composed of inorganic material. They are various forms of colloidal structure, made of metal (gold or silver), metal oxide (iron), and ceramic material (silica), encapsulating medication in their interior, transferring and liberation various substances, without which would be degraded by tissues on the way.10 Quantum Dots are nanocrystalline semiconductor material with an exclusive spectroscopy and with optical properties good candidates for diagnostic applications and delivery systems.23,24
ACTION MECHANISMS
The skin is a barrier to drug penetration due to the structure of the epidermis. Before a drug reaches the blood flow and has its systemic action, it must first be absorbed through the skin, crossing the horny layer and subsequent layers of the epidermis to reach the dermis. Cosmetic products do not aim to have a systemic action, but most have to provide greater penetration through epidermis layers.25 Three mechanisms are suggested for solute penetration of the horny extract:
a. Transfollicle permeation (through hair follicles) and sudoriparous hair ducts - Various investigations have established that the transfollicle route is a very significant penetration route for many compounds;25
b. Transcellular permeation: solutes pass directly through the horny cells and the intercellular lipid matrix;26
c. Intercellular permeation: the solutes tortuously diffuse around the horny cells, constantly remaining in the lipid matrix.27
Permeation through intact skin is very difficult for molecules larger than 200-350 Daltons; the maximum size is considered to be 400 Daltons.28 Most small non-electrolytic water soluble molecules diffuse to systemic circulation up to one thousand times faster when the horny layer is absent. So to maximise substance flow, we try to reduce this obstacle, even so, sometimes the follicle route can be important.29
From a penetration standpoint, skin reacts as a mechanical nano-porous barrier, penetrated by a large number of nearly semi-circular channels or pathways. Most publications estimate that these hydrophilic "pores" have a mean diameter of between 0.4 and 36.0 nm. As most passive permeation molecules, cross the skin by these intercellular "microchannels", different techniques have been proposed to improve this route and change the molecular architecture represented by corneocytes and by the many intercellular lipid layers. Nanoparticles actively participate in this.25,29
THE HAIR FOLLICLE AS A DRUG ACTION SITE
The pilosebaceous units have an important role in the permeation and penetration processes of topically applied compounds. The human hair follicle, as well as being a reservoir is an entry point for topically applied substances, and also contributes to transporting drugs through the skin. Liberation systems for drugs and formulations aimed selectively at the human hair follicle allow the delivery of effective doses of active compounds to the interior of the follicle duct. Possible applications include treating hair growth abnormalities as well as treating hair follicle associated diseases and general skin disorders.25,30
ACTIVE SUBSTANCE LIBERATION SYSTEMS FOR TOPICAL ADMINISTRATION
Although the concept of drug liberation system is not new, enormous progress has been made recently using it to treat a variety of diseases.31 One new area of research is the development of liberation systems to transport active substances in the epidermis and keeping them at the action site.32,33 The different properties of modified liberation systems bring various benefits for pharmaceutical and cosmetic products, in that they are not only dependent on the main active ingredients, but also on the liberation system in which they are transported. These systems can liberate the main active ingredient in specific areas, as well as predict their liberation rate in the skin.33,34
Liposomes and niosomes, cyclodextrines, microparticles (microcapsules, microspheres) and nanoparticles (nanocapsules and nanospheres) are some of the types of liberation systems used to transport active substances in topical administration.25,34 Of these, nanoparticles are promising systems as they have no technological limitation, have high physicochemical stability, and can be incorporated in different formulations. Nanoparticulate systems can be used as vehicles for the modified liberation of a wide variety of active substances.25,33,34
Therefore, this active substance liberation system for topical application aims to (1) facilitate labile substance transport, increasing compound efficacy, and improving final product appearance; (2) maximize the length of time compounds remain in the skin, minimising transdermal absorption; and (3) liberate products in specific areas.
It is not just the topical route which is hailed as promising in nanodermatology. Today there are many studies on the use of nanoparticles, mainly liposomes as delivery vehicles for drugs neoplasia treatment, such as melanoma skin cancer. Nanotechnology provides a way of encapsulating therapeutic agents which lead to improvements in circulation time, tumour absorption without compromising the reticuloendothelial system and minimising toxicity.35
DRUG TRANSPORT SYSTEMS FOR THE FOLLICULAR ROUTE
From the systems frequently studied for topical treatments, microparticles stand out as presenting good stability and for allowing a modified liberation of active compounds.25 Recent studies have shown that microparticle penetration through cutaneous appendages is proportional to their size.36 No microparticle larger than 10µm penetrates via follicle orifices or the horny layer, while particles with a diameter between 9 and 10µm concentrate around the follicle opening without any penetration. Microparticles of 7µm are frequently seen in much deeper regions of the follicle canal, but rarely penetrate the horny layer. Microparticles of 5µm display high concentrations in the follicle duct, but do not penetrate through the horny layer.36 However particles smaller than 3µm, studied by Rolland et al, reach the interior of this cutaneous appendage and have also been observed in surface layers of the horny layer, but never in viable epidermis.37
Different studies have proven that micro and nanoparticle systems improve drug permanence in the skin without increasing transdermal transport.38,39 With regard to exposure, the follicle route offers an extraordinary opportunity for drug transport in dermatological treatment and functional cosmetics.25
POLYMERIC MICRO AND NANOPARTICLES
Polymeric micro and nanoparticles have been investigated for their sustained release properties and their capacity to reach specific sites for drug action.40 Particles with a diameter less than 1 µm are considered nanoparticles, while particles with a diameter of 1 µm or more are called microparticles. The term micro/ nanoparticles also refers to two different types of structure: micro/nanospheres and micro/nanocapsules.
The spheres are systems in which the active substance is homogenously distributed within the polymeric matrix while micro/nanocapsules are reservoir systems, presenting a differentiated nucleus, with a cover material surrounding the central region, and containing a solid or liquid active substance.41 The cover material can be composed of organic polymers, fats, proteins, polysaccharides, etc. According to Finch, there are more than 200 methods of producing microcapsules.42 Depending on the processes and materials used in producing microparticle systems, content liberation can occur by mechanical rupture of the wall, bioerosion, or active substance diffusion.42
Micro and nanospheres differ from micro and nanocapsules by consisting of solid matrix systems where one polymerised material forms a three-dimensional net in which the active substance is absorbed, incorporated, or covalently bonded on the particle surface, and generate dissolving, dispersion or porous systems.25 These systems are formed using a variety of polymers, including gelatine, alginate, albumin, polysiloxanes, styrene copolymers, acrylates, lactic acid, and glycolic acid. A typical example of using microspheres in topical formulations is the Microsponge Delivery System (MDS), patented by Advanced Polymer Systems. This polymeric system consists of porous liberator microspheres for a wide range of active compounds including emollients, fragrances, essential oils, sun filters, antibacterials, antifungicides, and anti-inflammatories. Microsponges come in the form of rigid or soft structures, depending on polymeric composition, level of crosslinking, and parameters required to attain the required active component liberation rate through the pores. Content liberation is initiated by pressure or changes in temperature, or by active substance diffusion.32
Therefore nanoparticles in dermocosmetics are very important, as they present (1) greater bioavailability; (2) prolonged gradual release of the active component, with transport of smaller drug quantities; (3) improved tolerance; and (4) maximised action. The final objective is to carry the active ingredient to the deepest layers of the epidermis.
APPLICATIONS IN DERMATOLOGY
a. Consumer products: photoprotectors
There is a current increase in the use of nanoparticulate titanium dioxide (TiO2) and zinc oxide (ZnO) in photoprotector products.43 These nanoparticles promote less skin whitening than inorganic composition sun filters, generating more effective products in relation to the capacity to disperse, absorb, and reflect UV radiation as well as being more aesthetically elegant.44 However, it has become necessary to understand the properties of TiO2 and ZnO nanomaterials in relation to particle size, mainly in regard to skin penetration safety and their phototoxicity potential.
Skin penetration studies have shown that TiO2 and ZnO nanoparticles are safe when in contact with intact skin; however more tests are needed when skin integrity is compromised. It is still unknown whether injured skin permits higher penetration. However, it is known that in some cases such as hyperkeratotic psoriasis, thickening of the horny layer can reduce it.45-56
As for phototoxicity, during exposure to UV radiation, free radicals and reactive oxygen species are formed by these nanoparticles.57,58 Reactive oxygen species have the potential to damage cellular DNA and can generate mutations; they can also have a prejudicial effect on proteins and lipids, causing irreversible cell damage.59-61
b. Innovations in cosmetics
Nanomaterials and nanobiotechnology have the potential to radically change the way cosmetics and medicines provide their benefits. But nanoparticles are specifically used to encapsulate a vast range of substances beneficial to skin.62 In this way nanovesicles, characterised as a delivery system, in addition to solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) or nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC), are being developed for both pharmaceutical and cosmetic use.63
SLNs and NLCs have advantages in relation to delivery system over vesicles, mainly due to their high stability, as well as creating a lipid film on the skin, avoiding water evaporation and as a consequence increasing skin hydration.62 Furthermore, these nanostructured compounds promote more contact with the horny layer which increases the quantity of incorporated active ingredients reaching the action site. Cutaneous penetration is also optimised due to low surface tension in the whole system.62-64
Microcapsules also deserve a mention as insoluble nanoparticles used in cosmetics. They help resolve problems in relation to incompatibility between products as well as protecting substances susceptible to oxidation or affected by atmospheric humidity.10,65
Chitin nanofibrils are made from a natural polysaccharide obtained from crustacean shells after carbonate and protein removal. It is easily metabolised by endogenous body enzymes, and as well as possessing eco and bio compatible characteristics, can be used with safety.66,67 These nanofibrils activate keratinocyte and fibroblast proliferation, and regulate collagen synthesis and cytokine and macrophage secretion.68,69 There is interesting evidence in relation to their capacity to not just act on the appearance of photoaged skin, but also to promote wound healing reducing hypertrophic scars (Figure 1).70,71
FIGURE 1.
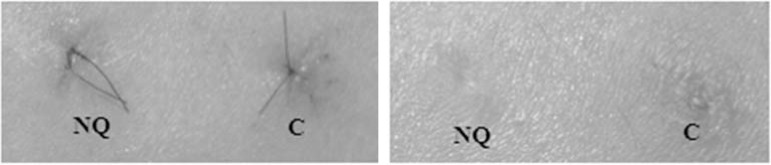
NQ – Chitin Nanofibril /C – Control: Healing activity of Chitin Nanofibril: left after 4 days, right after 20 days
Source: Morganti P, 2010.62
c. Treatment of inflammatory disorders
In diseases where the barrier function of the skin against irritants is prejudiced, such as in atopic dermatitis, emulsions with active ingredients are currently used to imprison or transform allergens.10 Nanoparticles can be used to more evenly distribute these substances, as for example in antioxidant carriers, protecting the skin from doxorubicin excretion by sweat glands.72 Similarly nanoparticle barrier creams are more effective than high lipid content moisturisers in protecting the skin against water loss and minimising the potential threat of contact dermatitis on the hands, also demonstrating better occlusive results and action against antioxidants.73
Corticoids, which have many applications in dermatology, are also associated with nanoparticles. Association with liposomal formulations minimise some known steroid side effects, such as cutaneous atrophy, which limits chronic use.74 Podophylotoxin encapsulated in SLN has similar effects to steroids in treating genital warts.75 Promising results have been seen with liposomal T cell inhibitor, Cyclosporine A, and Tachrolimus formulations.76,77 Besides, nanoparticles provide higher tolerability, improved safety, and excellent effects. Methotrexate, Psoralens, Dibranol, Clotrimazol, and other antifungal drugs have had excellent results.63,78-80
d. Antisepsis and asepsis
Antisepsis is another big area for nanoparticle operation. Chlorhexidine gluconate carried by nanoparticles (Nanochlorex®) as well as having an immediate antibacterial effect, due to fast absorption from the capsule wall, also has a prolonged effect due to sustained liberation from the particle nucleus.81,82 Particle efficacy in formulations is comparable to 60% isopropanol, making them a viable alternative to alcohol based hand products which can exhibit some skin damage after repeated exposure.83,84
Other nanoparticles, such as naked TiO2, have antibacterial properties due to their photocatalytic action. After exposure to UV radiation, naked TiO2 acts as a photocatalyst promoting peroxidation of the polyunsaturated phospholipid component of the prokaryotic lipid membrane.85 The most commercialised antibacterial nanomaterial to date is nanosilver, used not just in wound and burn dressings but also as water disinfectant and room spray. Its antibacterial effect probably results from its mitochondrial toxicity due to interaction with groups of internal membrane protein thiols, causers of oxidative stress.86 Many products are already on the market, for example, ACTISORB Silver 220® dressings.10
e. Phototherapy
Short Pulse Lasers have already been used in ophthalmology and in dermatology for targeting melanosomes, and therefore for treating skin hyperpigmentation and retina disorders. By the same principle of specific directioning for cell populations which do not have endogenous pigments, immune conjugates of iron oxide microparticles or gold nanoparticles have been tested as light absorbers. As both types of particle absorb light and liberate absorbed energy in the form of heat, after a laser pulse high temperatures are attained resulting in microscopic tissue rupture and cell damage.87
Photothermal Therapy (PTT) has used agitated gold nanoparticles to inhibit tumour growth in rats with squamous cell carcinoma. This effect also causes less surrounding tissue damage, making the remedial treatments viable.88 It is attained by conjugating nanoparticles to monoclonal antibodies or other ligands such as hormones, an active segmentation of malignant cell populations. Previous experience with different epithelial cell lines has shown that gold nanoparticles conjugated with anti-EGFR antibodies kill malignant cells after using half the energy required to kill benign cells, thus guaranteeing PTT safety.89 Recently, low weight gold nanospheres conjugated to melanocyte stimulating hormone analogues were developed to evaluate their potential for selective photothermal ablation in murine melanoma. We therefore look forward to the appearance of new treatment techniques in the near future.90
There is another promising treatment strategy for skin cancer and other cutaneous diseases; however its use is limited due to cost, patient adhesion, and mainly pain. It is based on the principle of optical activation of a photosensitive agent and subsequent conversion of local tissue oxygen into in various radicals harmful to tissue.91 The use of nanoparticles as passive carriers for photosensitive substances or as active participants has renewed interest in photodynamic treatment applications. The best treatment effect is attained by passive carriers thanks to sustained liberation. They can also counteract the side effects of general photosensitivity, as they can specifically accumulate in target cells saving the surrounding healthy tissues from the undesired effects of PDT.92 Preferential accumulation of nanoparticles in target tumour tissue also improves drug efficacy. With an identical dose, a higher concentration of photosenstiser is found in target cells when associated to nanoparticles than in isolated administration.93 Recent studies have shown the possible efficacy of nanoparticles in combination treatments, for example chemotherapy and photodynamic therapy. Mediator nanoparticles in combination with chemotherapy and photodynamic therapy using doxorubicin and methylene blue have had significant therapeutic effects against drug resistant tumours.94
f. Treatment of sebaceous gland diseases
The sebaceous gland is a key component of the pilosebaceous unit. The sebaceous duct opens into the hair follicle canal, that is to say, strategies for treating hair follicle associated diseases especially benefit by follicular penetration of topically applied particles.10 Initial experiments by Schaefer et al. with adapalene particles carried by polymerised particles (PLA and PLGA) have shown the beneficial role of particle systems in drug distribution for intrafollicular drug delivery and for much better success in treating sebaceous gland disorders such as acne and other pilosebaceous disorders.37
These initial indications of specific sebaceous glad segmentation using biodegradable PLA or PLGA particles were recently confirmed by Rancan et al.93 After particle penetration of follicles, encapsulated fluorescent stains were released from PLA particles which selectively stained the sebaceous gland.93 Recently, Taglietti et al. reviewed different DDS particles already in use for treating acne.95 A wide range of nanoparticles with different physicochemical properties, such as liposomes, SLN's, and polymerised nanoparticles increased follicle penetration, reaching much higher local drug concentrations, and optimising the therapeutic effect. Other retinoids besides PLGA particle encapsulated adapalene have been tested; they include liposomal retinol and tretinoin.38,96
A big advantage of these delivery systems is improved tolerability to irritation caused by retinoids. This improves patient treatment compliance as well as presenting systemic effects from substance absorption. Encapsulation design techniques are currently being studied to improve the therapeutic index of retinoid formulations.97 Castro et al. have shown that SLN's loaded with all-trans-retinoic acid (ATRA) were significantly less irritant than commercial retinoid cream. These new particle based formulations are a promising alternative to topical treatment of acne with retinoids.98,99
Current research on encapsulation of acne drugs in particle based distribution systems is not exclusively limited to retinoids. Bernard et al. demonstrated that liposome formulations of antiandrogenic RU-58841 displayed much deeper hair follicle penetration, specific target action on the sebaceous gland, and that various antiandrogens were carried by SLN's.100,101 An extended study over the last few years, has generated the commercialisation of certain particles as a basis for anti-acne products such as benzoyl peroxide (BP) such as BP microsphere cream 5.5% (NeoBenz Micro® , SkinMedica, Inc.) and a BP microsphere wash 7% (NeoBenz Micro Wash Plus Pack® , SkinMedica, Inc.). Clinical studies have shown high skin tolerance levels, aesthetic attributes, and patient satisfaction after treatment with BP-microsphere carrier creams.102
g. Treatment of scalp diseases
As they increase drug penetration in hair follicle openings, particle delivery systems for drugs are shown to be a key point in treating hair disorders, as well as acting as a deposit for sustained release of the drug contained within them. It is therefore believed that nanoparticle formulations are more suitable than aqueous solutions and alcohol used until now for treating heir disorders such as androgenic alopecia and alopecia areata. In effect, hair growth ingredients encapsulated in particles showed 2.0 to 2.5 times longer permanence in hair follicle regions than aqueous control solutions.10 Hinokitiol encapsulated in the same particles substantially strengthened the transition of hair follicles from the telogen to anagen phase than a simple solution of the same substance.103 Encapsulation of Minoxidil in 40-130 nm polyethylene glycol nanoparticles improved its permanence in the hair follicle region.104 Taking advantage of the preferential penetration for particle based systems of drug delivery in the hair follicle canal, Jain et al. demonstrated increased penetration of Minoxidil encapsulated in neutral liposomes in pilosebaceous units in comparison to conventional formulations of the same drug.105 Another well-established drug for treating alopecia is Finasteride. When carried in liposomes, delivery is more effective and local, and is an alternative to oral administration of the drug.106
Nanoparticle delivery systems for drugs show great success in treating alopecia areata, seeing that treatment of this autoimmune disease of the hair follicle is still a great challenge and its frequent failure can be frustrating to patients and doctors alike. The incorporation of immunomodulation agents into nanoparticles or nanoparticle delivery systems could replace the oral administration of drugs with serious side effects by more selective and effective topical treatments.10
Potential new topical treatments for alopecia areata in humans are liposomal formulations of cyclosporin A, hair growth inducers in rats.107 Recently, Nakamura et al. demonstrated controlled delivery of small interfering RNA using biodegradable cationised gelatine microspheres in a murine alopecia areata model, with disease remission.108 Due to a lack of other options, hair gene therapy has gained importance and these latest highlight the role of new particle based drug delivery systems.10
h. Nanobiotechnology in combating cancer
Cancer is one of the five commonest diseases in the world with ten million new cases expected every year. Characterised by its high morbidity and mortality, chemotherapy treatments are in most cases are only palliative in nature. Therefore there is an avid search for early diagnosis methods and forms of treatment to provide less patient suffering and increased survival.109 Chemotherapy cancer treatments have serious inconveniences such tumour cells easily becoming resistant to drugs, tissue barriers, need for high doses, toxicity, and side effects.110-112
Nanotechnology has emerged as one of the most fruitful areas in cancer treatment and is considered a promising method for improving diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of the disease.109 One example is the case of B cell lymphoma. These cells present the CD20 epitope on their surface. Rituximab, used in target-driven therapy, is an antibody with anti-CD20 activity, acting on cells which express this protein on their membrane by activating immunological reactions which cause cell lysis. Therefore their introduction into conventional chemotherapy schemes considerably increases the chances of cure.113-115
Melanoma treatment is mainly dependent on disease phase. From initial to the most advanced stages we have surgical removal, sentinel lymph node mapping, chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and biological therapy (interferon alpha and interleukin 2).116,117 Survival rate for Stage 1 melanoma is nearly 100%, but for more advanced cases of metastatic melanoma it is less than 10%.116-118 Identification of specific proteins, development of new agents, improvements in therapeutic schemes, and effective delivery of agents into tumour cells are the directions for developing a specific more effective strategy in delivering melanoma treatment. In relation to agent delivery, it searches for ways of increasing drug concentrations in tumours with minimal side effects and low effective doses.119 Nanotechnology provides an approach to encapsulate these agents that drive improvements in circulation time, tumour absorption, not compromising the reticuloendothelial system, and minimising toxicity. Liposomes in particular are a promising nanotechnology for effective agent delivery in melanoma treatment. Liposomes can deliver chemotherapies, siRNA, asODNs, DNA, and radioactive particles.35
NANODIAGNOSIS
Diagnosis by image is characterised by using contrasts in Magnetic Resonance. Particles such as gold, silver, gadolinium, iron oxide, are used for this function.109 Diagnostic agents associated to carrier particles for specific ligands to determine tumour cells, are more diffused in primary or secondary tumour tissue, which facilitates their visualisation in images and consequently topographical location and early diagnosis (Figure 1).109,120-122
New diagnostic applications test different nanoparticles due to many advantages, such as higher sensitivity of permissible detection methods to perform analysis on small quantities of tissue samples. An elevated specificity is attained when conjugated with monoclonal antibodies. Modification of the particle surface prevents aggregation and optimises cellular absorption.10 Gold nanoparticles are already used to study DNA. A variety of analytical techniques, such as optical absorption and fluorescence emission function as detectors in new methods of DNA nano-PCR sequencing.123 Gold nanoparticles also reacted as contrast intensifiers in photoacoustic cancer imaging in a rat model.124
Devices using nanotechnology for diagnosis will be fast, highly sensitive and specific and require miniscule quantities of analytical material. There are two promising methods currently in the development stage: Optical fabric and quantum dots.125 Clothing made from fibre optic fabric could have dermatological applications, characterised by nevus mapping or tracking psoriasis or atopic dermatitis on body surface areas, as well as providing the dimensions of skin lesions. By detecting changes in skin temperature, it could also monitor inflammatory diseases such as psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, or mycosis fungoides.126 Quantum dots are highly fluorescent, and their emission absorption spectrums can be tuned over a wide range of frequencies from infrared to ultraviolet, are intensely bright, and their fluorescence is stable and durable.123 This method is applied for tumour location without using radioactive substances. Topical application of quantum dots would allow sentinel lymph node evaluation without disturbing the skin or tumour evolution. Formulations of biocompatible quantum dots are being developed to make the procedure less toxic.125
In cases of malignant neoplasia, nanotechnology is of great value in both diagnosis and treatment. Different particles such as iron oxide and carbon, silica, and gold nanotubes generate improved treatment response in different tumours.126-130 In a rough way, these particles act as carriers, ligands, or boosters for chemotherapy drugs such as methotrexate, doxorrubicin, as genetic materials such as si-RNA, and others, with the intent to improve specificity, drug liberation time, posology, and the efficacy of cancer treatment.131-133
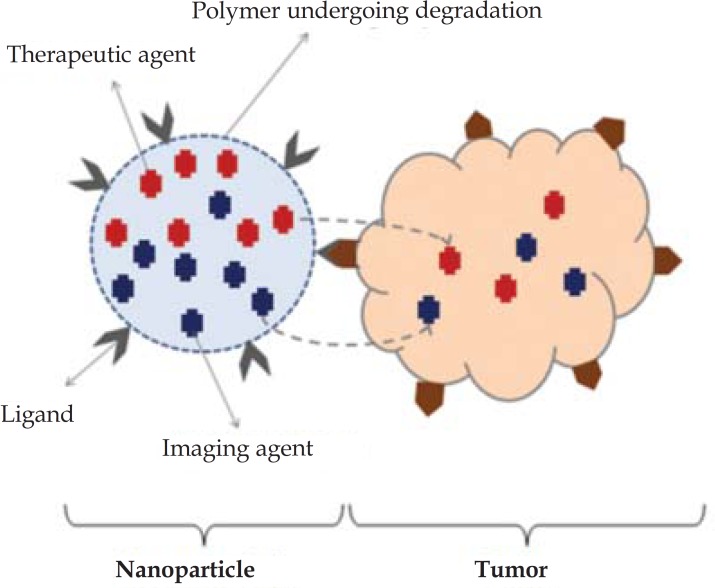
When a nanoparticle simultaneously carries therapeutic image diagnostic agents to a specific determined target, this is called a Theranostics (Figure 2).109
FIGURE 2.
Nanoparticle simultaneously containing a therapeutic and a diagnostic element - called a Theranostic
Source: Ahmed N et al, 2012.102
Nanotechnology has a crucial role in cancer treatment in relation to the use of different nanocarriers such as liposomes, micelles, dendrimers, carbon nanotubes, polymer-drug conjugates and other nanoparticles. These can act to protect a drug from early reticuloendothelial system degradation. It also allows higher drug serum concentrations to be carried through biological barriers, increasing drug availability in the intracellular compartment and consequently reducing toxicity and other associated side effects.133
RISKS OF NANOTECHNOLOGY
Nanotechnology is a relatively new branch of engineering and medicine and is making fast inroads in the area of health. As nanotechnology applies unique material properties on a nanometric scale, there is a potential risk for significant chemical volatility, which brings with it an increased risk of cell and tissue damage.2
At the moment gaps exist in understanding the environmental and human risks offered by nanoparticles, requiring a huge need to evaluate environmental and health impacts, as well as the life cycle of nanoparticles, human exposure routes, and the behaviour of these particles in the body.134 Therefore uncertainties exist on establishing the toxicity of more recent nanomaterials. There is no unequivocal correlation between the balance of characteristics verified in vitro (cellular and molecular) and in vivo (animals).135
The UC Center for the Environmental Implications of Nanotechnology (UC CEIN), and the UCLA Center for NanoBiology and Predictive Toxicology (UCLA CNPT), both located in California - USA, recommend evaluating nanomaterials at a cellular and molecular level in an attempt to predict potential dangers to the environment and individual, mainly in relation to the respiratory system.2,136,137
Andre Nel et al. in their study "Nanomaterial toxicity testing in the 21st century: use of a predictive toxicological approach and high-throughput screening" through the physicochemical properties of nanomaterials in vitro; and then correlating the toxic effects in animal models, established reasonable parameters for the toxic triage of nanomaterials.135 However, this initial triage is not able to predict the real immediate toxic effects in humans, or the consequence of chronic exposure, such as oncogenic potential, which for example, was verified in chronic asbestos exposure, strongly correlating to mesothelioma development.135,138 It is therefore especially essential to focus attention on biocompatibility, pharmacokinetics/ pharmacodynamics, toxicity, efficacy, and risks and benefits.139 In this way, the use of nanoparticles in humans, due to a lack of in vivo studies, is not sufficiently safe. It is hoped that technological development, improvements in systems of in vivo and in vitro triage through deeper studies bring an improved safety profile to nanoparticle use.135
CONCLUSION
Nanotechnology is a growing focus of attention in the scientific community. The use of particles on a nanometric scale is a relatively new technology more fully explored in the last few years. Its use covers engineering, oncology, infectology, dermatology, chemistry, and others. In the area of medicine, it is generating considerable enthusiasm in many researchers as a promising treatment for serious diseases such as cancer due to its specificity, half-life, penetration capacity in tissues, and the possibility of early diagnosis and better topographical location. In dermatology it has gained prominence mainly in relation to manufactured products, especially in the cosmetics industry, innovating the treatment of inflammatory and immunomediated dermatoses through more effective medications with less side effects. Over and above the biological activity of certain nanomaterials, micro and nanoparticles are being widely investigated as carriers or drug delivery systems. Their variable shape, functioning size, and load capacity give drug delivery systems new pharmacological properties, such as special route internalisation, selectivity, segmentation, and slow release. As nanomaterials represent a large group of variable physical and chemical substances, specific toxicological studies are needed for each product prior to commercialisation. There is still no established safety standard for human use. There are various limitations on the use of nanotechnology, for instance toxicity, tissue deposition, and long-term oncological potential. It is therefore necessary to better understand the potential of these new materials in a way that the potential negative effects of their chemistry on human health and the environment can be minimised or avoided. As technology develops, there will be a tendency towards a wider association between machines and nanotechnologies, with the probability of a deeper in vitro and in vivo understanding and new perspectives for an important reduction in morbimortality for different diseases.
Footnotes
Work performed at São José do Rio Preto State School of Medicine - (FAMERP), SP Brazil
Financial Support: None
Conflict of interest: None
REFERENCES
- 1.Bhushan B. Springer handbook of nanotecnology. 2nd ed. Heidelberg, Germany: Springer-Verlag; 2007. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Nasir A. Nanodermatology: a glimpse of caution just beyond the horizon - part II. Skin Therapy Lett. 2010;15:4–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Drexler KE. Machine-phase nanotechnology. Sci Am. 2001;285:74–75. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican0901-74. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Drexler KE. Nanosystems: molecular machinery, manufacturing, and computation. New York: John Wiley & Sons, Inc; 1992. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Hall JS. Nanofuture: what's next for nanotechnology. New York: Prometheus Books; 2005. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Nasir A. The Future of Nanotecnology in Dermatology. US Dermatology. 2008;3:9–13. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Nasir A. Nanotechnology and dermatology: part I-potential of nanotechnology. Clin Dermatol. 2010;28:458–466. doi: 10.1016/j.clindermatol.2009.06.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Saraceno R, Chiricozzi A, Gabellini M, Chimenti S. Emerging applications of nanomedicine in dermatology. Skin Res Technol. 2013;19:e13–e19. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0846.2011.00601.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Friedman A, Nasir A. Nanotechnology and dermatology education in the United States: data from a pilot survey. J Drugs Dermatol. 2011;10:1037–1041. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Papakostas D, Rancan F, Sterry W, Blume-Peytavi U, Vogt A. Nanoparticles in dermatology. Arch Dermatol Res. 2011;303:533–550. doi: 10.1007/s00403-011-1163-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Jung S, Otberg N, Thiede G, Richter H, Sterry W, Panzner S, et al. Innovative liposomes as a transfollicular drug delivery system: penetration into porcine hair follicles. J Invest Dermatol. 2006;126:1728–1732. doi: 10.1038/sj.jid.5700323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Peek LJ, Middaugh CR, Berkland C. Nanotechnology in vaccine delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2008;60:915–928. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2007.05.017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.de Vries JJ, Bungener L, Ter Veer W, van Alphen L, van der Ley P, Wilschut J, et al. Incorporation of LpxL1, a detoxified lipopolysaccharide adjuvant, in influenza H5N1 virosomes increases vaccine immunogenicity. Vaccine. 2009;27:947–955. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2008.11.046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Ludwig C, Wagner R. Virus-like particles-universal molecular toolboxes. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2007;18:537–545. doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2007.10.013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Mahe B, Vogt A, Liard C, Duffy D, Abadie V, Bonduelle O, et al. Nanoparticlebased targeting of vaccine compounds to skin antigen-presenting cells by hair follicles and their transport in mice. J Invest Dermatol. 2009;129:1156–1164. doi: 10.1038/jid.2008.356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Chirico F, Fumelli C, Marconi A, Tinari A, Straface E, Malorni W, et al. Carboxyfullerenes localize within mitochondria and prevent the UVB-induced intrinsic apoptotic pathway. Exp Dermatol. 2007;16:429–436. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0625.2007.00545.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Kato S, Taira H, Aoshima H, Saitoh Y, Miwa N. Clinical evaluation of fullerene-C60 dissolved in squalane for antiwrinkle cosmetics. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2010;10:6769–6774. doi: 10.1166/jnn.2010.3053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Villalonga-Barber C, Micha-Screttas M, Steele BR, Georgopoulos A, Demetzos C. Dendrimers as biopharmaceuticals: synthesis and properties. Curr Top Med Chem. 2008;8:1294–1309. doi: 10.2174/156802608785849012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Venuganti VV, Perumal OP. Poly(amidoamine) dendrimers as skin penetration enhancers: Influence of charge, generation, and concentration. J Pharm Sci. 2009;98:2345–2356. doi: 10.1002/jps.21603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Kristl J, Teskac K, Grabnar PA. Current view on nanosized solid lipid carriers for drug delivery to the skin. J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2010;6:529–542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Saupe A, Wissing SA, Lenk A, Schmidt C, Müller RH. Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) and nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC)-structural investigations on two different carrier systems. Biomed Mater Eng. 2005;15:393–402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Schäfer-Korting M, Mehnert W, Korting HC. Lipid nanoparticles for improved topical application of drugs for skin diseases. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2007;59:427–443. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2007.04.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Walther C, Meyer K, Rennert R, Neundorf I. Quantum dot-carrier peptide conjugates suitable for imaging and delivery applications. Bioconjug Chem. 2008;19:2346–2356. doi: 10.1021/bc800172q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Zhou M, Nakatani E, Gronenberg LS, Tokimoto T, Wirth MJ, Hruby VJ, et al. Peptidelabeled quantum dots for imaging GPCRs in whole cells and as single molecules. Bioconjug Chem. 2007;18:323–332. doi: 10.1021/bc0601929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Lourenço VA. Desenvolvimento e avaliação de micropartículas de quitosana para a veiculação de dimetilaminoetanol (DMAE) na pele [dissertação] Ribeirão Preto (SP): Universidade de São Paulo; 2006. 117 p [Google Scholar]
- 26.Gupchup GV, Zatz J. Target delivery to pilosebaceous structures. Cosmet Toiler. 1997;112:79–88. [Google Scholar]
- 27.Abraham MH, Chadha HS, Mitchell RC. The factors that influence skin permeation os solutes. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1955;47:8–16. [Google Scholar]
- 28.Cevc G, Blume G, Schätzlein A, Gebauer D, Paul A. The skin: a pathway for systemic treatment with patches and lipid based carriers. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 1996;18:349–378. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Barry BW. Novel mechanisms and devices to enable successful transdermal drug delivery. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2001;14:101–114. doi: 10.1016/s0928-0987(01)00167-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Vogt A, Mandt N, Lademann J, Schaefer H, Blume-Peytavi U. Follicular targeting-a promising tool in selective dermatotherapy. J Investig Dermatol Symp Proc. 2005 Dec;10(3):252–255. doi: 10.1111/j.1087-0024.2005.10124.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Kumar MN, Kumar N. Polymeric Controlled Drug-Delivery Systens: Perspective Issues and Opportunities. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2001 Jan;27(1):1–30. doi: 10.1081/ddc-100000124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Embil K, Nacht S. The microsponge Delivery System (MDS): a topical delivery system with reduced irritancy incorporating multiple triggering mechanisms for the release of actives. J Microencapsul. 1996;13:575–588. doi: 10.3109/02652049609026042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Rogers K. Controled release technology and delivery systems. Cosmet Toiler. 1999;114:53–60. [Google Scholar]
- 34.Nacht S. Encapsulation and other topical delivery systems: a review of the state-of-the-art for controlled topical delivery. Cosmet Toiler. 1995;110:25–30. [Google Scholar]
- 35.Tran MA, Watts RJ, Robertson GP. Use of liposomes as drug delivery vehicles for treatment of melanoma. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2009;22:388–399. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-148X.2009.00581.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Toll R, Jacobi U, Richter H, Lademann J, Schaefer H, Blume-Peytavi U. Penetration profile of microspheres in follicular targenting of terminal hair follicles. J Invest Dermatol. 2004;123:168–176. doi: 10.1111/j.0022-202X.2004.22717.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Rolland A, Wagner N, Chatelus A, Shroot B, Schaefer H. Site-specific drug delivery to pilosebaceous strutures using polymeric microspheres. Pharm Res. 1993;10:1738–1744. doi: 10.1023/a:1018922114398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Jenning V, Gysler A, Schäfer-Korting M, Gohla SH. Vitamin A loaded solid lipid nanoparticles for topical use: occlusive properties and drug targenting to the upper skin. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2000;49:211–218. doi: 10.1016/s0939-6411(99)00075-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Alvarez-Román R, Naik A, Kalia YN, Guy RH, Fessi H. Enhancemente of topical delivery from biodegradable nanoparticles. Pharm Res. 2004;21:1818–1825. doi: 10.1023/b:pham.0000045235.86197.ef. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Freitas MN, Marchetti JM. Nimesulide PLA microspheres as a potencial sustained release system for the treatment of inflammatory diseases. Int J Pharm. 2005;295:201–211. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2005.03.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Couvrer P, Covarraze G, Devissaguet JP, Puisiex F. Nanoparticles: Preparation and Caracterization. Microencapsulation Methods and Industrial Applications. New York: Marcel Dekker, Inc.; 1996. pp. 183–211. [Google Scholar]
- 42.Finch CA. Elvers B, Hawkins S, Schulza G. Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemitry. 5th ed. Neihein: VCH Verlagsgesell-sehaft; 1990. Microencapsulation; pp. 575–588. [Google Scholar]
- 43.Wang SQ, Tooley IR. Photoprotection in the era of nanotechnology. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2011;30:210–213. doi: 10.1016/j.sder.2011.07.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Schilling K, Bradford B, Castelli D, Dufour E, Nash JF, Pape W, et al. Human safety review of "nano" titanium dioxide and zinc oxide. Photochem Photobiol Sci. 2010;9:495–509. doi: 10.1039/b9pp00180h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Tan MH, Commens CA, Burnett L, Snitch PJ. A pilot study on the percutaneous absorption of microfine titanium dioxide from sunscreens. Australas J Dermatol. 1996;37:185–187. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-0960.1996.tb01050.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Dussert AS, Gooris E, Hemmerle J. Characterization of the mineral content of a physical sunscreen emulsion and its distribution onto human stratum corneum. Int J Cosmet Sci. 1997;19:119–129. doi: 10.1046/j.1467-2494.1997.171707.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Lademann J, Weigmann H, Rickmeyer C, Barthelmes H, Schaefer H, Mueller G, et al. Penetration of titanium dioxide microparticles in a sunscreen formulation into the horny layer and the follicular orifice. Skin Pharmacol Appl Skin Physiol. 1999;12:247–256. doi: 10.1159/000066249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Schulz J, Hohenberg H, Pflücker F, Gärtner E, Will T, Pfeiffer S, et al. Distribution of sunscreens on skin. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2002;54(Suppl 1):S157–S163. doi: 10.1016/s0169-409x(02)00120-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Gontier E, Ynsa M-D, Biro T, Hunyadij J, Kiss B, Gáspár K, et al. Is there penetration of titania nanoparticles in sunscreens through skin? A comparative electron and ion microscopy study. Nanotoxicology. 2008;2:218–231. [Google Scholar]
- 50.Cross SE, Innes B, Roberts MS, Tsuzuki T, Robertson TA, McCormick P. Human skin penetration of sunscreen nanoparticles: In-vitro assessment of a novel micronized zinc oxide formulation. Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 2007;20:148–154. doi: 10.1159/000098701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Mavon A, Miquel C, Lejeune O, Payre B, Moretto P. In vitro percutaneous absorption and in vivo stratum corneum distribution of an organic and a mineral sunscreen. Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 2007;20:10–20. doi: 10.1159/000096167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Pinheiro T, Pallon J, Alves LC, Veríssimo A, Filipe P, Silva JN. The influence of corneocyte structure on the interpretation of permeation profiles of nanoparticles across skin. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res B. 2007;260:119–123. [Google Scholar]
- 53.Zvyagin AV, Zhao X, Gierden A, Sanchez W, Ross JA, Roberts MS. Imaging of zinc oxide nanoparticle penetration in human skin in vitro and in vivo. J Biomed Opt. 2008;13: doi: 10.1117/1.3041492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Sadrieh N, Wokovich AM, Gopee NV, Zheng J, Haines D, Parmiter D, et al. Lack of significant dermal penetration of titanium dioxide from sunscreen formulations containing nano- and submicron-size TiO2 particles. Toxicol Sci. 2010;115:156–166. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfq041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Filipe P, Silva JN, Silva R, Cirne de Castro JL, Marques Gomes M, Alves LC, et al. Stratum corneum is an effective barrier to TiO2 and ZnO nanoparticle percutaneous absorption. Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 2009;22:266–275. doi: 10.1159/000235554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Durand L, Habran N, Henschel V, Amighi K. In vitro evaluation of the cutaneous penetration of sprayable sunscreen emulsions with high concentrations of UV filters. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2009;31:279–292. doi: 10.1111/j.1468-2494.2009.00498.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Johnston HJ, Hutchison GR, Christensen FM, Peters S, Hankin S, Stone V. Identification of the mechanisms that drive the toxicity of TiO2 particulates: The contribution of physicochemical characteristics. Part Fibre Toxicol. 2009;6:33. doi: 10.1186/1743-8977-6-33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Hirakawa K, Mori M, Yoshida M, Oikawa S, Kawanishi S. Photo-irradiated titanium dioxide catalyzes site specific DNA damage via generation of hydrogen peroxide. Free Radic Res. 2004;38:439–447. doi: 10.1080/1071576042000206487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Wamer WG, Yin JJ, Wei RR. Oxidative damage to nucleic acids photosensitized by titanium dioxide. Free Radic Biol Med. 1997;23:851–858. doi: 10.1016/s0891-5849(97)00068-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Nakagawa Y, Wakuri S, Sakamoto K, Tanaka N. The photogenotoxicity of titanium dioxide particles. Mutat Res. 1997;394:125–132. doi: 10.1016/s1383-5718(97)00126-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Hidaka H, Kobayashi H, Koike T, Sato T, Serpone N. DNA damage photoinduced by cosmetic pigments and sunscreen agents under solar exposure and artificial UV illumination. J Oleo Sci. 2006;55:249–261. [Google Scholar]
- 62.Morganti P. Use and potential of nanotechnology in cosmetic dermatology. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2010;3:5–13. doi: 10.2147/ccid.s4506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Souto EB, Müller RH. Challenging Cosmetics-Solid Lipid Nanoparticles (SLN) and Nanostructured Lipid Carriers (NLC) In: Wiechers JW, editor. Science and Application of Skin Delivery Systems. Coral Stream: Allured Publ.Co; 2008. pp. 227–250. [Google Scholar]
- 64.Abramovits W, Granowski P, Arrazola P. Applications of Nanomedicine in Dermatology: use of nanoparticles in various therapies and imaging. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2010;9:154–159. doi: 10.1111/j.1473-2165.2010.00492.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Vinetsky Y, Magdassi S. Magdassi S, Touitou E. Novel Cosmetic Delivery Systems. New York: Marcel Dekker Inc; 1999. Microcapsules in cosmetics; pp. 295–313. [Google Scholar]
- 66.Muzzarelli RAA. Chitin and its derivates: new trends off applied research. Carbohydr Polym. 1993;3:53–75. [Google Scholar]
- 67.Percot A, Viton C, Domard A. Optimization of chitin extraction from shrimp shell. Biomacromolecules. 2003;4:12–18. doi: 10.1021/bm025602k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Muzzarelli RAA, Mattioli-Belmonte M, Pugnaloni A, Biagini G. Biochemistry, histology and clinical uses of chitins and chitosans in wound healing. In: Jollés P, Muzzarelli RAA, editors. Chitin and Chitinases. Swizterland: Birkhaüser Verlag; 1999. pp. 251–264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Muzzarelli RAA, Muzzarelli C. Chitin nanofibrils. In: Dutta PK, editor. Chitin and Chitosan: Research Opportunities and Challenges. Contai: SSM International Publication; 2005. pp. 129–146. [Google Scholar]
- 70.Mattioli-Belmonte M, Zizzi Z, Lucarini G, Giantomassi F, Biagini g, Tucci G, et al. Chitin nanofibrils linked to chitosan glycolate as spray, gel and gauze preparations for wound repair. J Bioact Compat Polym. 2007;22:525–538. [Google Scholar]
- 71.Mezzana P. Clinical efficacy of a new chitin-nanofibrils based gel in wound healing. Acta Chir Plast. 2008;50:81–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Lademann J, Richter H, Golz K, Zastrow L, Sterry W, Patzelt A. Influence of microparticles on the homogeneity of distribution of topically applied substances. Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 2008;21:274–282. doi: 10.1159/000148043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.de Fine Olivarius F, Hansen AB, Karlsmark T, Wulf HC. Water protective effect of barrier creams and moisturizing creams: a new in vivo test method. Contact Dermatitis. 1996;35:219–225. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0536.1996.tb02361.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Santos Maia C, Mehnert W, Schaller M, Korting HC, Gysler A, Haberland A, et al. Drug targeting by solid lipid nanoparticles for dermal use. J Drug Target. 2002;10:489–495. doi: 10.1080/1061186021000038364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Chen H, Chang X, Du D, Liu W, Liu J, Weng T, Yang Y, et al. Podophyllotoxin-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles for epidermal targeting. J Control Release. 2006;110:296–306. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2005.09.052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Erdogan M, Wright JR, Jr, McAlister VC. Liposomal tacrolimus lotion as a novel topical agent for treatment of immune-mediated skin disorders: experimental studies in a murine model. Br J Dermatol. 2002;146:964–967. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2133.2002.04800.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Egbaria K, Ramachandran C, Weiner N. Topical application of liposomally entrapped cyclosporin evaluated by in vitro diffusion studies with human skin. Skin Pharmacol. 1991;4:21–28. doi: 10.1159/000210920. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Ali MF, Salah M, Rafea M, Saleh N. Liposomal methotrexate hydrogel for treatment of localized psoriasis: preparation,characterization and laser targeting. Med Sci Monit. 2008;14:PI66–PI74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Fang JY, Fang CL, Liu CH, Su YH. Lipid nanoparticles as vehicles for topical psoralen delivery: solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) versus nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC) Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2008;70:633–640. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2008.05.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Saraswat A, Agarwal R, Katare OP, Kaur I, Kumar B. A randomized, double-blind, vehicle-controlled study of a novel liposomal dithranol formulation in psoriasis. J Dermatolog Treat. 2007;18:40–45. doi: 10.1080/09546630601028729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Lboutounne H, Chaulet JF, Ploton C, Falson F, Pirot F. Sustained ex vivo skin antiseptic activity of chlorhexidine in poly(epsilon-caprolactone) nanocapsule encapsulated form and as a digluconate. J Control Release. 2002;82:319–334. doi: 10.1016/s0168-3659(02)00142-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Lboutounne H, Faivre V, Falson F, Pirot F. Characterization of transport of chlorhexidine-loaded nanocapsules through hairless and wistar rat skin. Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 2004;17:176–182. doi: 10.1159/000078820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Harbarth S, Pittet D, Grady L, Zawacki A, Potter-Bynoe G, Samore MH, et al. Interventional study to evaluate the impact of an alcohol-based hand gel in improving hand hygiene compliance. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2002;21:489–495. doi: 10.1097/00006454-200206000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Nhung DT, Freydiere AM, Constant H, Falson F, Pirot F. Sustained antibacterial effect of a hand rub gel incorporating chlorhexdine-loaded nanocapsules (Nanochlorex) Int J Pharm. 2007;334:166–172. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2006.10.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Tsuang YH, Sun JS, Huang YC, Lu CH, Chang WH, Wang CC. Studies of photokilling of bacteria using titanium dioxide nanoparticles. Artif Organs. 2008;32:167–174. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1594.2007.00530.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Chen X, Schluesener HJ. Nanosilver: a nanoproduct in medical application. Toxicol Lett. 2008;176:1–12. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2007.10.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Pitsillides CM, Joe EK, Wei X, Anderson RR, Lin CP. Selective cell targeting with light-absorbing microparticles and nanoparticles. Biophys J. 2003;84:4023–4032. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(03)75128-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Dickerson EB, Dreaden EC, Huang X, El-Sayed IH, Chu H, Pushpanketh S, et al. Gold nanorod assisted near-infrared plasmonic photothermal therapy (PPTT) of squamous cell carcinoma in mice. Cancer Lett. 2008;269:57–66. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2008.04.026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.El-Sayed IH, Huang X, El-Sayed MA. Selective laser photo-thermal therapy of epithelial carcinoma using anti-EGFR antibody conjugated gold nanoparticles. Cancer Lett. 2006;239:129–135. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2005.07.035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Lu W, Xiong C, Zhang G, Huang Q, Zhang R, Zhang JZ, et al. Targeted photothermal ablation of murine melanomas with melanocyte-stimulating hormone analogconjugated hollow gold nanospheres. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15:876–886. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-1480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Henderson BW, Dougherty TJ. How does photodynamic therapy work? Photochem Photobiol. 1992;55:145–157. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1992.tb04222.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Chatterjee DK, Fong LS, Zhang Y. Nanoparticles in photodynamic therapy: an emerging paradigm. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2008;60:1627–1637. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2008.08.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Rancan F, Helmreich M, Mölich A, Ermilov EA, Jux N, Röder B, et al. Synthesis and in vitro testing of a pyropheophorbide-a-fullerene hexakis adduct immunoconjugate for photodynamic therapy. Bioconjug Chem. 2007;18:1078–1086. doi: 10.1021/bc0603337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Khdair A, Chen D, Patil Y, Ma L, Dou QP, Shekhar MP, et al. Nanoparticle-mediated combination chemotherapy and photodynamic therapy overcomes tumor drug resistance. J Control Release. 2010;141:137–144. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2009.09.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Taglietti M, Hawkins CN, Rao J. Novel topical drug delivery systems and their potential use in acne vulgaris. Skin Therapy Lett. 2008;13:6–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Patel VB, Misra A, Marfatia YS. Topical liposomal gel of tretinoin for the treatment of acne: research and clinical implications. Pharm Dev Technol. 2000;5:455–464. doi: 10.1081/pdt-100102029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Queille-Roussel C, Poncet M, Mesaros S, Clucas A, Baker M, Soloff AM. Comparison of the cumulative irritation potential of adapalene gel and cream with that of erythromycin/tretinoin solution and gel and erythromycin/isotretinoin gel. Clin Ther. 2001;23:205–212. doi: 10.1016/s0149-2918(01)80003-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Castro GA, Coelho AL, Oliveira CA, Mahecha GA, Oréfice RL, Ferreira LA. Formation of ion pairing as an alternative to improve encapsulation and stability and to reduce skin irritation of retinoic acid loaded in solid lipid nanoparticles. Int J Pharm. 2009;381:77–83. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2009.07.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Castro GA, Oliveira CA, Mahecha GA, Ferreira LA. Comedolytic effect and reduced skin irritation of a new formulation of all-trans retinoic acid-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles for topical treatment of acne. Arch Dermatol Res. 2011;303:513–520. doi: 10.1007/s00403-011-1130-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Bernard E, Dubois JL, Wepierre J. Importance of sebaceous glands in cutaneous penetration of an antiandrogen: target effect of liposomes. J Pharm Sci. 1997;86:573–578. doi: 10.1021/js960394l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Münster U, Nakamura C, Haberland A, Jores K, Mehnert W, Rummel S, et al. RU 58841-myristate-prodrug development for topical treatment of acne and androgenética alopecia. Pharmazie. 2005;60:8–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Bikowski J, Del Rosso JQ. Benzoyl peroxide microsphere cream as monotherapy and combination treatment of acne. J Drugs Dermatol. 2008;7:590–595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Tsujimoto H, Hara K, Tsukada Y, Huang CC, Kawashima Y, Arakaki M, et al. Evaluation of the permeability of hair growing ingredient encapsulated PLGA nanospheres to hair follicles and their hair growing effects. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2007;17:4771–4777. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2007.06.057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Shim J, Seok Kang H, Park WS, Han SH, Kim J, Chang IS. Transdermal delivery of mixnoxidil with block copolymer nanoparticles. J Control Release. 2004;97:477–484. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2004.03.028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Jain B, Singh B, Katare OP, Vyas SP. Development and characterization of minoxidil-loaded liposomal system for delivery to pilosebaceous units. J Liposome Res. 2010;20:105–114. doi: 10.1080/08982100903161449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Kumar R, Singh B, Bakshi G, Katare OP. Development of liposomal systems of finasteride for topical applications: design, characterization, and in vitro evaluation. Pharm Dev Technol. 2007;12:591–601. doi: 10.1080/10837450701481181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Vogt A, Combadiere B, Hadam S, Stieler KM, Lademann J, Schaefer H. 40 nm.but not 750 or 1.500 nm.nanoparticles enter epidermal CD1a+ cells after transcutaneous application on human skin. J Invest Dermatol. 2006;126:1316–1322. doi: 10.1038/sj.jid.5700226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Nakamura M, Jo J, Tabata Y, Ishikawa O. Controlled delivery of T-box21 small interfering RNA ameliorates autoimmune alopecia (alopecia areata) in a C3H/HeJ mouse model. Am J Pathol. 2008;172:650–658. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2008.061249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Ahmed N, et al. Theranostic applications of nanoparticles in câncer. Drug Discov Today. 2012;17:928–934. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2012.03.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Persidis A. Cancer multidrug resistance. Nat Biotechnol. 1999;17:94–95. doi: 10.1038/5289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Parveen S, Sahoo SK. Nanomedicine: clinical applications of polyethylene glycol conjugated proteins and drugs. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2006;45:965–988. doi: 10.2165/00003088-200645100-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Sahoo SK, Parveen S, Panda JJ. The present and future of nanotechnology in human health care. Nanomedicine. 2007;3:20–31. doi: 10.1016/j.nano.2006.11.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Boye J, Elter T, Engert A. An overview of the current clinical use of the anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody rituximab. Ann Oncol. 2003;14:520–535. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdg175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Plosker GL, Figgitt DP. Rituximab: a review of its use in non- Hodgkin's lymphoma and chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Drugs. 2003;63:803–843. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200363080-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Coiffier B, Lepage E, Briere J, Herbrecht R, Tilly H, Bouabdallah R, et al. CHOP chemotherapy plus rituximab compared with CHOP alone in elderly patients with diffuse large-B-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2002;346:235–242. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa011795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Elder D. Tumor progression, early diagnosis and prognosis of melanoma. Acta Oncol. 1999;38:535–547. doi: 10.1080/028418699431113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Garbe C, Eigentler TK. Diagnosis and treatment of cutaneous melanoma: state of the art 2006. Melanoma Res. 2007;17:117–127. doi: 10.1097/CMR.0b013e328042bb36. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Guerry 4th D, Synnestvedt M, Elder DE, Schultz D. Lessons from tumor progression: the invasive radial growth phase of melanoma is common, incapable of metastasis, and indolent. J Invest Dermatol. 1993;100:342S–345S. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12470248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Wang MD, Shin DM, Simons JW, Nie S. Nanotechnology for targeted cancer therapy. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2007;7:833–837. doi: 10.1586/14737140.7.6.833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Solanki A, Kim JD, Lee KB. Nanotechnology for regenerative medicine: nanomaterials for stem cells imaging. Nanomedicine (Lond) 2008;3:567–578. doi: 10.2217/17435889.3.4.567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Li Z, Chen H, Bao H, Gao M. One-pot reaction to synthesize water-soluble magnetite nanocrystals. Chem Mater. 2004;16:1391–1393. [Google Scholar]
- 122.Souza KC, Salazar-Alvarez G, Ardisson JD, Macedo WA, Sousa EM. Mesoporous silica-magnetite nanocomposite synthesized by using a neutral surfactant. Nanotechnology. 2008;19:185603. doi: 10.1088/0957-4484/19/18/185603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Jain KK. Nanotechnology in clinical laboratory diagnostics. Clin Chim Acta. 2005;358:37–54. doi: 10.1016/j.cccn.2005.03.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Olafsson R, Bauer DR, Montilla LG, Witte RS. Realtime, contrast enhanced photoacoustic imaging of cancer in a mouse window chamber. Opt Express. 2010;18:18625–18632. doi: 10.1364/OE.18.018625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Hia J, Nasir A. Photonanodermatology: the interface of photobiology, dermatology and nanotechnology. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2011;27:2–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0781.2010.00536.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Eden JG, Park S-J, Ostrom NP, Chen K-F. Recent advances in microcavity plasma devices and arrays: a versatile photonic platform. J Phys D Appl Phys. 2005;38:1644–1648. [Google Scholar]
- 127.Lim JK, Majetich SA, Tilton RD. Stabilization of superparamagnetic iron oxide coregold shell nanoparticles in high ionic strength media. Langmuir. 2009;25:13384–13393. doi: 10.1021/la9019734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Kamei K, Mukai Y, Kojima H, Yoshikawa T, Yoshikawa M, Kiyohara G, et al. Direct cell entry of gold/iron-oxide magnetic nanoparticles in adenovirus mediated gene delivery. Biomaterials. 2009;30:1809–1814. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2008.12.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Kohler N, Sun C, Wang J, Zhang M. Methotrexate-modified superparamagnetic nanoparticles and their intracellular uptake into human cancer cells. Langmuir. 2005;21:8858–8864. doi: 10.1021/la0503451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Yu MK, Jeong YY, Park J, Park S, Kim JW, Min JJ. Drug-loaded superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for combined cancer imaging and therapy in vivo. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2008;47:5362–5365. doi: 10.1002/anie.200800857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Melancon MP, Lu W, Zhong M, Zhou M, Liang G, Elliott AM, et al. Targeted multifunctional gold-based nanoshells for magnetic resonance-guided laser ablation of head and neck cancer. Biomaterials. 2011;32:7600–7608. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2011.06.039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Yang X, Grailer JJ, Rowland IJ, Javadi A, Hurley SA, Steeber DA, et al. Multifunctional SPIO/DOX-loaded wormlike polymer vesicles for cancer therapy and MR imaging. Biomaterials. 2010;31:9065–9073. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.08.039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Parhi P, Mohanty C, Sahoo SK. Nanotechnology-based combinational drug delivery: an emerging approach for cancer therapy. Drug Discov Today. 2012;17:1044–1052. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2012.05.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Crosera M, Bovenzi M, Maina G, Adami G, Zanette C, Florio C, et al. Nanoparticle dermalabsorption and toxicity: a review of the literature. Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 2009;82:1043–1055. doi: 10.1007/s00420-009-0458-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Nel A, Xia T, Meng H, Wang X, Lin S, Ji Z, et al. Nanomaterial toxicity testing in the 21st century: use of a predictive toxicological approach and high-throughput. Acc Chem Res. 2013;46:607–621. doi: 10.1021/ar300022h. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Nel A, Xia T, Mädler L, Li N. Toxic potential of materials at the nanolevel. Science. 2006;311:622–627. doi: 10.1126/science.1114397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Nel AE, Mädler L, Velegol D, Xia T, Hoek EM, Somasundaran P, et al. Understanding biophysicochemical interactions at the nanobio interface. Nat Mater. 2009;8:543–557. doi: 10.1038/nmat2442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138.George S, Pokhrel S, Xia T, Gilbert B, Ji Z, Schowalter M, A, et al. Use of a rapid cytotoxicity screening approach to engineer a safer zinc oxide nanoparticle through iron doping. ACS Nano. 2010;4:15–29. doi: 10.1021/nn901503q. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Mura S, Couvreur P. Nanotheranostics for personalized medicine. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2012;64:1394–1416. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2012.06.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]