Abstract
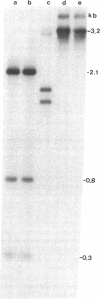
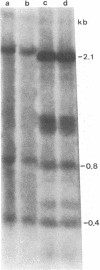
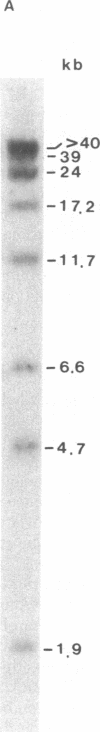
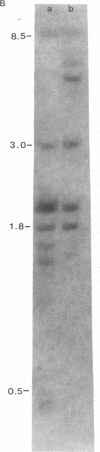
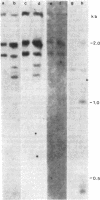
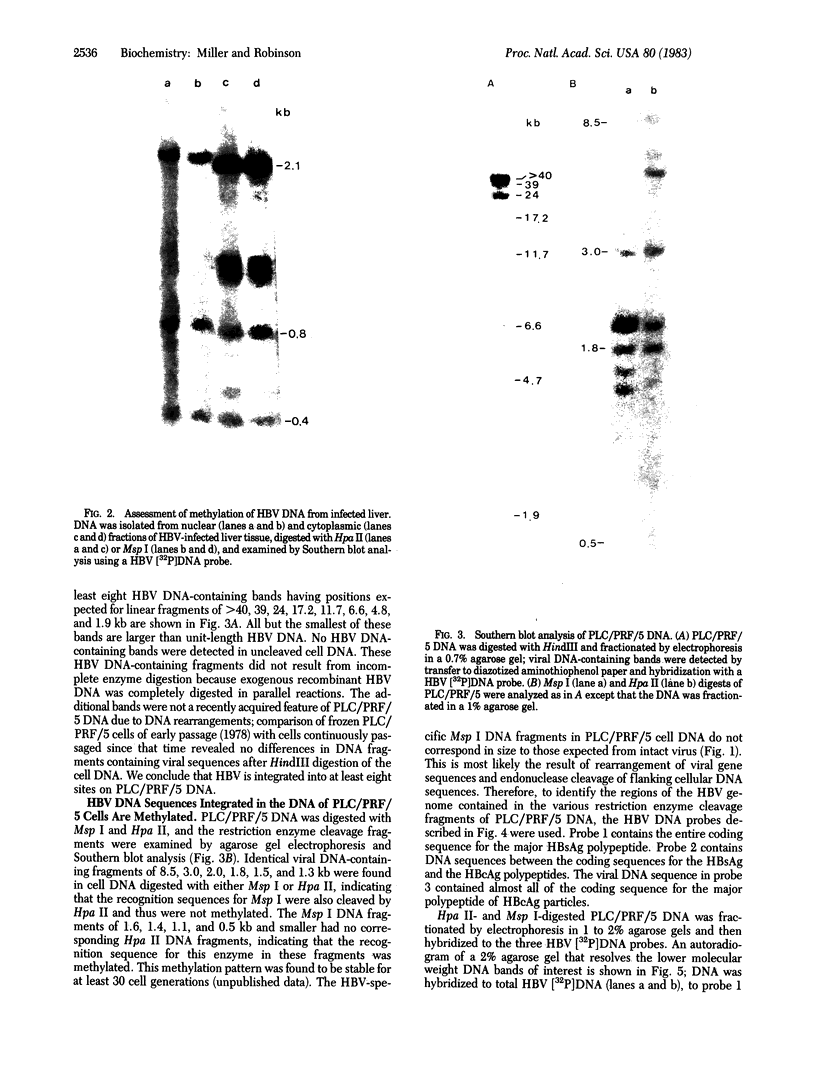
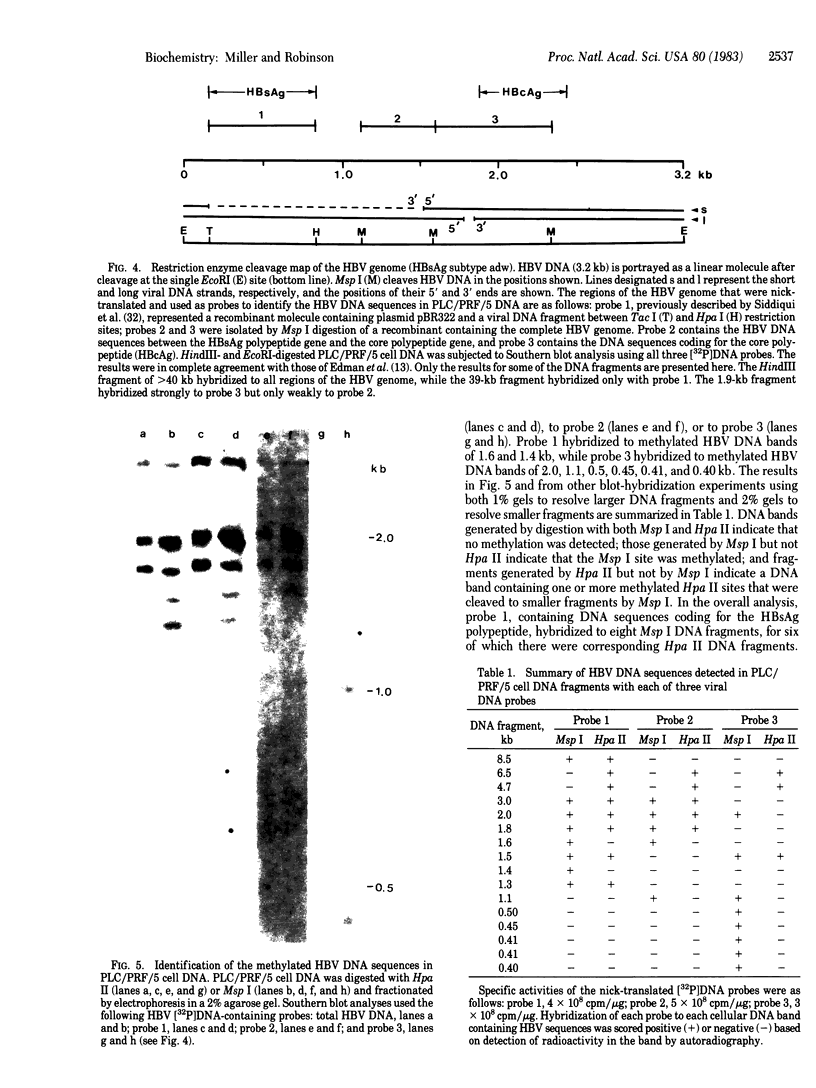
The methylation of various hepatitis B virus (HBV) DNA sequences was examined using the restriction endonucleases Hpa II and Msp I. HBV DNA from virions (Dane particles) and virus-infected liver tissue was digested with Hpa II or Msp I and fractionated by electrophoresis in agarose gels, and the restriction enzyme cleavage pattern was examined by Southern blot analysis. No methylation of the 5' C-C-G-G 3' recognition sequence was detected in either virion DNA or HBV DNA from infected liver tissue. The tissue culture cell line PLC/PRF/5, derived from a human hepatoma, possesses HBV DNA exclusively integrated at several sites. Digestion of PLC/PRF/5 DNA with Hpa II and Msp I revealed that the integrated HBV DNA sequences were methylated. Further analysis using probes specific for various regions of the HBV genome showed that some of the hepatitis B viral DNA sequences, including those specifying the major surface antigen polypeptide, were methylated infrequently or not at all. In contrast, the viral DNA sequences coding for the major core polypeptide were extensively methylated. Because the surface antigen is expressed in these cells while the core antigen is not, our results suggest that DNA methylation could account for the selective expression of HBV genes in this hepatoma cell line.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bird A., Taggart M., Macleod D. Loss of rDNA methylation accompanies the onset of ribosomal gene activity in early development of X. laevis. Cell. 1981 Nov;26(3 Pt 1):381–390. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90207-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brechot C., Pourcel C., Louise A., Rain B., Tiollais P. Presence of integrated hepatitis B virus DNA sequences in cellular DNA of human hepatocellular carcinoma. Nature. 1980 Jul 31;286(5772):533–535. doi: 10.1038/286533a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breznik T., Cohen J. C. Altered methylation of endogenous viral promoter sequences during mammary carcinogenesis. Nature. 1982 Jan 21;295(5846):255–257. doi: 10.1038/295255a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bréchot C., Hadchouel M., Scotto J., Fonck M., Potet F., Vyas G. N., Tiollais P. State of hepatitis B virus DNA in hepatocytes of patients with hepatitis B surface antigen-positive and -negative liver diseases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3906–3910. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborty P. R., Ruiz-Opazo N., Shouval D., Shafritz D. A. Identification of integrated hepatitis B virus DNA and expression of viral RNA in an HBsAg-producing human hepatocellular carcinoma cell line. Nature. 1980 Jul 31;286(5772):531–533. doi: 10.1038/286531a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clough D. W., Kunkel L. M., Davidson R. L. 5-Azacytidine-induced reactivation of a herpes simplex thymidine kinase gene. Science. 1982 Apr 2;216(4541):70–73. doi: 10.1126/science.6175023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeSimone J., Heller P., Hall L., Zwiers D. 5-Azacytidine stimulates fetal hemoglobin synthesis in anemic baboons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(14):4428–4431. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.14.4428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desrosiers R. C. Specifically unmethylated cytidylic-guanylate sites in Herpesvirus saimiri DNA in tumor cells. J Virol. 1982 Aug;43(2):427–435. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.2.427-435.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dretzen G., Bellard M., Sassone-Corsi P., Chambon P. A reliable method for the recovery of DNA fragments from agarose and acrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):295–298. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90296-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edman J. C., Gray P., Valenzuela P., Rall L. B., Rutter W. J. Integration of hepatitis B virus sequences and their expression in a human hepatoma cell. Nature. 1980 Jul 31;286(5772):535–538. doi: 10.1038/286535a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galibert F., Mandart E., Fitoussi F., Tiollais P., Charnay P. Nucleotide sequence of the hepatitis B virus genome (subtype ayw) cloned in E. coli. Nature. 1979 Oct 25;281(5733):646–650. doi: 10.1038/281646a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunthert U., Schweiger M., Stupp M., Doerfler W. DNA methylation in adenovirus, adenovirus-transformed cells, and host cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):3923–3927. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.3923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harbers K., Schnieke A., Stuhlmann H., Jähner D., Jaenisch R. DNA methylation and gene expression: endogenous retroviral genome becomes infectious after molecular cloning. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7609–7613. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ketner G., Kelly T. J., Jr Integrated simian virus 40 sequences in transformed cell DNA: analysis using restriction endonucleases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Apr;73(4):1102–1106. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.4.1102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koshy R., Maupas P., Müller R., Hofschneider P. H. Detection of hepatitis B virus-specific DNA in the genomes of human hepatocellular carcinoma and liver cirrhosis tissues. J Gen Virol. 1981 Nov;57(Pt 1):95–102. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-57-1-95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landers T. A., Greenberg H. B., Robinson W. S. Structure of hepatitis B Dane particle DNA and nature of the endogenous DNA polymerase reaction. J Virol. 1977 Aug;23(2):368–376. doi: 10.1128/jvi.23.2.368-376.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- London W. T. Primary hepatocellular carcinoma--etiology, pathogenesis, and prevention. Hum Pathol. 1981 Dec;12(12):1085–1097. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(81)80329-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutwick L. I., Robinson W. S. DNA synthesized in the hepatitis B Dane particle DNA polymerase reaction. J Virol. 1977 Jan;21(1):96–104. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.1.96-104.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacNab G. M., Alexander J. J., Lecatsas G., Bey E. M., Urbanowicz J. M. Hepatitis B surface antigen produced by a human hepatoma cell line. Br J Cancer. 1976 Nov;34(5):509–515. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1976.205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marion P. L., Salazar F. H., Alexander J. J., Robinson W. S. Polypeptides of hepatitis B virus surface antigen produced by a hepatoma cell line. J Virol. 1979 Dec;32(3):796–802. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.3.796-802.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naveh-Many T., Cedar H. Active gene sequences are undermethylated. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4246–4250. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasek M., Goto T., Gilbert W., Zink B., Schaller H., MacKay P., Leadbetter G., Murray K. Hepatitis B virus genes and their expression in E. coli. Nature. 1979 Dec 6;282(5739):575–579. doi: 10.1038/282575a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy P. H., Weissbach A. DNA methylase from HeLa cell nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1975 Oct;2(10):1669–1684. doi: 10.1093/nar/2.10.1669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sattler F., Robinson W. S. Hepatitis B viral DNA molecules have cohesive ends. J Virol. 1979 Oct;32(1):226–233. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.1.226-233.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafritz D. A., Shouval D., Sherman H. I., Hadziyannis S. J., Kew M. C. Integration of hepatitis B virus DNA into the genome of liver cells in chronic liver disease and hepatocellular carcinoma. Studies in percutaneous liver biopsies and post-mortem tissue specimens. N Engl J Med. 1981 Oct 29;305(18):1067–1073. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198110293051807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma S., Biswal N. Studies on the in vivo methylation of replicating herpes simplex virus type 1 DNA. Virology. 1977 Oct 15;82(2):265–274. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90002-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqui A., Marion P. L., Robinson W. S. Ground squirrel hepatitis virus DNA: molecular cloning and comparison with hepatitis B virus DNA. J Virol. 1981 Apr;38(1):393–397. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.1.393-397.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqui A., Sattler F., Robinson W. S. Restriction endonuclease cleavage map and location of unique features of the DNA of hepatitis B virus, subtype adw2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4664–4668. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skelly J., Copeland J. A., Howard C. R., Zuckerman A. J. Hepatitis B surface antigen produced by a human hepatoma cell line. Nature. 1979 Dec 6;282(5739):617–618. doi: 10.1038/282617a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sninsky J. J., Siddiqui A., Robinson W. S., Cohen S. N. Cloning and endonuclease mapping of the hepatitis B viral genome. Nature. 1979 May 24;279(5711):346–348. doi: 10.1038/279346a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein R., Razin A., Cedar H. In vitro methylation of the hamster adenine phosphoribosyltransferase gene inhibits its expression in mouse L cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(11):3418–3422. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.11.3418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuhlmann H., Jähner D., Jaenisch R. Infectivity and methylation of retroviral genomes is correlated with expression in the animal. Cell. 1981 Oct;26(2 Pt 2):221–232. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90305-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szmuness W. Hepatocellular carcinoma and the hepatitis B virus: evidence for a causal association. Prog Med Virol. 1978;24:40–69. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twist E. M., Clark H. F., Aden D. P., Knowles B. B., Plotkin S. A. Integration pattern of hepatitis B virus DNA sequences in human hepatoma cell lines. J Virol. 1981 Jan;37(1):239–243. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.1.239-243.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vardimon L., Kressmann A., Cedar H., Maechler M., Doerfler W. Expression of a cloned adenovirus gene is inhibited by in vitro methylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1073–1077. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waechter D. E., Baserga R. Effect of methylation on expression of microinjected genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1106–1110. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youssoufian H., Hammer S. M., Hirsch M. S., Mulder C. Methylation of the viral genome in an in vitro model of herpes simplex virus latency. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(7):2207–2210. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.7.2207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]