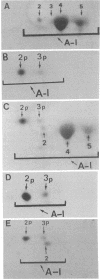
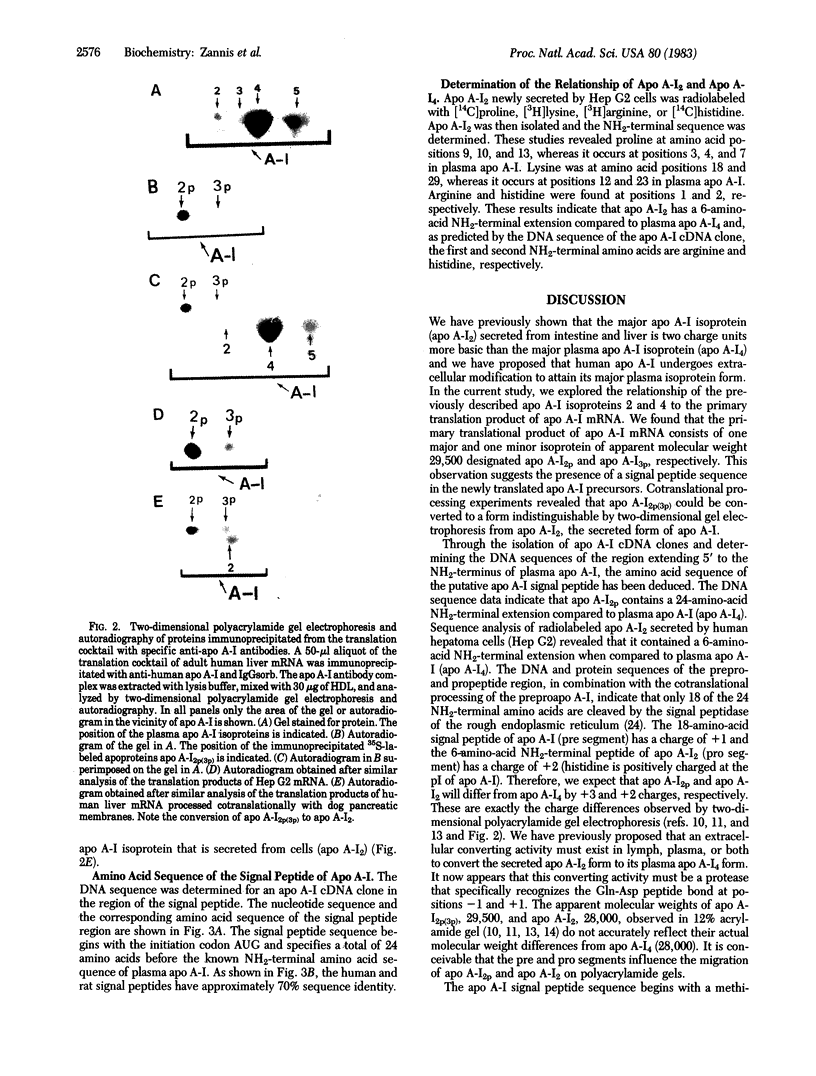
Abstract
We have recently proposed that the major secreted isoprotein form of human apolipoprotein A-I (designated apo A-I2) is modified extracellularly to become the predominant apo A-I form seen in plasma (designated apo A-I4). In the current report we demonstrate that the primary translation product of human apo A-I (designated apo A-I2p) has a 24-amino-acid NH2-terminal extension with a sequence of Met-Lys-Ala-Ala-Val-Leu-Thr-Leu-Ala-Val-Leu-Phe- Leu-Thr-Gly-Ser-Gln-Ala-Arg-His-Phe-Trp-Gln-Gln. The first 18 amino acids of this NH2-terminal extension are cleaved intracellularly by the signal peptidase, resulting in the formation of apo A-I2, which is the secreted form of apo A-I. Sequence analysis of apo A-I2 confirmed that it contains a hexapeptide extension at its NH2 terminus compared to apo A-I4. This observation demonstrates that apo A-I2 is a propeptide and that the apo A-I2 to apo A-I4 conversion involves the removal of the NH2-terminal hexapeptide of apo A-I2 by a protease in plasma, lymph, or both. Our findings indicate that apo A-I is synthesized as a prepropeptide, which undergoes intracellular and extracellular proteolysis to attain the major plasma apo A-I4 isoprotein form.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Assmann G., Capurso A., Smootz E., Wellner U. Apoprotein A metabolism in Tangier disease. Atherosclerosis. 1978 Aug;30(4):321–332. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(78)90125-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Austen B. M. Predicted secondary structures of amino-terminal extension sequences of secreted proteins. FEBS Lett. 1979 Jul 15;103(2):308–313. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)81351-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G., Walter P., Chang C. N., Goldman B. M., Erickson A. H., Lingappa V. R. Translocation of proteins across membranes: the signal hypothesis and beyond. Symp Soc Exp Biol. 1979;33:9–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blue M. L., Ostapchuk P., Gordon J. S., Williams D. L. Synthesis of apolipoprotein AI by peripheral tissues of the rooster. A possible mechanism of cellular cholesterol efflux. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 25;257(18):11151–11159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breslow J. L., Ross D., McPherson J., Williams H., Kurnit D., Nussbaum A. L., Karathanasis S. K., Zannis V. I. Isolation and characterization of cDNA clones for human apolipoprotein A-I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6861–6865. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer H. B., Jr, Fairwell T., LaRue A., Ronan R., Houser A., Bronzert T. J. The amino acid sequence of human APOA-I, an apolipoprotein isolated from high density lipoproteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Feb 14;80(3):623–630. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91614-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burstein Y., Schechter I. Amino acid sequence of the NH2-terminal extra piece segments of the precursors of mouse immunoglobulin lambda1-type and kappa-type light chains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):716–720. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castelli W. P., Doyle J. T., Gordon T., Hames C. G., Hjortland M. C., Hulley S. B., Kagan A., Zukel W. J. HDL cholesterol and other lipids in coronary heart disease. The cooperative lipoprotein phenotyping study. Circulation. 1977 May;55(5):767–772. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.55.5.767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fielding C. J., Shore V. G., Fielding P. E. A protein cofactor of lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Feb 25;46(4):1493–1498. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90776-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghiselli G., Brewer H. B., Jr, Windmueller H. G. Apolipoprotein A-I isoprotein synthesis by the perfused rat liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Jul 16;107(1):144–149. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91681-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. I., Smith D. P., Andy R., Alpers D. H., Schonfeld G., Strauss A. W. The primary translation product of rat intestinal apolipoprotein A-I mRNA is an unusual preproprotein. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jan 25;257(2):971–978. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green P. H., Tall A. R., Glickman R. M. Rat intestine secretes discoid high density lipoprotein. J Clin Invest. 1978 Feb;61(2):528–534. doi: 10.1172/JCI108963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habener J. F., Rosenblatt M., Kemper B., Kronenberg H. M., Rich A., Potts J. T., Jr Pre-proparathyroid hormone; amino acid sequence, chemical synthesis, and some biological studies of the precursor region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2616–2620. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye M., Halegoua S. Secretion and membrane localization of proteins in Escherichia coli. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1980;7(4):339–371. doi: 10.3109/10409238009105465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye S., Soberon X., Franceschini T., Nakamura K., Itakura K., Inouye M. Role of positive charge on the amino-terminal region of the signal peptide in protein secretion across the membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(11):3438–3441. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.11.3438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kannel W. B., Castelli W. P., Gordon T. Cholesterol in the prediction of atherosclerotic disease. New perspectives based on the Framingham study. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Jan;90(1):85–91. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-1-85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles B. B., Howe C. C., Aden D. P. Human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines secrete the major plasma proteins and hepatitis B surface antigen. Science. 1980 Jul 25;209(4455):497–499. doi: 10.1126/science.6248960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majzoub J. A., Rosenblatt M., Fennick B., Maunus R., Kronenberg H. M., Potts J. T., Jr, Habener J. F. Synthetic pre-proparathyroid hormone leader sequence inhibits cell-free processing of placental, parathyroid, and pituitary prehormones. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 10;255(23):11478–11483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris K. M., Aden D. P., Knowles B. B., Colten H. R. Complement biosynthesis by the human hepatoma-derived cell line HepG2. J Clin Invest. 1982 Oct;70(4):906–913. doi: 10.1172/JCI110687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D., Gagnon J., Ericsson L. H., Walsh K. A. Precursor of egg white lysozyme. Amino acid sequence of an NH2-terminal extension. J Biol Chem. 1977 Sep 25;252(18):6386–6393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Jackson R. J. An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rachmilewitz D., Albers J. J., Saunders D. R., Fainaru M. Apoprotein synthesis by human duodenojejunal mucosa. Gastroenterology. 1978 Oct;75(4):677–682. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefer E. J., Blum C. B., Levy R. I., Jenkins L. L., Alaupovic P., Foster D. M., Brewer H. B., Jr Metabolism of high-density lipoprotein apolipoproteins in Tangier disease. N Engl J Med. 1978 Oct 26;299(17):905–910. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197810262991701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schonfeld G., Bell E., Alpers D. H. Intestinal apoproteins during fat absorption. J Clin Invest. 1978 Jun;61(6):1539–1550. doi: 10.1172/JCI109074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schonfeld G., Pfleger B. The structure of human high density lipoprotein and the levels of apolipoprotein A-I in plasma as determined by radioimmunoassay. J Clin Invest. 1974 Aug;54(2):236–246. doi: 10.1172/JCI107758. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soutar A. K., Garner C. W., Baker H. N., Sparrow J. T., Jackson R. L., Gotto A. M., Smith L. C. Effect of the human plasma apolipoproteins and phosphatidylcholine acyl donor on the activity of lecithin: cholesterol acyltransferase. Biochemistry. 1975 Jul 15;14(14):3057–3064. doi: 10.1021/bi00685a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner D. F., Quinn P. S., Chan S. J., Marsh J., Tager H. S. Processing mechanisms in the biosynthesis of proteins. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1980;343:1–16. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1980.tb47238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Windmueller H. G., Wu A. L. Biosynthesis of plasma apolipoproteins by rat small intestine without dietary or biliary fat. J Biol Chem. 1981 Mar 25;256(6):3012–3016. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods D. E., Markham A. F., Ricker A. T., Goldberger G., Colten H. R. Isolation of cDNA clones for the human complement protein factor B, a class III major histocompatibility complex gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5661–5665. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu A. L., Windmueller H. G. Relative contributions by liver and intestine to individual plasma apolipoproteins in the rat. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 10;254(15):7316–7322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zannis V. I., Breslow J. L., Katz A. J. Isoproteins of human apolipoprotein A-I demonstrated in plasma and intestinal organ culture. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 25;255(18):8612–8617. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zannis V. I., Breslow J. L., SanGiacomo T. R., Aden D. P., Knowles B. B. Characterization of the major apolipoproteins secreted by two human hepatoma cell lines. Biochemistry. 1981 Dec 8;20(25):7089–7096. doi: 10.1021/bi00528a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zannis V. I., Kurnit D. M., Breslow J. L. Hepatic apo-A-I and apo-E and intestinal apo-A-I are synthesized in precursor isoprotein forms by organ cultures of human fetal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jan 10;257(1):536–544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zannis V. I., Lees A. M., Lees R. S., Breslow J. L. Abnormal apoprotein A-I isoprotein composition in patients with Tangier disease. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 10;257(9):4978–4986. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]